Introduction
- Business is any economic activity that includes the purchase or sale of goods or services with the basic objective of earning profit and satisfying the individuals’ needs of society. Every individual has different needs, and to fulfill these needs, they perform different activities. These activities are categorized as economic and non-economic activities.
Economic Activities | Non-economic Activities |
Economic activities refer to those activities that are performed with the objective of earning money and creating wealth. Economic activities are of three types, namely, Business, Profession, and Employment. For example, an individual running an organization is a business, a teacher teaching at a school is a profession, and an employee working in an organization is employment. | Non-economic activities refer to those activities which are performed with the objective of satisfying emotional, social, and psychological needs. Earning money and livelihood is not the motive of human beings while performing non-economic activities; instead, people perform them out of sympathy, love, affection, etc. For example, a mother cooking food for her children, a sports teacher coaching his daughter, and friends teaching each other before exams are considered non-economic activities. |
- All economic activities that involve the sale and/or purchase of goods and services with some element of risk and motive of earning profits are known as business. All business activities also aim at satisfying the needs of human beings in society.
Understanding The Concept Of Business
The term business often refers to an entity that operates for commercial, industrial, or professional reasons. The concept begins with an idea and a name, and extensive market research may be required to determine how feasible it is to turn the idea into a business.
Businesses often require business plans before operations begin. A business plan is a formal document that outlines the company’s goals and objectives and lists the strategies and plans to achieve these goals and objectives. Business plans are essential when you want to borrow capital to begin operations.
Most businesses operate to generate a profit, commonly called for-profit. However, some businesses that have a goal to advance a certain cause without profit are referred to as not-for-profit or non-profit. These entities may operate as charities, arts, culture, educational, and recreational enterprises, political and advocacy groups, or social services organizations.
A company often defines its business by the industry in which it operates. For example, the real estate business, advertising business, or mattress production business are examples of industries. Business is a term often used to indicate transactions regarding an underlying product or service.
Types Of Business
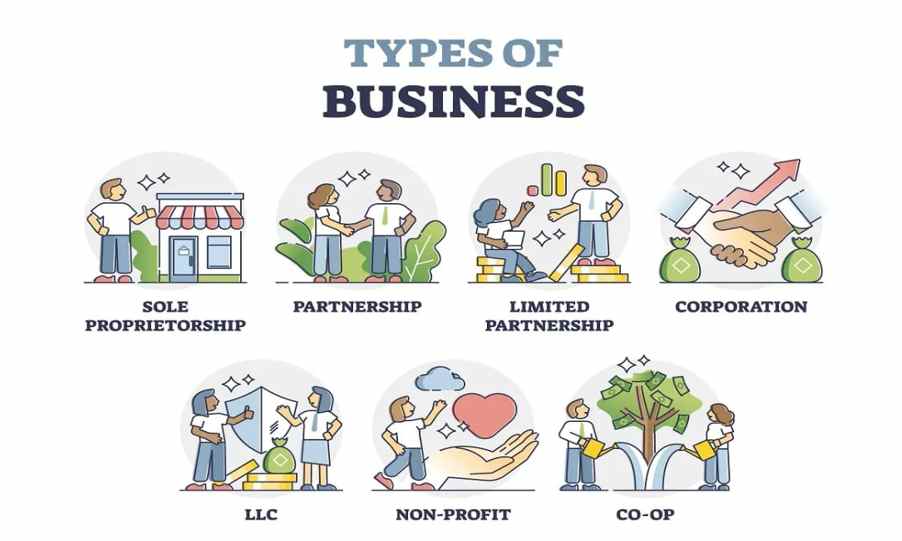
When beginning a business, you must decide what form of business entity to establish. Your form of business determines which income tax return form you must file. Legal and tax considerations enter into selecting a business structure.
There are many ways to organize a business, and there are various legal and tax structures that correspond with these.
