- Umang Sagar
- Recent article, Technology
Nanotechnology
Introduction
Nanotechnology is science, designing, and technology conducted at the nanoscale, which is around 1 to 100 nanometers.
Physicist Richard Feynman, the dad of nanotechnology.
Nanoscience and nanotechnology are the review and utilization of minuscule things and can be utilized across a wide range of various science fields, like science, science, physical science, materials science, and designing.
Nanotechnology is the term given to those areas of science and design where peculiarities that happen at aspects in the nanometer scale are used in the plan, characterization, creation and utilization of materials, constructions, gadgets, and frameworks. Albeit in the normal world, there are numerous instances of designs that exist with nanometer dimensions (henceforth alluded to as the nanoscale), including essential molecules within the human body and parts of food varieties, and albeit numerous advances have unexpectedly involved nanoscale structures for a long time, it has just been in the last quarter of a century that it has been feasible to effectively and deliberately adjust particles and constructions inside this size range. It is this control at the nanometer scale that recognizes nanotechnology from different areas of innovation.
The different structures of nanotechnology have the possibility to have an extremely huge effect on society. Overall it could be accepted that the utilization of nanotechnology will be exceptionally gainful to people and associations. A considerable lot of these applications include new materials which give drastically various properties through working at the nanoscale, where new peculiarities are related with the exceptionally huge surface region to volume proportions experienced at these aspects and with quantum impacts that are not seen with bigger sizes. These remember materials for the type of exceptionally slight movies utilized in catalysis and gadgets, two-dimensional nanotubes and nanowires for optical and attractive frameworks, and as nanoparticles used in beauty care products, drugs and coatings.
How It Started?
The thoughts and ideas driving nanoscience and nanotechnology began with a discussion named “There’s Plenty of Room at the Bottom” by physicist Richard Feynman at an American Physical Society meeting at the California Institute of Technology (CalTech) on December 29, 1959, sometime before the term nanotechnology was utilized. In his discussion, Feynman portrayed a cycle in which researchers would have the option to control and control individual particles and atoms. More than 10 years after the fact, in his investigations of ultra-precision machining, Professor Norio Taniguchi instituted the term nanotechnology. It was only after 1981, with the improvement of the checking burrowing magnifying instrument that could “see” individual particles, that cutting-edge nanotechnology started.
The rise of nanotechnology as a field during the 1980s happened through the assembly of Drexler’s hypothetical and public work, which created and promoted a calculated structure for nanotechnology, and high-permeability trial progresses that caused extra wide-scale notice of the possibilities of nuclear control of the issue. During the 1980s, two significant forward leaps started the development of nanotechnology in the advanced time. To start with, the development of the scanning burrowing microscope in 1981 gave an extraordinary representation of individual molecules and bonds, and was effectively used to control individual iotas in 1989? The magnifying instrument’s developers Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer at IBM Zurich Research Laboratory received a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986. Binnig, Quate, and Gerber likewise concocted the analogous atomic force microscope that year.
Fundamental Concepts In Nanoscience And Nanotechnology
It’s difficult to imagine just how little nanotechnology is. One nanometer is a billionth of a meter or 10-9 of a meter. The following are a couple of illustrative models:
There are 25,400,000 nanometers in an inch sheet of paper is around 100,000 nanometers thick on a similar scale, in the event that a marble was a nanometers, one meter would be the size of the Earth
Nanoscience and nanotechnology include the capacity to see and to control individual particles and atoms. Everything on Earth is comprised of particles the food we eat, the garments we wear, the structures and houses we live in, and our own bodies.
However, something however little as an iota may be difficult to see with the unaided eye. As a matter of fact, it’s difficult to see with the magnifying instruments regularly utilized in secondary school science classes. The magnifying lens expected to see things at the nanoscale was developed in the mid-1980s.
When researchers had the right apparatuses, for example, the scanning burrowing magnifying instrument (STM) and the nuclear power magnifying lens (AFM), the time of nanotechnology was conceived.
Albeit current nanoscience and nanotechnology are very new, nanoscale materials were used for quite a long time. Substitute estimated gold and silver particles made colors in the stained glass windows of archaic holy places many years prior. The specialists in those days simply didn’t realize that the interaction they used to make these excellent things of beauty really prompted changes in the structure of the materials they were working with.
