Caste System In India
Origin of castes: There are five theories on why the caste system was invented in India. In ancient times caste word was not much popular; people were divided by the varna system. Varna system was not like it that you will be called the varna in which you were born. If you were born in Brahmin varna but if you like selling, and want to do business then you will be considered of Vaishya varna. Who used to work as he called off that varna. Just like, the son of the king will not be king.
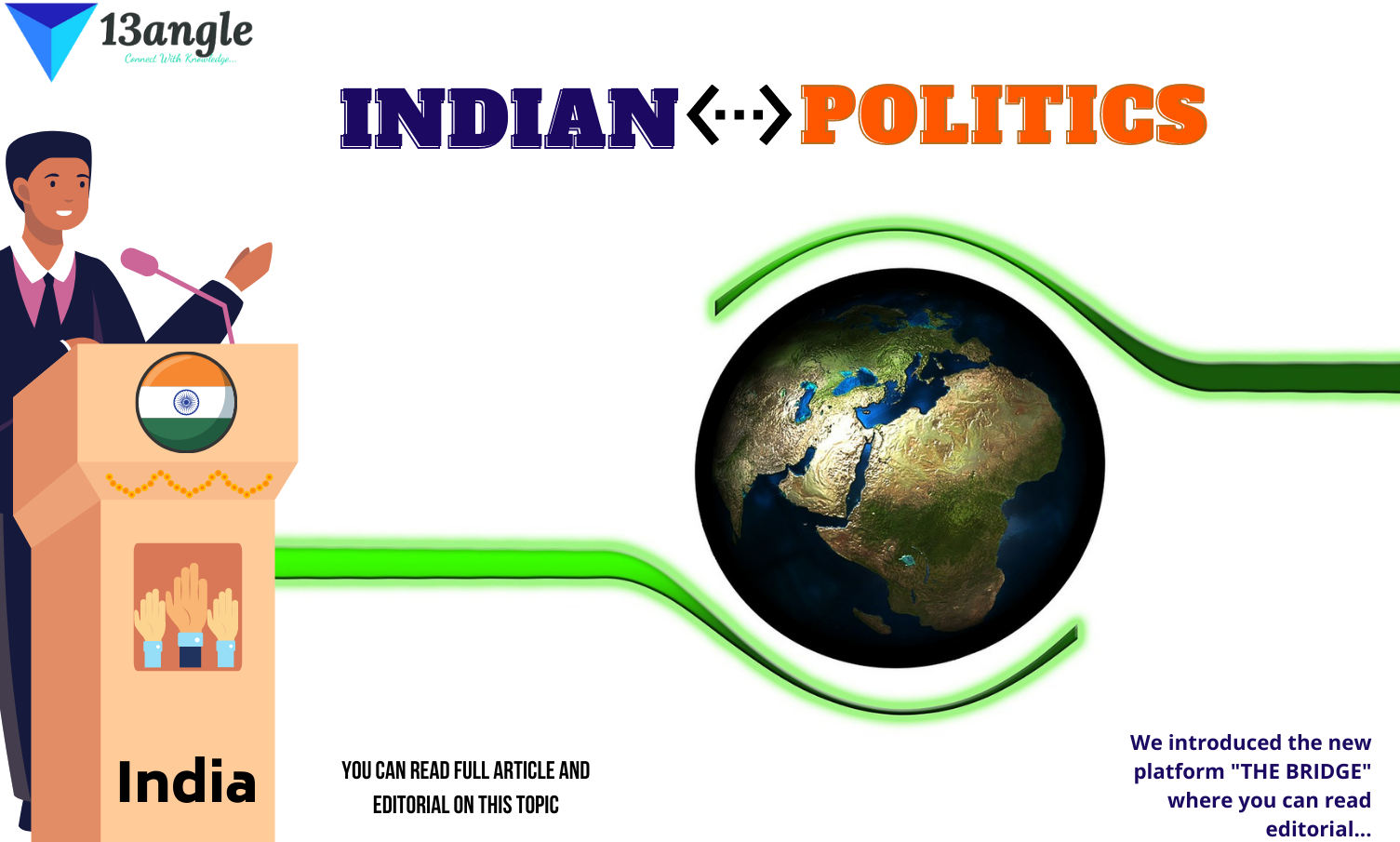
1. Traditional Theory: This is the oldest theory that says the caste system amplifies the varna system. In ancient times people didn’t use caste word, the method of division people was running was by varna system. The Sanskrit word varna means color. Four varnas came from the body of Lord Brahma. Which were Brahmin, Kshatriya, Vaishya, and Shudra.
