- Umang Sagar
- Disease, Recent article
Alzheimers Disease

What Is Alzheimers Disease?
Alzheimer’s is usually memory loss or poor memory.
It destroys memory power, and thinking ability and makes difficulties in our daily activity performances.
Mainly this type of person asks wrong questions, is wrongly focused, uses too much brain, and don’t think freely, a lot about small things and Judgment.
Alzheimer’s is the commonest form of dementia.
Above the age of 65 years, people have there is a 10% chance to have this disease. And over the age of 80 years of people have a 50% chance to contract this disease.
About 1 in 9 aged 65 and older (10.7%) has Alzheimer’s disease.
According to its definition – Alzheimer’s disease is a neurological disorder in which there is a progressive shrinkage of brain cells and death of brain cells; which leads to cognitive, motor, and behavioral impairment.
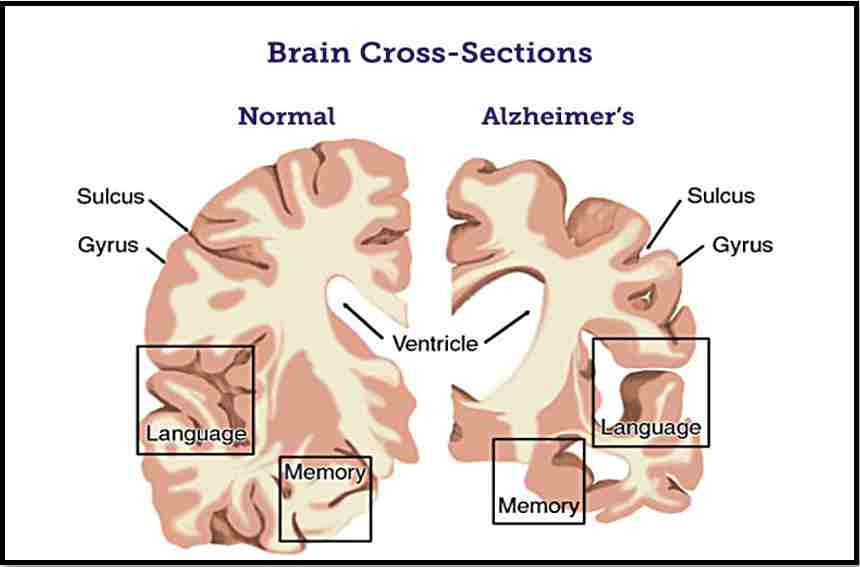
- When we see the brain cross-section of an Alzheimer’s person there will be:
- narrowed gyrus
- widen sulcus
- shrinkage of brain
- expanded ventricle in the brain
- We can see many elderly ones suffering from memory impairment in their surroundings, it’s best to advise them to consult a physician to find it out about Alzheimer’s disease.
What Is The History Behind The Origin Of Alzheimers Disease?
Alzheimer’s disease was first described by Dr. Alois Alzheimer.
Alois Alzheimer was a German physician who described Alzheimer’s ain the year 1906.
Alzheimer had a patient named Auguste D.
Auguste D is suffering from some mental illness in her fifties.
Finally, the patient died.
Dr. Alois Alzheimer did an autopsy of the patient brain.
The autopsy showed dense deposits (now known as plaques) on the outside and around the nerve cells in the brain.
Inside the nerve cells, there were twisted strands of fibers (now known as neurofibrillary tangles).
Since Dr. Alois Alzheimer was the first person to describe the disease it was named after him as Alzheimer’s disease.
What Are The Stages Of Alzheimers Disease?
