- Umang Sagar
- Disease, Recent article
Breast Cancer

What Is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer is a type of cancer in the breast; when your healthy breast cells become abnormal, grow out of control by dividing more rapidly and forming tumors.
Breast cancer can occur in women and rarely in men.
1 in 8 women is at risk of developing breast cancer and 1 in 1000 men is at risk of developing breast cancer.
Breast cancer is a global cause for concern owing to its high incidence around the world.
With some 1,78,000 new cases being diagnosed every year, the incidence of breast cancer has overtaken cervical cancer to become the most common cancer in Indian women.
Breast cancer is a leading health concern among women due to its high mortality and morbidity rate.
What Are The Different Types Of Breast Cancer?
Overview of the breast:-
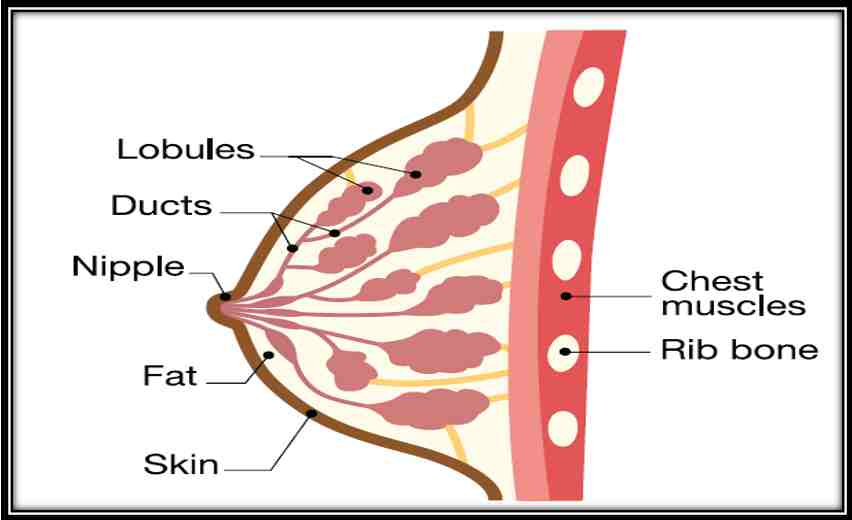
The breast is an organ whose structure reflects its special function: the production of milk for lactation (breastfeeding).
A breast is made up of three main parts: lobules, ducts, and connective tissue.
The lobules are the glands that produce milk.
The ducts are tubes that carry milk to the nipple.
The connective tissue (which consists of fibrous and fatty tissue) surrounds and holds everything together.
The chest muscles are responsible for moving the arms across the body and up and down, as well as other movements like flexion, adduction, and rotation.
Ribs give support to breasts.
Types Of Breast Cancers:-
There are several different types of breast cancer, the main types including:
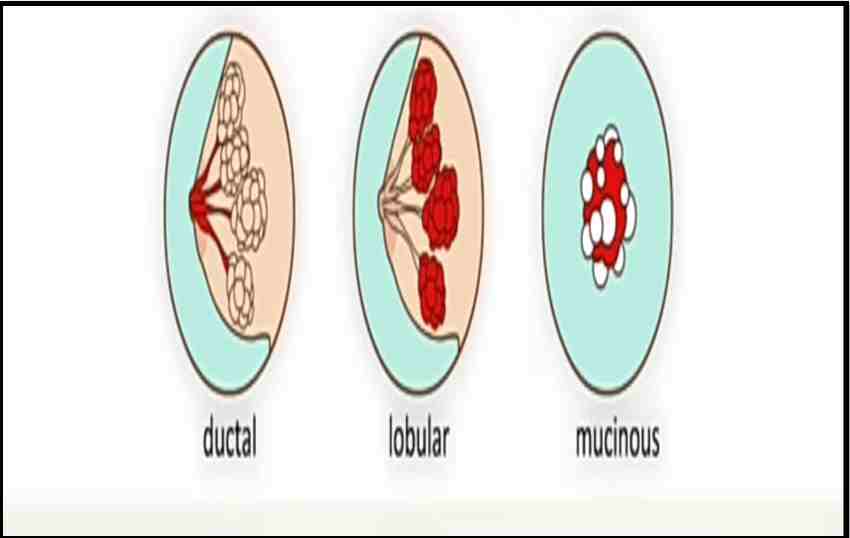
1. Ductal carcinoma:
Its presence of abnormal cells inside a milk duct in the breast. It is of two types: Infiltrating and Ductal carcinoma in situ.