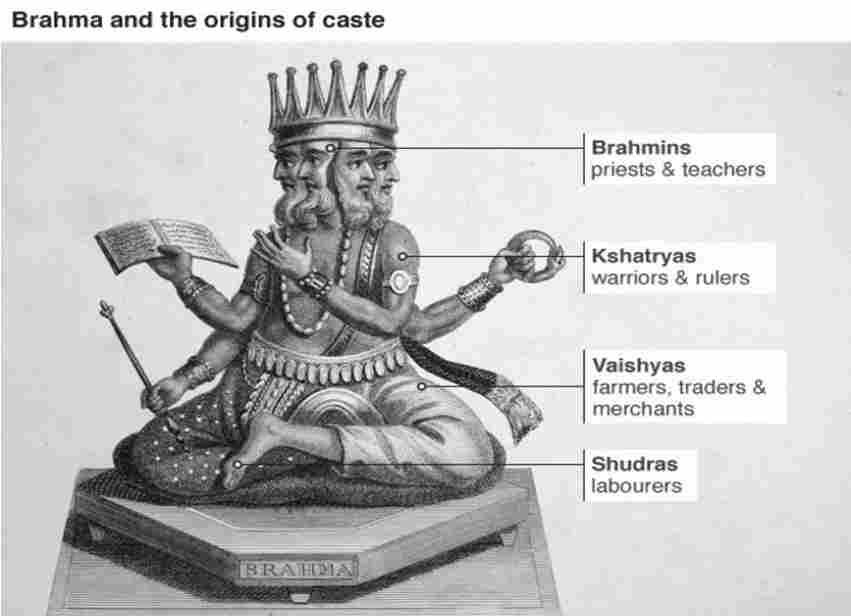

Brahmin: Those people who came out from the head of Lord Brahma were called Brahmin, and because they came from the top so they were put first. Basically, they were teachers or well-educated people. In short, those who used to worship recitation, and teach another and those who had knowledge of Shastras, Vedas, and Epics were called Brahmin.
Kshatriya: Kshatriyas were warriors and rulers who protected people and helped people. They came out from the arms or shoulders, and there is a lot of strength in our arms, that’s why Kshatriyas were strong people who were able to fight.
Vaishya: Trading, production, agricultural activities, and distribution were done by them. They came from the thighs of Lord Brahma’s body. The people who did business and trading were called vaishya.
Shudra: Those people who came from the feet of Lord Brahma were called Shudra and because they came from feet and as we know we stand up on our feet and there is much importance of them to serve other people who can teach, protect, and trading, so they were put at the last. They used to serve people, they were servants and servitors.
2. Racial Theory:-
According to this theory, people were divided by their color and physical features, in short, it is based on the physical features of people. The Sanskrit word Varna means color. During the time ancient Aryanas invaded north India, they captured all homes, accommodation, and properties of North Indian people. Robbed their house and drove them out of their places. So the people who lived in North India were Aryanas, they were white complexion and some about clean language. And after they invaded, the people who went to south India were called non-Aryanas, their complexion was dark and they used their local language. This is what the racial theory says and the caste system is an extension of Aryanas and Nn-Aryanas.
And this thing is remaining on somewhere even today. Many times we see discrimination in people against white and dark-colored people, who have white complexion they believe themselves upper than people with a dark complexion.
3. Political Theory: This theory is inspired by the traditional theory and it’s an extension of that. Brahmin varna’s people had cleverly invented this thing. They wanted to put themselves on the top. So they told rulers if they do prayer or worship before any war, they can easily win that fight. And who will help rulers to help them with any prayer? Obviously, Brahmins, because that was their profession. That’s the reason why Brahmin was put first, they had to stay on the top because they wanted to remain in that system further with a view to don’t lose their respect. This is the political theory, Brahmin wanted to keep them at the top and carry forward the tradition that was going on.