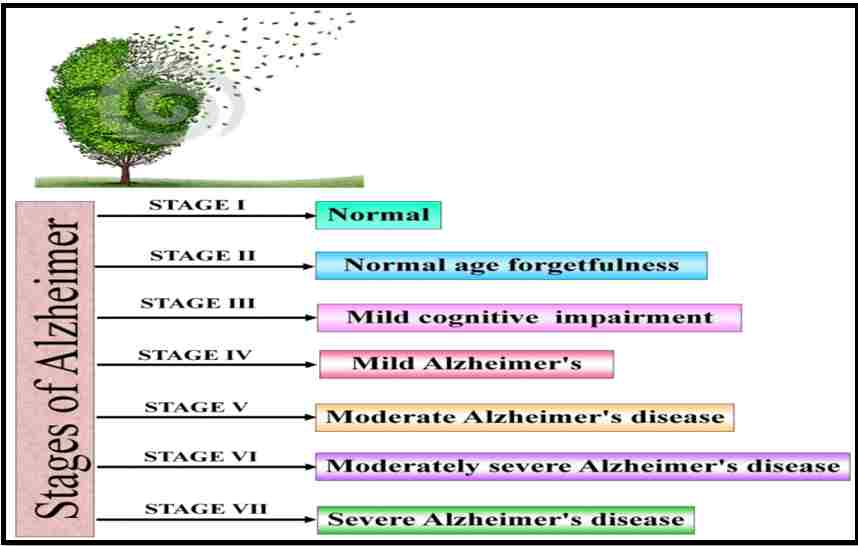
Stage 1- Normal:
- It is Before Symptoms Appear
- Also called ‘pre-clinical Alzheimer’s disease.
- It begins 10 or 15 years before people have symptoms.
- Currently, there is no treatment for this stage.
- Because the risk of Alzheimer’s increases with age, it’s important to keep up with regular primary care visits to allow for screening to detect the earliest signs of the disease.
Stage 2- Normal age forgetfulness:
- It’s common to be forgetful from time to time, and that’s likely to happen more often with age.
- It is the very early stages of Alzheimer’s that can look like normal-aged forgetfulness.
- You might have memory lapses, including forgetting basic things like people’s names or where they left their keys, but they can still drive, work and be social.
- These memory lapses become more frequent.
- You will probably notice this.
Stage 3- Mild cognitive impairment:
- Noticeable Memory Difficulties are seen in this stage.
- It’s common to be diagnosed in this stage because this is when a person’s daily routine becomes more disrupted.
- Common difficulties in this stage are:
- Having trouble in remembering recently read material, such as books or magazines.
- Find remembering plans and organizing increasingly difficult.
- Have more difficulty retrieving a name or word.
- Experience challenges in social settings or at work.
- The best way to keep symptoms at bay is to talk to a physician about treatment options, including medications, and care planning.
Stage 4- Mild Alzheimer’s:
- It’s beyond memory loss
- In this stage, damage to the brain often involves other aspects of cognition outside of memory, including some difficulties with language, organization, and calculations.
- These problems can make it more challenging
- This stage lasts for many years.
- Their memory of the distant past will usually be significantly better than their memory of day-to-day information, such as what they saw on the news or a conversation from earlier in the day.
- Confusion about what day it is and where they are, Increased risk of wandering off or getting lost, Changes in sleep patterns like restlessness at night and sleeping during the day, and Difficulty choosing appropriate clothing for the weather or the occasion.
Stage 5- Moderate Alzheimer’s:
- Decreased Independence is seen in this stage.
- They were able to function without your regular assistance.
- In this stage, the patient will likely have trouble remembering people that are important to them, such as close family and friends. They may struggle with learning new things, and basic tasks like getting dressed might be too much for them.
- Emotional changes are also common during this stage, including Hallucinations (Seeing things that aren’t there), Delusions (False beliefs that you believe to be true), and Paranoia (The feeling that others are against you).
Stage 6- moderately severe Alzheimer’s:
- Severe Symptoms are seen in this stage.
- Impact his or her ability to manage their own care like knowing what to do if the fire alarm goes off or the phone rings
- Communicating may also become difficult during this stage.
- Significant personality changes may continue to occur, including increased anxiety, hallucinations, delusions and paranoia.
- There are both medicines and behavioral strategies that may help in these instances which you can discuss with your care team.
Stage 7- Severe Alzheimer’s:
- A lack of Physical Control is seen in this stage.