The present researchers and engineers are tracking down a wide assortment of approaches to deliberately make materials at the nanoscale to exploit their improved properties, for example, higher strength, lighter weight, increased control of light range, and more prominent synthetic reactivity than their larger-scale partners.
Why Does Nanotechnology Matter?
Surprising physical, compound, and organic properties can arise in materials at the nanoscale. These properties might contrast in significant ways from the properties of mass materials and single iotas or particles.
The mass properties of materials regularly change significantly with nano fixings. Composites produced using particles of nano-size pottery or metals less than 100 nanometers can abruptly turn out to be a lot more grounded than anticipated by existing materials-science models.
For instance, metals with a supposed grain size of around 10 nanometers are basically as much as multiple times harder and harder than their common partners with grain sizes in the many nanometers. The reasons for these extreme changes come from the unusual universe of quantum physical science. The mass properties of any material are simply the normal of all the quantum powers influencing every one of the particles. As you make things more modest and more modest, you in the end arrive where the averaging does not work anymore.
=> The properties of materials can be different at the nanoscale for two primary reasons:
1. Surface Area
- First, nanomaterials have a moderately bigger surface region when contrasted with a similar mass of material delivered in a bigger structure. This can make materials all the more artificially responsive (at times materials that are inactive in their bigger structure are receptive when delivered in their nanoscale structure), and influence their solidarity or electrical properties.
2. Quantum side effects
Second, quantum impacts can start to rule the conduct of issues at the nanoscale – especially at the lower end – influencing the optical, electrical and attractive conduct of materials. This impact depicts the physical science of electron properties in solids with incredible decreases in molecule size. This impact doesn’t become an integral factor by going from large scale to miniature aspects. Be that as it may, it becomes predominant when the nanometer size range is reached.
We explain surface region and quantum size effects in detail in our explainer of why nanotechnology is so extraordinary.
The interest in nanotechnology originates from these special quantum and surface peculiarities that matter shows at the nanoscale. They work on existing modern cycles, materials, and applications in many fields – and permit totally new ones.
Applications
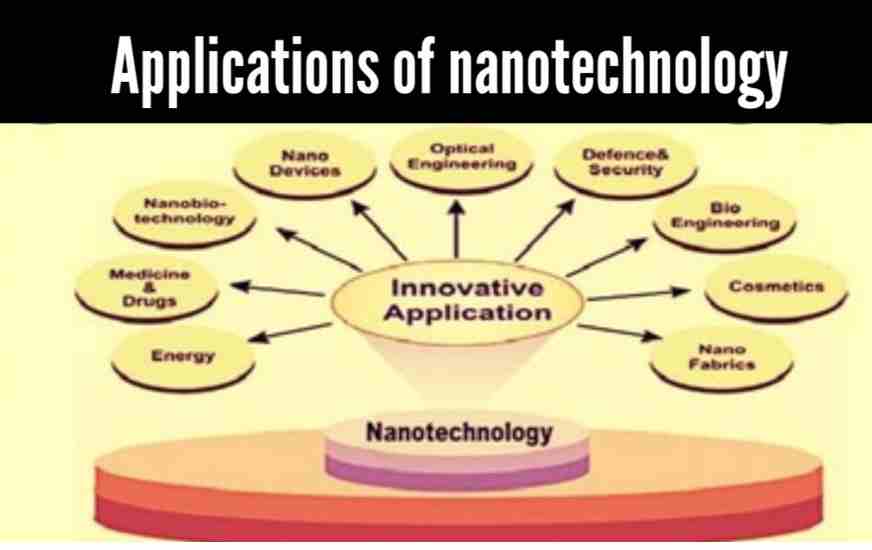
As of August 21, 2008, the Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies estimates that north of 800 producers recognized nanotech items as freely accessible, with new ones hitting the market at a speed of 3-4 for each week. The project records every one of the items in an openly available internet-based data set. Most applications are restricted to the utilization of “original” detached nanomaterials which remembers titanium dioxide for sunscreen, beauty care products, surface coatings, and some food items; Carbon allotropes used to produce gecko tape; silver in food bundling, dress, sanitizers, and home devices; zinc oxide in sunscreens and beauty care products, surface coatings, paints, and outside furniture stains; and cerium oxide as a fuel catalyst.