4. Occupational Theory: Like traditional theory, this theory is also based on the profession of people. So according to occupational theory, people remained on the top that did respectable work. And the people who did dirty work meant work cleaning roads, gutters, bathrooms, and toilets; they were called the lowest caste. And this thing also has been remaining till date, because today’s caste system is also like it’s an extension.
5. Evolutional Theory: This theory claims that the caste system did not come quickly in India, people have been believing many for time upper caste and lower caste. Brahmins who taught people and work to pray and work of worship were called upper caste and Shudra who did dirty work or cleaned roads, bathrooms, and toilets were called lower caste. On one side Brahmin held their position on the top and Shudra went down and down with less respect for their work.
- So these were three theories of how the caste system was invented in India. Now we are going to discuss the Kshatriya caste in detail.
History Of Kshatriyas

Kshatriya is one of the four varnas of Hindu culture and it is less of a caste and more of a community. Protect all other religions and community and patriotism were their identity.
They were so brave, expert, and smart in war and fights.
Be fearless, valiant, daring, truthful, and full of dignity these qualities were commonly and easily found.
Properties And Identities Of Kshatriya
- Courage, grace, and brilliance were seen in every Kshatriyas. According to the 43rd shlok 18th chapter of Shrimad Bhagavad Geeta,
शौर्यं तेजो धृतिर्दाक्ष्यं युद्धे चाप्यपलायनम् ।
दानमीश्वरभावश्च क्षात्रं कर्म स्वभावजम् ।।
Kshatriyas should have a quality of bravery; Kshatriyas should be valor and strong determination in war. It’s the duty of every king to protect their people, state, and kingdom. It was necessary to be determined to follow and protect his religion. He should be a genius in taking all decisions. He always moved forward in war, and never ran away from the battleground. He should be a good donor, who donates the funds to the people of the state. He filled the necessaries of all people. If there is any deficiency or some mistake has happened, then he considers himself guilty.
Kshatriyas never took decisions without thinking, in his court he keep some experts or ministers for the right suggestions.
What Is Written About Kshatriyas In Vedic Texts?
- Kshatriyas was at the top not second in Vedic texts. It has been mentioned that Kshatriyas were destroyed by Parshurama the sixth avatar of Lord Vishnu.
- Brahmanic texts claim the victory of Brahmins but some epics claim it differently.
- People of the Hindu religion were considered as the protector of state land and maintained their image strong.
- Kshatriyas did the profession of war and captured lands of another state by defeating its rulers.
What Is Written About Kshatriyas In Rigveda?
Rigveda also claims the description of the symbolic structure of four varnas.
It has used the Rajanya word instead of the Kshatriya word in Purusha Sukta.
In the end time of Vedic Rajany word was changed into Kshatriyas.
Sages believe that Rajanya were political people and rulers who ruled on state and protect people and fight battles to increase their state and image, prestige, and own state.
In the Sanskrit language, Kshatra is the meaning of ruler and that word also describes the meaning of power and energy.
They had the idea of monarchy and owning the land.
Sanskrit Shlokas Of Shrimad Bhagwat Geeta

स्वधर्ममपि चावेक्ष्य न विकम्पितुमर्हसि ।
धर्म्याद्धि युद्धाच्छ्रेयोऽन्यत्क्षत्रियस्य न विद्यते ॥
Meaning: “Even after seeing your religion (Kshatriya religion), you should not be disturbed or distraught, because nothing is more beneficial to a Kshatriya than a war of religion.”
यदृच्छया चोपपन्नां स्वर्गद्वारमपावृतम् ।
सुखिनः क्षत्रियाः पार्थ लभन्ते युद्धमीदृशम् ।।
Meaning: “O Partha! The Kshatriyas attain this war on their own, that is, spontaneously and as the opened gates of heaven.”