Infiltrating (invasive) ductal carcinoma:
- Infiltrating (invasive) ductal carcinoma starts in the milk ducts of your breast, this cancer breaks through the wall of your duct and spreads to surrounding breast tissue.
- It accounts for 80% of all cases
- This is the most common type of breast cancer.
Ductal carcinoma in situ:
- Also called Stage 0 breast cancer
- Ductal carcinoma in situ is precancerous because the cells haven’t spread beyond your milk ducts.
- This condition is very treatable.
- Care is necessary to prevent cancer from becoming invasive and spreading to other tissues.
2. Lobular carcinoma:
- Its presence of abnormal cells inside the lobules in the breast. It is two types Infiltrating (invasive) lobular carcinoma and Lobular carcinoma in situ.
Infiltrating (invasive) lobular carcinoma:
- This cancer forms in your breast’s lobules and spreads to surrounding breast tissue.
- It accounts for 10% to 15% of breast cancers.
Lobular carcinoma in situ:
- Lobular carcinoma in situ is a precancerous condition with abnormal cells in your breast’s lobules.
- It isn’t true cancer.
- But this marker can indicate the potential for breast cancer later.
- So, it’s essential for women with lobular carcinoma in situ to have regular clinical breast exams and mammograms.
3. Mucinous carcinoma:
- Mucinous carcinoma of the breast is an uncommon form of breast tumour, often presenting as a lobulated
- characterized by the presence of extracellular mucin
- invasive breast carcinoma.
Other types include:
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC):
- Triple-negative breast cancer has a BRCA1
- Making up about 15% of all cases.
- It’s called triple negative because it doesn’t have three markers associated with other types of breast cancer. This makes prognosis and treatment difficult.
Inflammatory breast cancer:
- Rare and aggressive, this type of cancer resembles an infection.
- People with inflammatory breast cancer usually notice redness, swelling, pitting, and dimpling of their breast skin.
- It’s caused by obstructive cancer cells in the skin’s lymph vessels.
What Age Does Breast Cancer Occur?
- The main factors that influence your risk include being a woman and getting older. Most breast cancers in women occur at ages around 50 and above years. In a few cases, breast cancer is occurring in the. Most breast cancers in men occur at age around 60 and above years.
What Are The Risk Factors Of Breast Cancer?
The risk of developing breast cancer in women occurs in the following conditions like:
Older age: with increasing age, there is an increased risk of breast cancer that is at age around 50 and above years are at more risk of breast cancer.
Dense breast: The denser your breasts are, the higher your risk. Women with dense breasts are 4-5 times more likely to get breast cancer than women with fatty breasts.
Having breast cancer before: There is a chance of reoccurrence of breast cancer in people having breast cancer before.
Family history: Having a mother, sister or daughter (first-degree relative) diagnosed with breast cancer approximately doubles the risk of breast cancer.
Inherited gene mutation: The most common cause of hereditary breast cancer is an inherited mutation in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene.
Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry: Ashkenazi Jewish men and women have more BRCA1/2 mutation. So, there is a more increased risk of breast cancer.
Alcohol use: Even moderate consumption of alcohol consumption can increase by 30-50% of increased risk.
- Overweight or obesity: Fat tissue (also called adipose tissue) produces excess amounts of estrogen, high levels of which have been associated with increased risks of breast cancer.

The risk of developing breast cancer in men occurs in the following conditions like:
Older age: with increasing age there is an increased risk of breast cancer that is at age around 60 and above years are at risk of breast cancer.