Further applications allow tennis balls to last longer, golf balls to fly straighter, and even bowling balls to become tougher and have a harder surface. Trousers and socks have been mixed with nanotechnology so they will endure longer and keep individuals cool in the summer. Bandages are being mixed with silver nanoparticles to mend cuts faster. Video game consoles and personal computers may become less expensive, quicker, and contain more memory because of nanotechnology. Also, to assemble structures for on-chip figuring with light, for instance, on-chip optical quantum data handling, and picosecond transmission of information.
Nanotechnology might be able to make existing clinical applications less expensive and simpler to use in places like the general specialist’s office and at home. Cars are being made with nanomaterials so they might require fewer metals and less fuel to work in the future.
Researchers are presently going to nanotechnology trying to foster diesel motors with cleaner fumes exhaust. Platinum is presently utilized as the diesel engine catalyst in these motors. The impetus cleans the exhaust seethe particles. Initial a decreased impetus is utilized to take nitrogen iotas from NOx particles to free oxygen. Next, the oxidation impetus oxidizes the hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide to shape carbon dioxide and water. Platinum is utilized in both the decrease and the oxidation catalysts. Using platinum, however, is wasteful in that it is costly and unreasonable. Danish organization Innovations Fonden put DKK 15 million in a quest for new impetus substitutes utilizing nanotechnology.
Nanotechnology additionally plays a noticeable part in the quick-creating field of Tissue Engineering. While planning frameworks, scientists endeavor to imitate the nanoscale highlights of a cell’s microenvironment to coordinate its separation down a reasonable lineage. For the model, while making platforms to help the development of bone, analysts may mimic osteoclast resorption pits.
Implications
An area of concern is the impact that modern scale assembling and utilization of nanomaterials would have on human wellbeing and the climate, as proposed by nanotoxicology research. Thus, a few gatherings advocate that nanotechnology be managed by states. Others counter that overregulation would smother logical exploration and the improvement of advantageous innovations. Public health research organizations, for example, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health are effectively leading the examination of potential wellbeing impacts originating from openings to nanoparticles.
Some nanoparticle items may have unintended outcomes. Analysts have found that bacteriostatic silver nanoparticles utilized in socks to decrease foot scent are being delivered in the wash. These particles are then flushed into the wastewater stream and may annihilate microbes which are basic parts of regular biological systems, ranches, and squander treatment processes.
Nanofibers are utilized in a few regions and in various items, in everything from airplane wings to tennis rackets. Breathing in airborne nanoparticles and nanofibers might prompt a number of pulmonary infections, e.g. fibrosis. Researchers have found that when rodents took in nanoparticles, the particles got comfortable in the mind and lungs, which prompted huge expansions in biomarkers for irritation and stress response and that nanoparticles initiate skin maturing through oxidative pressure in bald mice.
A two-year learn at UCLA’s School of Public Health observed lab mice consuming nano-titanium dioxide showed DNA and chromosome harm to a certain extent “connected to every one of the enormous enemies of man, specifically malignant growth, coronary illness, neurological illness, and aging”.
Regulations
Calls for tighter guidelines for nanotechnology have happened close by a developing discussion connected with the human wellbeing and dangers of nanotechnology. There is a huge discussion about who is liable for the guideline of nanotechnology. A few administrative offices right now cover a few nanotechnology items and cycles (to changing degrees) – by “rushing on” nanotechnology to existing guidelines – there are clear holes in these regimes. Davies (2008) has proposed an administrative guide portraying steps to manage these shortcomings.
Partners worried by the absence of an administrative structure to survey and control gambles related to the arrival of nanoparticles and nanotubes have drawn matches with bovine spongiform encephalopathy (“mad cow” disease), thalidomide, hereditarily altered food, nuclear energy, regenerative innovations, biotechnology, and asbestosis. Dr. Andrew Maynard, the boss science consultant to the Woodrow Wilson Center’s Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies, presumes that there is inadequate financing for human wellbeing and security research, and therefore there is as of now restricted comprehension of the human well-being and dangers related to nanotechnology. As an outcome, a few scholastics have called for stricter utilization of the precautionary standard, with postponed advertising endorsement, upgraded marking, and extra wellbeing information advancement necessities corresponding to specific types of nanotechnology.