Businesses are commonly classified and generally structured as:
1. Sole Proprietorships
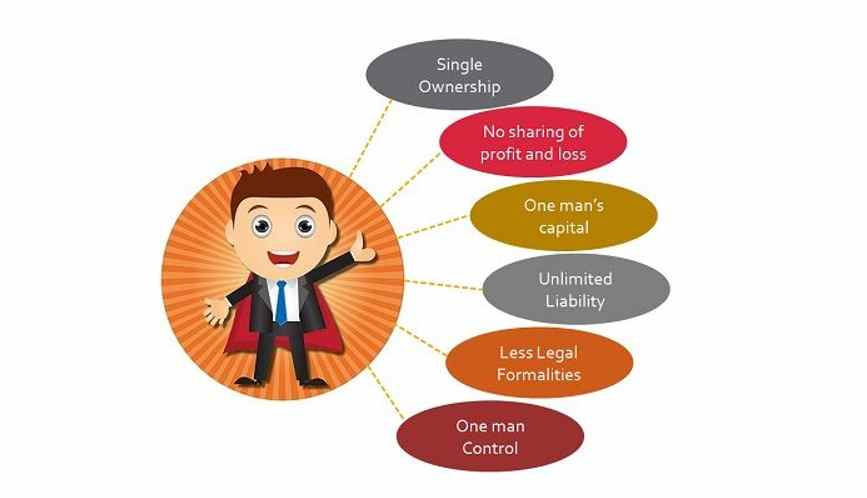
This is the simplest type of business ownership. It is owned and operated by a single person. There is no legal separation between the business and the owner, which means the tax and legal liabilities of the business are the responsibility of the owner.
In India, you don’t require a Permanent Account Number (PAN) for a sole proprietorship, the PAN of the individual (Proprietor) is enough to vouch for the Proprietorship firm. Enlistments with different government divisions are taken into consideration if needed.
If you’re operating a one-person business, you’re automatically considered a sole proprietor by the government. However, depending on your products and location, you may need to register for local business permits with your city or state.
One important thing to note is that there isn’t a legal or financial distinction between the business and the business owner. This means that you as the business owner are accountable for all the profits, liabilities, and legal issues that your business may encounter. This is not typically an issue if you pay your bills and keep your business practices honest.
Sole proprietorships are the most common type of online business due to their simplicity and how easy they are to create. If you’re starting an e-commerce business by yourself, a sole proprietorship is probably the best type of business for you.
Process For Registration:-

Registrations Required for A Sole Proprietorship:-
In addition to the above documents, there are a few registrations required to establish the existence of the firm:
1. Registering as SME:-
- You can get yourself registered as a Small and Medium Enterprise (SME) under the MSME Act. The application can be filed electronically. Although it isn’t compulsory to register as an SME, it is highly beneficial, especially at the time of taking a loan for the business. The Government runs various schemes for SMEs where loans are provided at the concessional rate of interest.
2. Shop and Establishment Act License:-
- The Shops and Establishment Act License is required to be obtained according to the local laws. It is issued on the basis of the business and the number of employees. Generally, all sole proprietors who own a shop or establish a commercial establishment must obtain this license.
3. GST Registration:-
- You can get yourself registered under GST if your annual turnover is more than Rs. 40 lakhs. Also, if you are doing online business (selling through amazon, Flipkart, etc.), you are required to get a GST number. For registering under GST, you need the following documents –
- PAN card, photo, and Aadhar Card of the proprietor.
- Proof of business place (electricity bill/ rent agreement)
- Bank statement copy (first page for verifying bank account number, address, and IFSC code)
- GST registration is easy and can be done via the GST portal. Normally GST number is received within 3-4 days of submitting the application.
2. General Partnership

A business owned by two or more people who share responsibilities and profits. Each partner contributes resources and money to the business and shares in the profits and losses of the business. The shared profits and losses are recorded on each partner’s tax return.
A partnership must file an annual information return to report the income, deductions, gains, losses, etc., from its operations, but it does not pay income tax. Instead, it “passes through” profits or losses to its partners. Each partner reports their share of the partnership’s income or loss on their personal tax return.
A partnership with another individual offers many benefits—you can pool resources and knowledge with another, secure private funding, and more. Just keep in mind that within a general partnership, responsibilities and liability are split equally among each member.
A partnership does require that you register your business with your state and establish an official business name. After that, you’ll be required to obtain a business license, along with any other documentation that your state office can help you with. Beyond that, you’ll also need to register your business with the IRS for tax purposes.
Although this may seem like a complicated process, there are lots of benefits to a partnership, so if you’re looking to have a co-owner, don’t be afraid to go for it—many online companies are formed using partnerships. Having someone to help share the work of starting a new business is worth the extra paperwork.