Exposure to estrogen: If you take estrogen-related drugs, such as those used for hormone therapy for prostate cancer, your risk of breast cancer is increased.
Family history of breast cancer: If you have a close family member with breast cancer, you have a greater chance of developing the disease.
Klinefelter’s syndrome: Klinefelter’s syndrome causes abnormal development of the testicles. As a result, men with this syndrome produce lower levels of certain male hormones and more female hormones.
Liver disease: Certain conditions, such as cirrhosis of the liver, can reduce male hormones and increase female hormones, increasing your risk of breast cancer.
Obesity: Obesity is associated with higher levels of estrogen in the body, which increases the risk of male breast cancer.
- Testicle disease or surgery: Having inflamed testicles (orchitis) or surgery to remove a testicle (orchiectomy) can increase your risk of male breast cancer.
What Are The Causes Of Breast Cancer?
Age: women aged 50 and above are more prone to breast cancer.
Gender: women are more prone to breast cancer than men.
Alcoholics: Alcoholics women are more prone to breast cancer than normal women.
Smoking: Tobacco consumption is linked to being more prone to breast cancer.
Obesity: Fat tissues produce excess amounts of estrogen, high levels of which have prone to breast cancer.
Family history or genetics: BRCA1/2 gene mutations can lead to breast cancer.
Hormone replacement therapy: In the case of Hormone replacement therapy, it leads to hormonal imbalance leading to uneven hormonal levels and thus causing breast cancer.
Radiation exposure: Radiation exposure may trigger the tumor growth factor and sometimes thereby can induce cancer.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: If you are never pregnant or never breastfed feed you may be prone to breast cancer.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer?

Signs and symptoms of breast cancer include:
- Nipple Discharge from the breast
- Lumping or thickening of the breast
- Skin texture changes
- Pain in the armpit
- Changes in the nipple
- Visible lumps
- Dimpling
- Pulled in nipples
- Skin irritation near the breast
- Skin dimpling
What Are The Stages Of Breast Cancer?
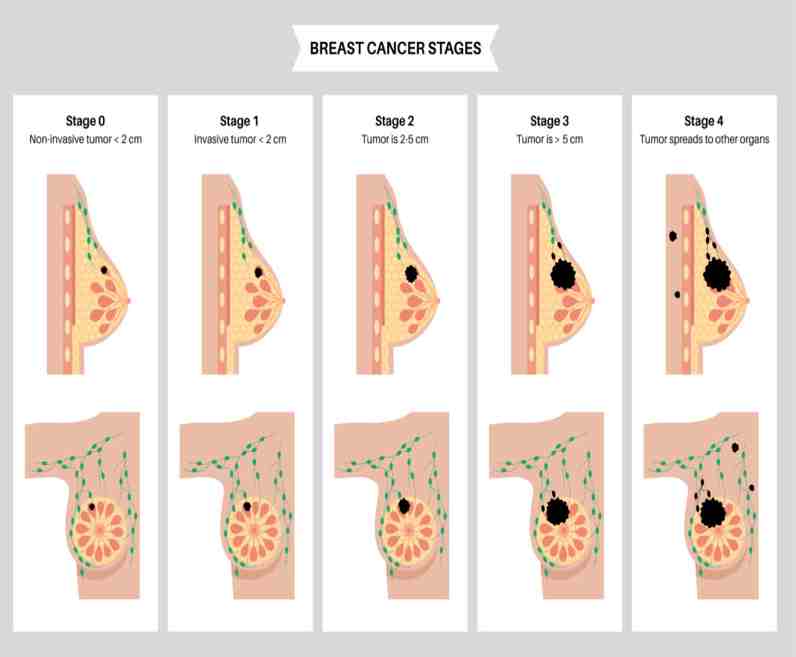
There are 5 stages of breast cancer and these stages help in finding the severity of the disease.
They include stage 0, stage 1, stage 2, stage 3, stage 4
- Stage 0: The disease is non-invasive in this stage. This means cancer did not spread.