The Royal Society report identified a gamble of nanoparticles or nanotubes being delivered during removal, annihilation, and reusing, and suggested that “makers of items that fall under extended maker responsibility regimes, for example, end-of-life guidelines distribute techniques illustrating how these materials will be figured out how to limit conceivable human and ecological openness”.
The Center for Nanotechnology in Society has observed that individuals answer nanotechnologies in an unexpected way, contingent upon application – with members in public deliberations more sure about nanotechnologies for energy than wellbeing applications – recommending that any open calls for nano guidelines might contrast by innovation sector.
Benefits Of Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology can possibly acquire significant advances in medication. Nanobots could be sent into a patient’s courses to gather up blockages. Medical procedures could turn out to be a lot quicker and more precise. Wounds could be fixed cell-by-cell. It might even become conceivable to mend hereditary circumstances by fixing the harmed qualities. Nanotechnology could likewise be utilized to refine drug creation, fitting medications at an atomic level to make them more compelling and diminish aftereffects.
In 2021, Nonwoven News reported that specialists at the University of Rhode Island have fostered a savvy swathe that can recognize and screen contamination in injuries utilizing single-walled carbon nanotubes. The nanotubes can recognize diseases by distinguishing centralizations of hydrogen peroxide. The swathe is observed remotely with a smaller than usual wearable gadget and sent to a cell phone to alarm the patient or a medical services supplier when contamination is recognized.
Conclusion
As an outcome, a few scholastics have called for stricter utilization of the precautionary standard, with postponed advertising endorsement, upgraded marking, and extra wellbeing information advancement necessities corresponding to specific types of nanotechnology.
The Royal Society report identified a gamble of nanoparticles or nanotubes being delivered during removal, annihilation, and reusing, and suggested that “makers of items that fall under extended maker responsibility regimes, for example, end-of-life guidelines distribute techniques illustrating how these materials will be figured out how to limit conceivable human and ecological openness”.
The Center for Nanotechnology in Society has observed that individuals answer nanotechnologies in an unexpected way, contingent upon application – with members in public deliberations more sure about nanotechnologies for energy than wellbeing applications – recommending that any open calls for nano guidelines might contrast by innovation sector.
Top 13 Interesting Facts About Nanotechnology
A nanometer is about the width of a strand of DNA; assuming that you configure, fabricate, or utilize practical frameworks less than 100 of these, you’re a nanotechnologist.
By that definition, we have been doing nanotech for quite a long time. For example, the colors in middle age stained glass windows result from nanocrystals created in the warming and cooling of the glass.
At the nanoscale, materials take on strange properties. Their tone, straightforwardness, and softening point frequently contrast essentially from those of bigger clusters of similar stuff.
Nanoscale pieces of metal oxide, carbon fiber, or metal mixes can detoxify risky waste: Their outrageous solvency and synthetic reactivity assist them in focusing on the terrible stuff.
This approach is now being utilized at destinations in twelve states, generally to clean groundwater fouled by solvents, metals, and petrol.
More splendid tones! More extravagant flavors! Less waste! Those are a portion of the justifications for why organizations are unloading nanoparticles into many items, including beauty care products, sunscreens, and food.
Experts say the worldwide market for fabricated merchandise utilizing nanomaterials could hit $1.6 trillion by 2013.
Oh, dear. Concentrates show that nanoparticles can work their direction into the circulation system, enter cells, and move beyond the blood-mind hindrance. Research has connected such particles to lung harm; the mind might be impacted as well.
Be that as it may, on the off chance that those particles don’t kill us, they could possibly save us. Researchers at U.C. San Diego have planned a fluorescent nanoparticle that shines inside the body, making it simpler to picture cancers and organ harm.
Yale analysts have created plastic nanospheres that epitomize proteins called cytokines, which animate the invulnerable framework’s executioner T-cells. An infusion of those circles could assist with battling illness and disease.
The USC group is attempting to gather these neurons into utilitarian organizations, which would carry us nearer to assistive mind inserts.
In 1989, utilizing a nuclear power magnifying instrument, IBM engineer Don Eigler turned into the main individual to move and control a solitary particle.
However, they’re not playing cowboy. The breakthrough could lead to strong quantum PCs that store and control information in the twist of individual electrons.