Rajputs
- The meaning of the Rajput word is the son of a king. They believe a Kshatriya themselves. The Rajput rule was from 700 CE to1200 CE, and some historian reports claim duration between 700 CE to 1200 CE in middle, North-West India and there are some Muslim Rajputs in East Pakistan. Personal honor, ideal, and dignity these qualities are included in them.
The Origination Of Rajput
It started in the middle of the 5th century with a huge division in Indian society.
Some historical notes say that some aboriginal people got the status of Rajput, some of them mean aboriginal ministers considered Rajput.
Some epics like Mahabharata claim that Rajputs and Kshatriyas are the same. But there is a lot of controversy going on between Rajput and Kshatriya, whether they are different or the same.
Are Rajputs Kshatriyas or not? There are some different theories on this topic.
Theory of Colonel James Tod: He was a British historian, who claimed that Rajput is an extension of some foreign castes, which were invented in India. And he said that the same people who had won during the war would go ahead and become Rajputs. But Indian historians do not believe that because Tod was an officer of the British East India Company.
Theory of Gaurishankar Harichand Auja: He is a historian who claims that Kshatriya who was connected to Araya became Rajput.
Theory of Chand Bardai: He was a state poet and good friend of Chauhan dynasty ruler Prithviraj Chauhan. Chand Bardai claimed Bakshish Rishi prayed on mount Abu for help to fight enemies. AndRishi Bakshish got four Rajput castes from the fire pit. Which were Gurjar Pratihar, Chauhan, Parmar and Chalukya. But this story is considered an imaginary story.
Theory of Gopinath Sharma and Bhandarkar: These two historians claim that Rajput originated from of Brahmin caste.
- According to Colonel James Tod and Prithviraj Raso a book of Chand Bardai, there were 36 gautra (clans) in ancient India. Which are given below,
Suryavanshi | 10 |
Chandravanshi | 10 |
Agnikund (fire pit) | 04 (Gurjar Pratihar, Chauhan, Parmar, and Chalukya) |
Krishivanshi | 10 |
Rajput Rule Started In 800 Ce In North Indian States. Like, As Gujarat, Rajasthan, Maharastra, Delhi, Punjab, Kannauj, And Madhya Pradesh. Muslim Rulers Started Entering India From 700 To 1200 Ce. Rajputs Were The Biggest Resistance To Muslim Rulers.
During The Rule Of The Rajputs, The King Of The Following Dynasties Ruled India.
1. Gurjara-Pratihara

- Gujarat and jodhpur Rajasthan (between the 6th and 9th centuries). Nagbhata was founder of Pratihar (Gurjara-Pratihar) dynasty. Ujjain was the capital of them in the starting but after some time main capital was Kannauj. They were descendants of Lakshman brother of Lord Ram and that’s why they were called Dwarpal, Pratihar. Mir Kasim was the first Muslim ruler who invented them. Mihir Bhoj was the major ruler of this dynasty whose kingdom grew well and Yashpal was the last one.
2. Chalukya

- After the ending of the Gurjar Pratihara dynasty, Gujarat and Rajasthan (between the 6th and 12th centuries). Mulraj Pratham was the founder. During the rule of Bhim Pratham, Ghori first time invaded Somnath. One minister of Bhim Pratham made a Jain temple on mount Abu. Siddhraj Jaysinh was the chief ruler of the Chalukya dynasty. He made seven statues of his lineage on Mount Abu. Modhera Sun temple was also structured at that time.
3. Chauhan Dynasty

- It is the most important dynasty which ruled India, Ajmer, and Delhi (between the 6th to 12th centuries). Chauhan dynasty was divided into 24 different subcastes. Its founder is Vasudev but some say Chahamana is the founder that’s why that dynasty was named by Chauhan. Ajmer was tier capital. Somdev wrote Lalit Vigrahraj, about king Vigrahraja. Prithviraj Chauhan was the chief ruler of the Chauhan dynasty. Chand Bardai was his friend and state poet who wrote Prithviraj Raso, and Jaynaka wrote Prithviraj Vijaya. The first war of Tarain and the second war of Tarain are the most famous wars in Indian culture. Prithviraj was the last ruler of the Rajput dynasty.