1. Procedure for Registering a Partnership Firm:
Step 1: Application for Registration
An application form must be filed to the Registrar of Firms of the State in which the firm is situated along with prescribed fees. The registration application must be signed and verified by all the partners or their agents.
- The application can be sent to the Registrar of Firms through post or by physical delivery, which contains the following details:
- The name of the firm.
- The principal place of business of the firm.
- The location of any other places where the firm carries on business.
- The date of joining of each partner.
- The names and permanent addresses of all the partners.
- The duration of the firm.
Step 2: Selection of Name of the Partnership Firm
Any name can be given to a partnership firm. But certain conditions need to be followed while selecting the name:
The name should not be too similar or identical to an existing firm doing the same business.
- The name should not contain words like emperor, crown, empress, empire, or any other words which show sanction or approval of the government.
Step 3: Certificate of Registration
If the Registrar is satisfied with the registration application and the documents, he will register the firm in the Register of Firms and issue the Registration Certificate. The Register of Firms contains up-to-date information on all firms, and anybody can view it upon payment of certain fees.
- An application form along with fees is to be submitted to the Registrar of Firms of the State in which the firm is situated. The application must be signed by all partners or their agents.
2. Documents for Registration of Partnership:-
- The documents required to be submitted to the Registrar for registration of a Partnership Firm are:
- Application for registration of partnership (Form 1)
- Certified original copy of Partnership Deed.
- Specimen of an affidavit certifying all the details mentioned in the partnership deed and documents are correct.
- PAN Card and address proof of the partners.
- Proof of principal place of business of the firm (ownership documents or rental/lease agreement).
If the registrar is satisfied with the documents, he will register the firm in the Register of Firms and issue a Certificate of Registration.
Register of Firms contains up-to-date information on all firms and can be viewed by anybody upon payment of certain fees.
3. Partnership Firm Registration Fees:-
The government fees applicable for a partnership firm registration varies from state to state depending on the partner’s contribution. However, you can file for partnership firm registration online through the Clear Tax Partnership Firm Registration Plan.
Partnership Firm Registration Plan amount – ₹5499*
The Partnership Firm Registration Plan amount includes the following services:
- PAN application
- Partnership deed drafting
- Filing of deed and other documents with the Registrar of Firms
- Issue of registration certificate
- 100% online process
- Session with a Clear tax expert
» Price shown above may vary.
4. Name Given to the Partnership Firm:-
- Any name can be given to a partnership firm if you fulfill the following conditions:
- The name shouldn’t be too similar or identical to an existing firm doing the same business,
- The name shouldn’t contain words like an emperor, crown, empress, empire, or any other words which show sanction or approval of the government.
3. Limited Partnership (LP)

A limited partnership, or LP, is an offshoot version of a general partnership. With a limited partnership, there are two sets of partners: The General Partner and the Limited Partner. The general partner is usually involved in everyday business decisions and has personal liability for the business. The limited partner (typically an investor) is not liable for debts and doesn’t partake in regular business management of the company.
LPs differ from other partnerships in that partners can have limited liability, meaning they are not liable for business debts that exceed their initial investment.
General partners are responsible for the daily management of the limited partnership and are liable for the company’s financial obligations, including debts and litigation. Other contributors, known as limited (or silent) partners, provide capital but cannot make managerial decisions and are not responsible for any debts beyond their initial investment.
Procedure for Registering Limited Partnership (LP):-
LLPs shall be registered with the Registrar of Companies (ROC) (appointed under the Companies Act, 1956) after following the provisions specified in the LLP Act. Every LLP shall have a registered office. An Incorporation Document subscribed by at least two partners shall have to be filed with the Registrar in a prescribed form. Contents of LLP Agreement, as may be prescribed, shall also be required to be filed with Registrar, online.
Contents of the LLP Agreement or any changes made therein, if any, may be filed in Form 3, and details of partners/designated partners may be filed in Form 4 in accordance with LLP Rules, 2009.
1. Whether foreigners can incorporate LLP?
- Yes, the LLP Act 2008 allows Foreign Nationals including Foreign Companies & LLPs to incorporate an LLP in India provided at least one designated partner is a resident of India. However, the LLP/Partners would have to comply with all relevant Foreign Exchange Laws/ Rules/ Regulations/ Guidelines.