- Stage I: The disease is non-invasive in this stage. The cancer cells have spread to the nearby breast tissue.
- Stage II: The disease is non-invasive in this stage. Tumours at this stage can measure between 2 to 5 centimeters across and may or may not affect the nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage III: It is locally advanced breast cancer. At this stage, cancer has spread beyond the point of origin.
- Stage IV. It is the most advanced stage. Cancer has spread to areas away from your breasts, such as your bones, liver, lungs, or brain.
How Can You Detect Breast Cancer Before The Spread?
- Breast cancer can be detected earlier by Breast self-exam, get routine mammograms, have your breasts examined by a healthcare provider.
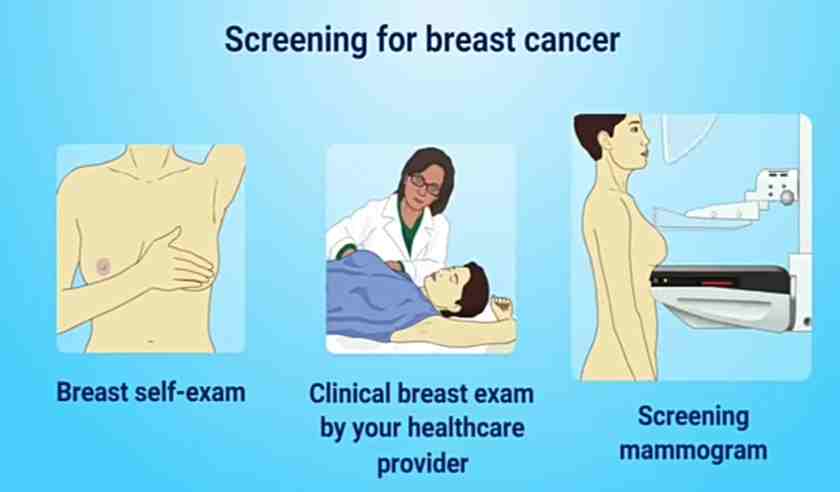
1. Breast self-exam
- Do a Breast self-exam every month after age 20. It helps to detect cancer earlier. Using your left hand, move the pads of your fingers around your right breast gently covering the entire breast area and armpit. Use light, medium, and firm pressure. Squeeze the nipple; check for discharge and lumps. Repeat these steps for your left breast.
2. Get routine mammograms:
- Once you cross 35 start getting mammogram checks every year.
3. Clinical breasts examination by a healthcare provider
- At least once every three years after age 20, and every year after age 40. Clinical breast exams can detect lumps that mammograms may not find.
How Can You Diagnose Breast Cancer?
- Diagnosing breast cancer is a vital step. The breast cancer diagnosis can be done through the following diagnostic tests

1. Diagnostic mammogram:
- A diagnostic mammogram is a special x-ray of the breast.
- It can detect abnormalities in the breast like lumps.
2. Breast ultrasound:
- Breast ultrasound uses sound waves to take pictures of the tissues inside of your breast.
- It’s used to help diagnose breast lumps or abnormalities.
3. Breast MRI:
- This test uses magnets and radio waves.
- Breast MRI produces clear, detailed images of the structures inside of your breast.
4. Breast Biopsy:
- It is the most confirmative test to identify breast cancer.
- In a breast biopsy, small piece of breast tissue is removed and checked in a lab.
- This is done to see if cancer or other abnormal cells are present.
How Is Breast Cancer Treated?
- There are several breast cancer treatment options which include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted drug therapy. The doctor will provide you with the right treatment option by considering lab tests, the location and size of tumour, and the spread of the cancer. You may also get combination therapy based on your health condition.
Surgery: It aids in the removal of the cancerous portion of the breast. The different types of surgeries include:
Mastectomy– Mastectomy is the surgical removal of the entire breasts many women, choose to undergo breast reconstruction after their mastectomy.
Lumpectomy– Lumpectomy is the surgical removal of the tumour and the surrounding cells present around the tumour. It may also involve the removal of the lymph nodes in the tumour area. Many people undergo radiation therapy after the lumpectomy.