- Alzheimer’s destroys brain cells, and eventually, this can cause severe mental and physical impairment.
- The patient may begin to shut down as their mind struggles to communicate and delegate tasks effectively.
- They may need round-the-clock care to help with walking, sitting and swallowing.
- Because of their reduced mobility, their body can also become vulnerable to infections, such as pneumonia. To help avoid infections, keep their teeth and mouth clean, treat cuts and scrapes with an antibiotic ointment right away, and make sure they get their flu shot each year.
What Are Predisposing Factors Of Alzheimer’s Disease?
- The predisposing factors of Alzheimer’s disease are:
- Age: age above 60 years are more prone to Alzheimer’s disease.
- Gender: Females are more prone to Alzheimer’s disease than males.
- Family history: people with a family history of Alzheimer’s disease are more prone to Alzheimer’s disease.
- Low socio-economic people are more prone to Alzheimer’s disease due to somewhat low use of their brains.
- Poor education is more prone to Alzheimer’s disease due to somewhat low use of their brain.
- Head injury may damage the brain.
- Genetic people have more APP genes, and Presenilin genes are more prone to Alzheimer’s disease.
- Down Syndrome
How Does The Alzheimers Disease Occur?
Alzheimer’s disease occurs due to the following:
- Amyloid Cascade hypothesis
- Neurofibrillary Tangles
- Cholinergic hypothesis
- Inflammation
- Brain Vasculature
- Post-menopausal loss of estrogen in women
1. Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis:-
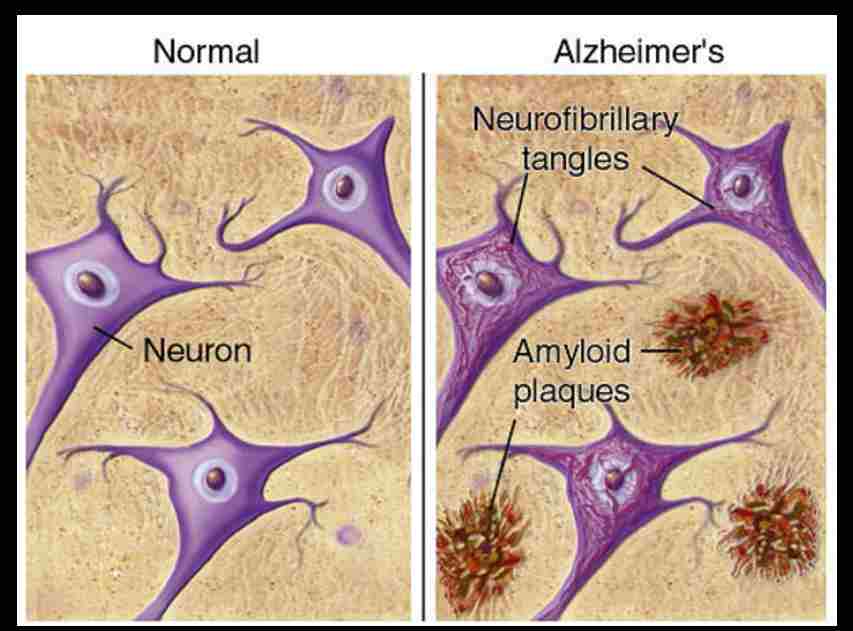
The Prenisilin-1 and Prenisilin-2 genes in our body are used for the processing of (APA)Amyloid precursor protein.
Amyloid precursor protein aids in the neurofunctional and in the development of the cerebral part of the brain.
Mutations in the Prenisilin-1 and Prenisilin-2 genes in our body lead to abnormalities in the processing of (APA)Amyloid precursor protein.
It causes the formation of amyloid beta-monomers which in turn produces beta-oligomers.
All the beta-oligomers aggregate and form senile plaques.
senile plaques block the neural communications in the brain which further causes neuronal damage leading to Alzheimer’s disease.
2. Neurofibrillary Tangles:-
Generally, in a cell microtubules are present.
Tau proteins combine with the microtubule in the cell; providing structural support to the cell.