2. What are the broad provisions of the Act in respect of names of LLPs?
- Every limited liability partnership shall have either the words “limited liability partnership” or the acronym “LLP” as the last words of its name. LLPs would not be given names, which, in the opinion of the Central Government, are undesirable. The registrar would be under obligation to follow such rules, which would be framed by the Central Government in connection with allotting names to LLPs. There are also provisions in respect of ‘rectification of name’ in case two LLPs have been registered with the same name, inadvertently.
3. For what period a name can be reserved by Registrar?
- The name can be reserved by ROC on approval of Form 1, for a period of 3 months from the date of intimation by the Registrar. However, Foreign LLP/Companies have an option to reserve their existing names, under which they are operating outside India, for a period of 3 years in India, which can be further renewed on application to Registrar in Form 25.
4. Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
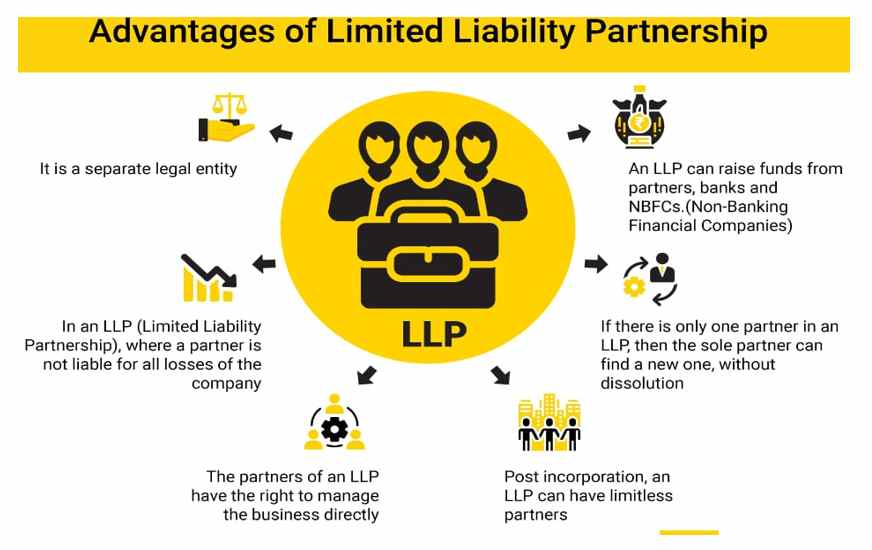
This is a relatively new business structure and was first available in Wyoming in 1977 and in other states in the 1990s. A limited liability company combines the pass-through taxation benefits of a partnership with the limited liability benefits of a corporation.
Is a business structure allowed by state statute? Each state may use different regulations, you should check with your state if you are interested in starting a Limited Liability Company.
Owners of an LLP are called members. Most states do not restrict ownership, so members may include individuals, corporations, other LLPs, and foreign entities. There is no maximum number of members. Most states also permit “single-member” LLPs, those having only one owner.
A few types of businesses generally cannot be LLPs, such as banks and insurance companies.
The main difference between an LLP and a corporation is that LLPs aren’t taxed as separate business entities. Instead, all profits and losses are moved from the business to the LLP members, who report profits and losses on a personal federal tax return.
1. LLP Registration Process:-
Step 1: Obtain Digital Signature Certificate (DSC)
- Before initiating the process of registration, you must apply for the digital signature of the designated partners of the proposed LLP. This is because all the documents for LLP are filed online and are required to be digitally signed. So, the designated partner must obtain their digital signature certificates from government-recognized certifying agencies.
Step 2: Apply for Director Identification Number (DIN)
You must apply for the DIN of all the designated partners or those intending to be designated partners of the proposed LLP. The application for allotment of DIN must be made in Form DIR-3.
You must attach the scanned copy of documents (usually Aadhaar and PAN) to the form. The form shall be signed by a Company Secretary in full-time employment of the company or by the Managing Director/Director/CEO/CFO of the existing company in which the applicant shall be appointed as a director.
Step 3: Name Approval
LLP-RUN (Limited Liability Partnership-Reserve Unique Name) is filed for the reservation of the name of the proposed LLP which shall be processed by the Central Registration Centre under Non-STP. But before quoting the name in the form, it is recommended that you use the free name search facility on the MCA portal.