Modified radical mastectomy– Modified radical mastectomy is the surgical removal of the entire breast in addition to your nipple and nearby lymph nodes in your underarm area. Breast reconstruction can often be an option if desired.
The radical mastectomy–This procedure is performed when the breast cancer has spread to your chest wall muscles. Radical mastectomy is the surgical removal of the entire breast in addition to your nipple and nearby lymph nodes in your underarm area and chest wall muscles. People who undergo this procedure may choose to have breast reconstruction.
Sentinel node biopsy– The doctors inject a dye which tracks the first lymph node that cancer would spread to. If that lymph node has cancer in it is called a sentinel lymph node, and it may be necessary to remove additional lymph nodes.
Chemotherapy:
- Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses powerful chemicals to kill fast-growing cancer cells in your body.
- Chemotherapy acts by either shirking or destroying the cells.
Radiation therapy:
Radiation therapy for breast cancer uses high-energy X-rays, protons, or other particles to kill cancer cells.
Radiation therapy may be used to treat breast cancer at almost every stage.
Radiation therapy for breast cancer may be delivered through:
- External radiation. It delivers radiation from outside your body to the breast. This is the most common type of radiation therapy used for breast cancer.
- Internal radiation (brachytherapy): It delivers radiation directly to the breast area. This type is used after the surgery.
Hormone therapy:
- Hormonal therapy is mainly used to prevent the reoccurrence of breast cancer.
- Hormonal therapy works by either decreasing the estrogen levels or by stopping the estrogen to bind to the estrogen receptors thereby reducing cancer.
Immunotherapy:
- Immunotherapy is the use of medicines to boost a person’s own immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively.
- Monoclonal antibodies and PD-1 inhibitor like Pembrolizumab.
Targeted drug therapy:
- Some drugs can target specific cell characteristics that cause cancer.
- Some of the most common drugs used in breast cancer treatment include monoclonal antibodies (like trastuzumab, pertuzumaband margetuximab), antibody-drug conjugates (like ado-trastuzumab emtansine and fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan) and kinase inhibitors (such as lapatinib, neratinib, and tucatinib).
How Can You Prevent Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer may be prevented by the following things:
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking.
- Have regular checkups if you are taking hormone replacement therapy or an oral contraceptive.
- Breastfeed your infants.
- Be physically active.
- Eat more plant-based foods.
- Do a Breast self-exam every month after age 20.
- Once you cross 35 starts getting a mammogram to check every year.
- Participate in yoga, exercises, and stress-relieving activities.
How Can You Create Awareness About Breast Cancer?
- October is breast cancer awareness month, an annual campaign to educate people about breast cancer.

- Don’t ignore any lumps or nodes in your breast
- Self-examine your breast regularly.
- Raise awareness about risk factors.
- Spread the news like mammograms save lives.
- Motivate and give emotional support to breast cancer warriors.
- Share survivor stories.
Top 13 Interesting Facts On Breast Cancer
-
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death among women.
-
A woman’s risk for developing breast cancer increases as she gets older.
-
1 in 8 women develops breast cancer.
-
October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month.
-
Most patients diagnosed with breast cancer will not experience a recurrence.
-
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, you shed breast tissue. This shedding can help remove cells with potential DNA damage, thus helping to reduce your chances of developing breast cancer.
-
Most breast cancers are found in women who are 50 years old or older.
-
Nipple discharge can be the earliest presenting symptom of breast cancer.
-
Most breast cancers begin in the ducts or lobules of the breast.
-
Breast self-examinations can help in the early detection of breast cancer early, thereby improving the chances of a full recovery.
-
About 1 out of every 100 breast cancers diagnosed in the United States is found in a man.
-
Current trends point out that a higher proportion of the disease is occurring at a younger age in Indian women, as compared to the West.
-
India has just over 2000 oncologists for 10 million patients, and the number of oncologists is unevenly spread, being lower in semi-urban and rural areas.