4. Parmar Dynasty

- Malwa and west-central India (between 9th and 14th centuries) Dhar and Mandu capitals. It is said that the founder of the Parmar dynasty is Upendra or Krishnaraj or Ajab Dev Parmar. Dharanagari was the main capital of the Parmar dynasty. Raja Bhoj was the major ruler of this that dynasty. He was so brilliant and clever. He is known as Kaviraj, he wrote books on science, maths, Ayurveda, and therapy. He made a Sanskrit Vidhyalaya (school) and Sarasvati temple.
5. Chandela Dynasty
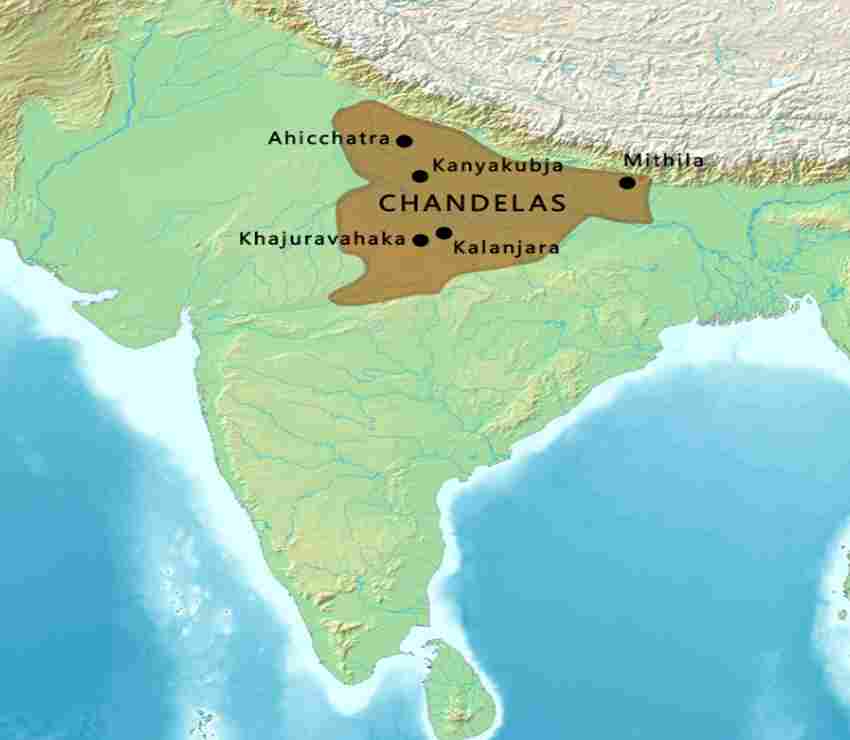
- After the ending of the Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty, Bundelkhand. (Between 8th and 12th centuries). It was founded by Nannuka. Khajuraho was the capital. At that time Parmardi dev was defeated by Prithviraj Chauhan.
6. Sisodiya Dynasty

- Mewar and Rajasthan (Hammira Singh founded this dynasty in 1326). It is also called the “House of Mewar”. Bhagwat Singh was the final ruler of this dynasty.
7. Gaekwad Dynasty

- Kannauj to Varanasi(from the 18th century until 1947). Their rule started after the end of the Pratihar dynasty. Chandra dev was the founder of this dynasty but some notes claim the name of Damaji. Jaichand was one of the rulers of the Gaekwad dynasty. Many people know the story of Jaichand and Prithviraj, where Prithviraj took the daughter of Jaichand from the crowded assembly. And they became enemies of each other. Muhammad Ghori killed Jaichand in 1194.
What Did They Do For The Country?
- Kshatriya Rajputs were so brave, strong, powerful and so firm for the matter of their image and prestige. There are great sacrifices of Rajput rulers for the country. They always fought for their motherland, their religion, and their self-respect. And there is no doubt that they were not a patriot.
The Rajput race is the noblest and proudest of India. There is a big contribution of Rajputs to save the country and people.
They protected India many times from different types of invaders and dedicated their lives to the military. It is said that there is a major contribution of them to the country.
They gave money and much more wealth to the country and its welfare. They provided funds for the start-up and helped much for the nation.