The system will provide a list of closely resembling names of existing companies/LLPs based on the search criteria filled up. This will help you in choosing names not like already existing names. The registrar will approve the name only if the name is not undesirable in the opinion of the Central Government and does not resemble any existing partnership firm or an LLP or a body corporate or a trademark.
The form RUN-LLP must be accompanied by fees as per Annexure ‘A’ which may be either approved/rejected by the registrar. A re-submission of the form shall be allowed to be made within 15 days for rectifying the defects. There is a provision to provide for 2 proposed names of the LLP.
Step 4: Incorporation of LLP
The form used for incorporation is FiLLiP (Form for incorporation of Limited Liability Partnership) which shall be filed with the Registrar who has jurisdiction over the state in which the registered office of the LLP is situated. The form will be an integrated form.
Fees as per Annexure ‘A’ shall be paid.
This form also provides for applying for allotment of DPIN, if an individual who is to be appointed as a designated partner does not have a DPIN or DIN.
The application for allotment shall be allowed to be made by two individuals only.
The application for reservation may be made through FiLLiP too.
- If the name that is applied for is approved, then this approved and reserved name shall be filled as the proposed name of the LLP
Step 5: File Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) Agreement
LLP agreement governs the mutual rights and duties amongst the partners and between the LLP and its partners.
LLP agreement must be filed in form 3 online on MCA Portal.
Form 3 for the LLP agreement must be filed within 30 days of the date of incorporation.
The LLP Agreement must be printed on Stamp Paper. The value of Stamp Paper is different for every state.
- Documents Required for LLP Registration
2. Documents of Partners:-
PAN Card/ ID Proof of Partners – All the partners are required to provide their PAN at the time of registering LLP. PAN card acts as a primary ID proof.
Address Proof of Partners – Partner can submit any one document out of Voter’s ID, Passport, Driver’s license or Aadhar Card. The name and other details as per address proof and PAN card should be the same. If the spelling of own name or father’s name or date of birth is different in address proof and PAN card, it should be corrected before submitting to RoC.
Residence Proof of Partners – Latest bank statement, telephone bill, mobile bill, electricity bill, or gas bill should be submitted as residence proof. Such a bill or statement shouldn’t be more than 2-3 months old and must contain the name of the partner as mentioned in the PAN card.
Photograph – Partners should also provide their passport-size photograph, preferably on white background.Passport (in case of Foreign Nationals/ NRIs) – For becoming a partner in Indian LLP, foreign nationals and NRIs must submit their passport compulsorily. Passports must be notarized or apostilled by the relevant authorities in the country of such foreign nationals and NRI, else Indian Embassy situated in that country can also sign the documents.
Foreign nationals or NRIs must submit proof of address also which will be a driving license, bank statement, residence card, or any government-issued identity proof containing the address.
If the documents are in other than the English language, a notarized or apostilled translation copy will also be attached.
3. Documents of LLP:-
Proof of Registered Office Address: Proof of registered office must be submitted during registration or within 30 days of its incorporation.
If the registered office is taken on rent, a rent agreement, and a no-objection certificate from the landlord must be submitted. No objection certificate will be the consent of the landlord to allow the LLP to use the place as a ‘registered office.
Besides, any one document out of utility bills like gas, electricity, or telephone bill must be submitted. The bill should contain the complete address of the premise and the owner’s name and the document shouldn’t be older than 2 months.
Digital Signature Certificate: One of the designated partners needs to opt for a digital signature certificate also since all documents and applications will be digitally signed by the authorized signatory.
4. Cost Involved in LLP Registration:-
Step 1 – DSC: – Around Rs. 1500-2000 for 2 partners (varies depending on the agency)
Step 2 – DIN: – Rs. 1000 for 2 partners
Step 3 – Name Reservation: – 200
Step 4 – Incorporation Depends on capital contribution. Contribution up to Rs. 1 lakh – Rs. 500, Contribution between Rs. 1 and 5 lakhs – Rs. 2000
Step 5 – LLP Agreement: – Depends on capital contribution. Contribution up to Rs 1 lakhs – Rs 50 for filing Form 3 and stamp duty based on the state where LLP is formed.
5. Time Involved for LLP Registration:-
- LLP formation starting from obtaining DSC to Filing Form 3 takes approximately 10 days, subject to departmental approval and revert from the respective department.