When there is a mutation or Hyperphosphorylation of the Tau proteins, they cannot combine with the microtubule in the cell; structural support to the cell is lost and cellular activity is decreased.
These Tau proteins get accumulated in the cell as masses called Neurofibrillary Tangles
- Neurofibrillary Tangles are toxic to cells which further damages the brain leading to Alzheimer’s disease.
3. Cholinergic hypothesis:-
Acetylcholine is the most important neurotransmitter in the brain’s cholinergic system.
Acetylcholine is an excitatory neurotransmitter that keeps the brain active.
In the Cholinergic hypothesis, Acetylcholine and other neurotransmitter release is impaired.
The Acetylcholine and serotonin levels are decreased which is necessary for cognition.
- Hence leading to Alzheimer’s disease.
4. Inflammation:-
Deposition or accumulation of any substances in the brain causes increased release of Inflammatory mediators.
Inflammatory mediators produce inflammation and further destroy the neurons in the brain
- The neurons in the brain hence lead to Alzheimer’s disease.
5. Brain Vasculature:-
Brain Vasculature is the supply of blood vessels to the brain.
interruptions in the blood vessels to the brain cause decrease in the supply of blood to the brain further causing brain damage and hence leading to Alzheimer’s disease.
In case of high cholesterol levels lead to the deposition of LDL cholesterol in blood vessels that are supplied to the brain; decreasing blood supply and causing Alzheimer’s disease.
Insulin plays a vital role in the degradation of the Amyloid Cascade hypothesis and Neurofibrillary Tangles; in the case of diabetes due to the impaired insulin levels there is no proper degradation of the Amyloid Cascade hypothesis and Neurofibrillary Tangles hence leading to Alzheimer’s disease.
6. Post-menopausal loss of estrogen in women:-
Estrogen helps in the regulation of blood supply to the brain, degradation of Amyloid Cascade hypothesis and Neurofibrillary Tangles, and preventing of cholesterol from depositing in blood levels.
- In postmenopausal women, the estrogen levels are low so the estrogen cannot perform all the functions properly. Hence there is a risk of increased Alzheimer’s disease.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Alzheimers Disease?
The signs and symptoms are as follows:
1. Cognitive- Cognitive functioning refers to multiple mental abilities, including learning, thinking, reasoning, remembering, problem-solving, decision-making, and attention.
- Memory loss.
- Aphasia (language disorders).
- Disorientation of speech.
- Impaired executive functions (difficulty in managing their own thoughts. Emotions and actions)
2. Non-Cognitive– Noncognitive or “soft skills” are related to motivation, integrity, and interpersonal interaction.
- Depression
- Hallucinations
- Delusions
- Behavioral disturbances
- Repetitive mannerisms and activities
- Uncooperativeness
- Physical aggression
- Verbal aggression
3. Functional- Inability to self-care
- Inability to self-bath
- Inability to self-dress
- Inability to self-toilet
- Inability to self-eat
How Can We Diagnose Alzheimers Disease?
- There are some useful Laboratory tests to identify Alzheimer’s disease:
- Electrolyte test
- Vitamin B12 test
- Thyroid test
- Diagnostic tests
- CT Scan and MRI Scan are used to check brain shrinkage and damage.
- Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE)
- Temporal Orientation (5 Points)
- The questions asked in temporal Orientation are as follows:
- What is the appropriate time now?
- What day of your week is it?
- What is today’s date?
- Which month is this?
- Which year is this?
1. Spatial Orientation (5 Points):
The questions asked in Spatial Orientation are as follows:
- Where are we now?
- What is this place?
- What is this address?
- Which town is this?
- Which state is this?
2. Registration (3 Points):
Ask the patients to repeat the words and give any 3 similar words that pronounce same like:
- care
- gear
- wear
3. Attention and calculation (5 Points):
Ask the patient to solve few simple subtractions and additions like:
- 2+2
- 4+2
- 2-2
- 7+2
- 7-2
4. Remote emergencies (3 Points):
Ask the patient can they remember the 3 words you said before.