Many kings supported India in uniting small states and forming a federation.
Even during British rule, many Rajput kings are known to have a nationalist movement against them.
Bappa Rawal, Rana Kumbha, and Prithviraj Chauhan are the well-known Rajput kings for their power, impact, impression and their war skills, etc.
Yes, there are some things that history does not forgive, such as Prithviraj Chauhan letting Ghori go and on the contrary, it went heavy on him. But it is not like, that’s the only reason why Muslim invaders established their rule on the country. We can’t say that he did nothing but he did everything to let them stop. His sacrifices and efforts to save the country were not so little that we can ignore them.
OBC (Educationally And Socially Backward Class)
Kshatriya is a big class of Hindu castes in India. After the varna system was invented in India, subcastes of four varnas began to emerge. The feeling of difference between people started spreading more. Now Kshatriya varna has many subcastes in Indian society. We know the Chauhan caste had been divided into 24 different subcastes. Many times before there were castes like ST, SC, and general but OBC wasn’t. OBCs are described as socially and educationally backward caste by the Indian Constitution.
The backward class (The castes which are educationally and socially disadvantaged) is the term used by the Government of India. According to the Mandal Commission report, in 1980 OBCs were 55% country’s population of India. And the National Sample Survey Organization claimed about 41% in 2006.
Until 1985, the backward classes’ cell in the ministry of home affairs took care of backward classes. But another ministry was established in 1985, especially for backward classes.
Top 13 Interesting Facts About Kshatriyas
Kshatriyas are at the second stage in the ancient varna system and came from the arms of Lord Bramha. And because our arms are strong so Kshatriyas were called warriors and rulers. To rule the state, fight, protect people, and maintain the welfare of people were the professions of Kshatriya.
Kshatriyas are also known as Rajputs, yet some people believe that both are different. But some Indian historians, historical notes/reports, and books claim both to be the same.
These were some of the qualities that were seen in him, brave, strong, intelligent, donor, an expert in war/battles, fearless, etc. They also protected their religion, and it is said that they never stepped back from the battleground.
Many people claim that OBCs have been left behind in teaching. Most of the people of the OBC caste believe in superstitions.
Rule of Rajputs was from 647 A.D. (or around 7th century A.D.) to 1200 A.D., from the death of Harshvardhan to the 12th century. They ruled for about 500 years in India. The rule of the Rajput dynasty ended after the death of Prithviraj Chauhan.
Many times it is mentioned that Rajputs used to fight and quarreled inside. And the foreign Muslim rulers took the advantage of this. And that’s why the Rajput rule ended and Muslim rule started in India.
The practice of Sati was so famous during the rule of Rajputs, the practice of Sati promotes injustice against women in society. It’s a long story in Hindu religious texts where Goddess Sati jumped in the fire of yajna. In Rajput rule when a man is killed by any invader then his wife would self destroy herself by jumping in the fire. This system was protested by Raja Rammohan Roy and good results were seen.
In Ramayana, Lord Ram didn’t become a king because he was a big son but he became a king because he had those qualities which are the same as Kshatriya. Basically, it means the son of the king will not become the king, but he will become the king who has the qualities of Kshatriya. If I am the son of a Brahmin, but I love marketing, business, or agriculture so I could be a Vaishya.
OBC is a socially and educationally backward caste not economically.
OBC, ST, SC, and genera these castes can not prove that the people of the following cast are Kshatriyas or Brahmins and Shudras or Vaishyas. Kshatriya was varna not a caste only, there are many castes under Kshatriya varna.
Four gautra came out from the fire pit (Agnikund), which were Gurjar Pratihar, Chauhan, Parmar, and Chalukya. Chauhan was divided into 24 different castes.
There is a big discussion on the number of people who are OBCs. It is considered a large number but some people and their reports claim that is bigger than the report of the National Semple Survey.
Even if we talk about today’s society, we can easily see that four varnas according to the varna system. The teachers who give the knowledge are Brahmins. The soldiers, army officers, ministers whoever does the work of power and public welfare is Kshatriya. Traders and businessmen are Vaishyas and people who work for cleaning and servicing are Shudras.