5. Corporation

A type of fully independent business with shareholders. One of the most complex business types. It is a business in which a group of people acts as a single entity.
Owners are commonly referred to as shareholders who exchange consideration for the corporation’s common stock. Incorporating a business releases owners of the financial liability of business obligations. A corporation comes with unfavorable taxation rules for the owners of the business.
In forming a corporation, prospective shareholders exchange money, property, or both, for the corporation’s capital stock. A corporation generally takes the same deductions as a sole proprietorship to figure out its taxable income. A corporation can also take special deductions. For federal income tax purposes, a C corporation is recognized as a separate taxpaying entity. A corporation conducts business, realizes net income or loss, pays taxes, and distributes profits to shareholders.
The profit of a corporation is taxed to the corporation when earned and then is taxed to the shareholders when distributed as dividends. This creates a double tax. The corporation does not get a tax deduction when it distributes dividends to shareholders. Shareholders cannot deduct any loss of the corporation.
Procedure for Registering Corporation:-
- Incorporating a company through Simplified Proforma for Incorporating Company electronically (SPICe -INC-32), with eMoA (INC-33), eAOA (INC-34), is the default option and most companies are required to be incorporated through SPICe only.
1. How to Register a Company Online – the Registration Process:
- Company registration in India benefits start-ups since it offers them an advantage over those who have not registered.
Step 1: Obtain DSC
Step 2: Apply for the DIN
Step 3: Application for the name availability
Step 4: Submission of MoA and AoA to register a private limited company
Step 5: Apply for the PAN and TAN of the company
Step 6: RoC issues a certificate of incorporation with a PAN and TAN
2. Documents Required for Online Company Registration:
In India, private limited company registration cannot be done without proper identity and address proof. Listed below are the documents accepted by the MCA for the online company registration process:
Identity and Address Proof: –
- Scanned copy of PAN card or passport (foreign nationals & NRIs)
- Scanned copy of voter ID/passport/driving license
- Scanned copy of the latest bank statement/telephone or mobile bill/electricity or gas bill
- Scanned passport-sized photograph specimen signature (blank document with signature [directors only])
Registered Office Proof: –
- Scanned copy of the latest bank statement/telephone or mobile bill/electricity or gas bill
- Scanned copy of the notarized rental agreement in English
- Scanned copy of no-objection certificate from the property owner
- Scanned copy of sale deed/property deed in English (in case of owned property)
Note: Your registered office need not be a commercial space; it can be your residence too.
3. How can foreign companies establish a place of business in India?
Any foreign company can establish its place of business in India by filing eForm FC-1 (Information to be filed by a foreign company).
Note: The eForm needs to be digitally signed by an authorized representative of the foreign company. There is no need to apply and obtain DIN for Directors of a foreign company. However, it is mandatory to register the DSC of the authorized representative of the foreign company via the associate DSC service available at the MCA portal.
5. S Corporations
An S corporation or S corp, also known as an S subchapter, refers to a type of corporation that meets specific Internal Revenue Code requirements. The S corp is a structure that offers certain tax advantages over C corporations, or C corps, which make up the bulk of corporations. For example, an S corp—but not a C corp—may pass income (along with other credits, deductions, and losses) directly to shareholders, without having to pay federal corporate taxes.
Shareholders of S corporations report the flow-through of income and losses on their personal tax returns and are assessed tax at their individual income tax rates. This allows S corporations to avoid double taxation on corporate income. S corporations are responsible for tax on certain built-in gains and passive income at the entity level.
To qualify for S corporation status, the corporation must meet the following requirements:
- Be a domestic corporation
- Have only allowable shareholders
- Maybe individuals, certain trusts, estates and
- May not be partnerships, corporations, or non-resident alien shareholders
- Have no more than 100 shareholders
- Have only one class of stock
- Not be an ineligible corporation (i.e., certain financial institutions, insurance companies, and domestic international sales corporations).
- S corp status effectively gives a business the regular benefits of incorporation while enjoying the tax-exempt privileges of a partnership.
S Corp requirements for Formation
1. Eligibility: –
- Shareholders between 1 to 100, not more than that form an S Corporation.
- All shareholders must agree to an S corp election.