5. Naming 2 objects (2 Points):
Show the patient any two objects and ask him/her to name them like chair, pen etc.
6. Repeat (1 Point):
Ask the patient to repeat no, if, and, or, but.
7. Stage command (3 Points):
Pass any 3 commands and notice if whether the patient is doing it or not example:
- Take the paper
- Fold the paper
- Throw it in the dustbin.
8. Wring a complete sentence (2 Points):
Ask the patient to speak out any complete Sentence about anything
example: Speak about the cow.
9. Reading and obeying (1 Point):
Ask the patient to read any one sentence and whether he reads or not.
10. Copy the diagram(1Point):
Ask the patient to draw the diagram and repeat the same.
This total examination consists of 30 points:-
- If the score is between 0-5, the patient is in the advanced stage -the patient must be placed in a nursing home.
- If the score is between 6-10, the patient is in the advanced stage -the patient represents many behavioural changes.
- If the score is between 11-15, the patient is in the modern stage -the patient has lost independent activities.
- If the score is between 16-20, the patient is in the modern stage -the patient has dementia.
- If the score is between 21-25, the patient is in the modern stage-patient can experience symptoms like short time loss of memory.
- If the score is between 26-30, the patient is in the mild stage-patient is in starting stage of Alzheimer’s disease.
What Are The Treatment Options For Alzheimers Disease?
There is no permanent cure for Alzheimer’s.
- The main treatment options for cognitive symptoms include Choline esterase Inhibitors and Antiglutaminergic drugs.
- Choline esterase Inhibitors are used to treat mild to moderate disease. They enhance the cholinergic activity in the brain thereby increasing cognitive functioning. The drugs used are Donepezil, rivastigmine, and Galantamine.
- Antiglutaminergic drugs are used to treat moderate to severe diseases. They block glutaminergic neurotransmissions thereby increasing cognitive functioning. The one and only drug are Memantine.
- The other treatment options for cognitive symptoms include lipid-lowering agents and dietary supplements.
- Lipid-lowering agents’ usage causes a low incidence of Alzheimer’s disease. The drugs include Pravastatin and Lovastatin.
- Dietary supplements like vitamin E act by clearing the plaques and tangles with its anti-oxidant properties, Ginkobiloba is a flavonoid that acts by preventing damage to the brain caused by the plaques and tangles by increasing the blood supply to the brain, and huperzine is an alkaloid which inhibits choline esterase thereby increasing cognitive functioning of the brain.
- The main treatment options for non-cognitive symptoms include Anti-psychotics, Anti-depressants, Anti-convulsants, and benzodiazepines depending of on the symptom.
Can We Prevent Alzheimers Disease?

- Alzheimer’s disease can b prevent by both physical and mental habits like exercise like walking and aerobic exercises, healthy food like plant-based food 15mg of vit E each day, 2.4mcg of vit B12 each day, choosing vitamins and minerals without iron or copper, cutting unhealthy fats, choosing aluminum free foods, mentally active activities like swimming, reading, learning new languages, playing games, playing music, watching adult education courses.

Top 13 Interesting Facts About Alzheimer’s Disease
Eating More Sugar Increases Alzheimer’s Risk.
About 1 in 9 aged 65 and older (10.7%) has Alzheimer’s.
Globally, the lowest validated rates of Alzheimer’s in the world are in rural India, where they eat low-meat, high-grain, high-bean, and high-carb diets.
There’s no cure for Alzheimer’s, but there are treatments that may change disease progression and options that may help treat symptoms.
A lower education level is associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Every 65 seconds, someone in America develops Alzheimer’s.
A surprisingly common source of memory loss symptoms is a Vitamin B-12 deficiency.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia.
Vigorous exercise of 30mins daily can reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s.
Women are more prone to Alzheimer’s than men.
Caffeine and coffee consumption may have a positive effect on slowing down memory loss.
The short-term memory only lasts 20 to 30 seconds.
The human brain gets smaller as we get older.