- Individuals, estates, and trusts may be shareholders, but non-residents, partnerships, and companies are not.
- There should only be one type of stock.
- Choose a tax year that is agreeable to you.
- Must not be a financial institution that accounts for bad debts using the Section 585 reserve system, an insurance firm that pays taxes under Subchapter L, a possessions corporation, or a current or former Domestic International Sales Corporation (DISC).
Important Note: You will lose your S corporation tax status and revert to the less favorable tax status of a regular business if any of these standards are not completed at any moment.
2. Registration Process for S Corporation in the USA:-
- The following procedures must be followed to form an S corporation:
- Choose a business name and double-check that it is not already in use by another company in your state.
- Send the Secretary of State the Articles of Incorporation.
- If your state requires it, create corporation by-laws.
- Minutes of every shareholder and board meeting should be kept.
- Fill out IRS Form SS-4 to obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN).
- If necessary, apply for state and local permits.
3. Form 2553 Submission: –
- You must complete and submit Form 2553 to the IRS within two months and 15 days of the start of your chosen tax year, or any time during the tax year before your S corporation’s first effective tax year, after incorporating your corporation. When filling out Form 2553, ensure to include the following information:
- Name of your business
- EIN number and address of your company
- The state in which your business is incorporated
- The effective date of the S corporation election is the date of formation.
- Details on the shareholders
- Information on the fiscal year
- All shareholders’ signatures are required
- Your S corporation tax status will be in force once your application is approved until it is withdrawn or terminated. If you fail to meet all the S corporation’s requirements, your company’s corporate status and liability protection will be terminated, making your assets vulnerable to confiscation.
6. Non-Profit Organization

- A non-profit organization is self-explanatory, in that it’s a business organization that is intended to promote educational or charitable purposes. The “non-profit” aspect comes into play in that any money earned by the company must be kept by the organization to pay for its expenses, programs, etc.
1. How to Register as NGO – Section 8 Company in India:-
NGO (Non-Government Organisation) is an organization that works for non-profit/ charitable purposes. An NGO established as a Section 8 company under the Companies Act, 2013 (‘Act’) is governed by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (‘MCA’) whereas the NGO registered as a trust or society is governed by the registrar of state under the State Government.
Section 8 company incorporation has more benefits in comparison to trust and society. This type of company has more credibility among government departments, donors, and other stakeholders. In this article, we will explain how to register as an NGO in the form of Section 8 Company, under the Companies Act, 2013.
2. Laws in India applicable to an NGO:-
- NGOs can be registered in India under any of the following laws:
- Trust under the Indian Trusts Act, 1882
- Society under Societies Registration Act, 1860
- Section 8 Company under Companies Act, 2013
3. Benefits of Section 8 Company Registration:-
- There are many advantages of registering an NGO under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013, which are as follows:
No minimum capital: There is no minimum capital requirement for a Section 8 company incorporation and the capital structure of Section 8 can be altered at any time as per the growth requirement of the company. Thus, the funds required for carrying the business operations can be brought in later, through donations and subscriptions from members and the general public.
Tax Benefits: The Company Auditor’s Report Order (CARO) does not apply to the Section 8 company. A Section 8 company enjoys tax benefits under 80G of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
No Stamp Duty: There is no stamp duty imposed for Section 8 company incorporation in India. The Section 8 company need not pay the stamp duty imposed on the Memorandum of Association (MOA) or Articles of Association (AOA) of a private or public limited company.
Separate Legal Identity: Section 8 Company registration acquires a distinct legal identity from its members. A registered partnership firm can also become a member in its individual capacity and obtain a Directorship of Section 8 company. It has perpetual existence and thus, the entry or exit of any member will not affect the operation of the Section 8 company.
Limited liability: The members of the Section 8 company have limited liability as per their share subscribed. They are not personally liable for the losses of the company.
Credibility: Section 8 companies are more credible and reliable than any other form of a charitable organization. It is regulated under the provisions of the Act; thus, they need to have mandatory audits every year and the Memorandum of Association cannot be altered relating to the non-profit’s objectives of the company.
- Exemption to the donors: The tax exemption is granted to the donations received by the section 8 company under Section 12A and 80G of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
4. Section 8 Company Incorporation Eligibility:-
- An Individual, HUF is eligible to start a Section 8 company in India.
- Two or more persons who will act as Directors or shareholders should fulfill all the compliances and requirements of the Section 8 company incorporated under the Act.
- There must be at least one director who should be a resident of India in the Section 8 company.
- The objective must be one or more of the following – promotion of sports, social welfare, the advancement of science and art, education, and financial assistance to lower-income groups.
- Founders, directors, and members directors of the company cannot draw any remuneration in any form of cash or kind.
- No profit should be distributed among the members and directors of the company directly or indirectly.
5. Section 8 Company Incorporation Requirement:-
Directors:- A minimum of two directors is required if the Section 8 company is to be incorporated as a private limited company, and a minimum of three directors in case of incorporation as a public limited company. The maximum number of members is 200 in the case of a private limited company, whereas for a public limited company, there is no such limit.
Capital Requirement and Name:- There is no requirement for minimum paid-up capital in the case of a Section 8 company incorporation. NGOs established as a Section 8 company need not use the words ‘Limited’ or ‘Private Limited’ in their name.
Charitable Objects:- Section 8 companies are incorporated with non-profit objectives. The MOA and AOA must mention the non-profit objective or purpose for which it is established. Any profits earned by the section 8 company are utilized for the furtherance of its main objectives, i.e., charitable purposes, or reinvested in the company. The profits will not be distributed among its members.
Management:- Section 8 company is managed by the Board of Directors as per the MOA and AOA of the company, unlike other trusts that are managed by the Trustees as per the Trust Deed.
A regulation under Various Acts:- A Section 8 company needs to follow the rules and regulations prescribed under the Companies Act, 2013. It needs to maintain books of account, and file returns with the Registrar of Companies. Section 8 company cannot make any changes to the provisions of MoA and AoA without the prior approval of the Central Government. It also needs to follow the provisions of the Income Tax Act and GST Law.
Obtain DSC (Digital Signature Certificate):- Digital signatures of the proposed directors of the company are required as the forms for the registration process are filed online and should be digitally signed. Digital signature certificates (DSC) are issued by a government-recognized certifying agency. The list of such certified agencies can be accessed here. The cost of obtaining a DSC varies depending upon the certifying agency. You must obtain a Class 3 category DSC.
6. Apply for Director Identification Number (DIN):-
- You must apply for a DIN for the proposed directors of the company. The application for allotment of DIN must be made in Form DIR-3 or along with the SPICe+ form for registration. You must attach the scanned copy of the necessary documents such as a self-attested copy of PAN, Identity, and Address proof of directors along with the form and submit it online on the MCA Portal. The form must be attested by a practicing professional who can be a chartered accountant, a company secretary, or a cost accountant.
7. Forms Required for Section 8 Company Registration:-
Name of the form Purpose of the Form
SPICE+ – Application for Incorporation of Company
INC 12- Application for License
INC 13- Memorandum of Association
INC 14- Declaration from each person making the application
INC 16- License to incorporate as Section 8 Company
INC 22- Situation of Registered Office
DIR 2- Consent of Directors
DIR 3- Application to ROC to get DIN
DIR 12- Appointment of Directors.
Top 13 Interesting Facts About Business Structures
Businesses can be for-profit entities or non-profit organizations.
A good name is often one of the most valuable assets of a business, so it’s important that business owners choose their names wisely.
Partnership agreements should be created to outline the specific responsibilities and rights of both general and limited partners.
There are three types of partnerships: limited partnership, general partnership, and limited liability partnership.
Most U.S. states govern the formation of limited partnerships, requiring registration with the Secretary of State.
Limited partners can become personally liable if they take a more active role in the LP.
A sole proprietorship is an unincorporated business with only one owner who pays personal income tax on profits earned.
Sole proprietorships are easy to establish and dismantle due to a lack of government involvement, making them popular with small business owners and contractors.
A sole proprietorship has no separation between the business entity and its owner, setting it apart from corporations and limited partnerships.
In a general partnership company, all members share both profits and liabilities. Professionals like doctors and lawyers often form a limited liability partnership.
When drafting a partnership agreement, an expulsion clause should be included, detailing what events are grounds for expelling a partner.
An important element of a corporation is limited liability, which means that its shareholders are not personally responsible for the company’s debts.
Some businesses run as small operations in a single industry while others are large operations that spread across many industries around the world.






