- Umang Sagar
- Environment, Recent article
Waste Management

Introduction
Waste is what we call unwanted substances that have no use anymore. Waste generated by humans, in particular, is very hard to manage in the ecosystem. With all the different types of wastes and all of which require different types of disposal techniques, it becomes very difficult for people to remember all these facts and methods.
Waste management, if you hadn’t gleaned the idea already, is the broad categorization that includes how and why each kind of waste should be disposed of or recycled and why they should be separated and how they actually harm the environment and the ecosystem if left unattended.
Unfortunately, we humans don’t seem very bothered about these harmful side effects. Well, not all of us. Some of us are very concerned about the long-term effect of leaving waste unattended and unmanaged and are working our best towards educating people and waste management.
Below are some of these companies and NGOs that are working towards helping the world and creating a better future for the coming generations.
Companies:-
| Advanced Disposal |
 |
| Biffa Group |
 |
| Waste Ventures India |
 |
| Eco Green |
 |
| Hitachi Zosen |
 |
| A2Z Green Waste Management |
 |
NGOs:-
| Skrap |
 |
| Citizengage |
 |
| Vital Waste |
 |
| RARE |
 |
| Wasteless |
 |
| SWaCH (Solid Waste Collection and Handling) |
 |
Why Is Waste Management A Requisite For Society?
Waste management is important because the lack of proper waste management initiatives and practices leads to a lot of problems. These problems include, in the highest intensity, Global Warming and Pollution, and everyone is aware of how problematic these problems are. Isn’t it interesting how people can recognize and know so much about global warming and pollution but most don’t realize that these problems are rising in intensity because of lack of waste management?
Waste management has become an integral problem in the current society because now the previous, outdated methods of burying and burning waste do not work. Now that most of our waste is biodegradable waste, we have used different, newer ways of disposal and management of this waste. With the advancement in technology, the creativity of human minds has also increased, alongside a drive, however small, to help save the environment.
With most environmental problems arising because of improper waste management, and sustainable able development strategies increasing in potential and drive, many unique methods of waste management are popping up, presented, and put into practice by members of the society, who are all glad to be able to bring this change.
With these innovative ideas, we have described some ways below of what different types of management and disposal are and subsequently, how waste management will help you, as an individual and the society as a whole, and take care of the planetary ecosystems as well.
Different Types Of Waste Management And Disposal
- Refuse
- Reduce
- Reuse
- Repurpose
- Recycling
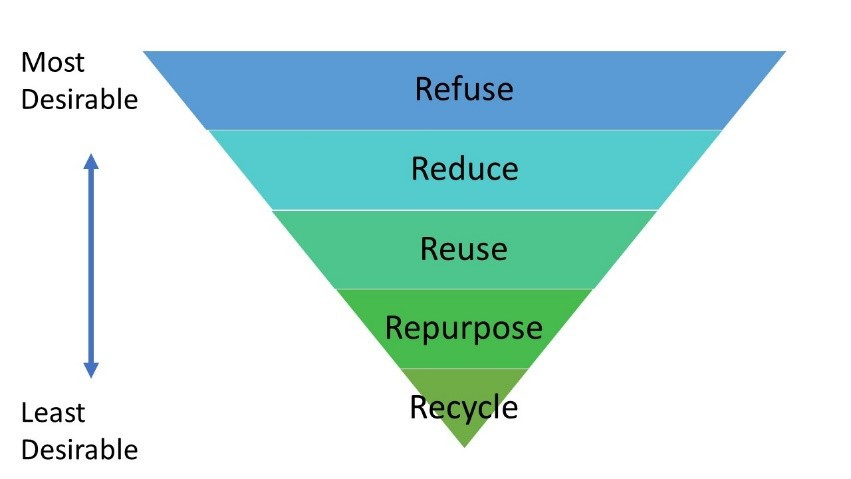
These are the three R’s of waste management, now taught to students in schools and other educational institutes. Though it seems, most people still remain unaware of the purpose of each R and what difference each includes, so below, we have explained what each part entails for us and how we can apply them to our daily lives.
Refuse
Refusing means that we have to take measures to prevent the accumulation of waste in our daily lives. Make sure not to buy extra plastic or paper cups during get-togethers, or too many disposable things that are not required and then thrown out. It would take time, but starting out with small changes in your own environment will unconsciously make people follow your example.
This is the first step, which begins with our own selves.
Reduce
- Reducing means that we have to stop buying products that cannot be reused or recycled and will inevitably harm our planet. By reducing items that are going to end up in landfills anyway, we can help reduce the amount of landfill garbage in short, slow amounts and maybe slow down these landfills from growing bigger.
Reuse
- Reuse, we assume, is something we all know about. It is when you try to use the waste in ways other than it is meant to be used or make use of it instead of other products. A common example would be plastic bottles, which can be reused as glasses, small feeding platforms for birds or other animals, or even as pots!
Repurpose
In some ways, this is related to reusing but at the same time, not really. Most people in the environmental community try to reduce their consumption of products by using other products and making those serve multiple purposes. Reusing and repurposing have the same purpose, to reduce the amount of waste getting decomposed in the landfills and to reduce the growing areas of landfills, which are slowly leading to soil pollution.
Repurpose is also promoted by DIYs, so be sure to always looks for safe ways to DIY any waste or extra product that can actually be a waste!
Recycling
- Recycling includes a wide range of different types of methods, out of which, the commonly known ones are physical and biological reprocessing and energy recovery. Different types of waste can be recycled, which means that these products can be recovered and reused.
What do The World’s Governing Bodies Have to Say on Waste Management?
- As mentioned before, waste management is an integral part of society, and hence, in the long run, has become an integral part of the world. It is the reason why the world’s governments include so many schemes and initiatives for waste management and how these schemes always try to get society to get involved in them. It has now become a common trend among all governments and governing bodies to set up initiatives to help address these issues for citizens falling under their area of governance.
=> The best examples of these would be:-
1. The Global Waste Management Outlook

- An initiative taken on jointly by the United Nations Environment Programme and the International Waste Management Association, this initiative is a follow-up for the Rio +20 summit and as a response to UNEP Governing Council decision GC 27/12.
2. Swachh Bharat, Unnat Bharat Abhiyan
This initiative by the Office of Principal Scientific Advisor (PSA) to the Government of India is set up under the Prime Minister’s Science, Technology and Innovation Advisory Council and has set up a PMU (Project Management Unit) partnering with Invest India* to help achieve the commitments that India has promised to the United Nations.
(*Invest India is India’s National Investment Promotion and Facilitation Agency.)
The initiative is to spread awareness among the citizens of India about waste management and its safe disposal. The Abhiyan overview states that it will be working to thwart the prediction that by the year 2021, each person in India would have an average waste generation of 0.77 kg per day, which is more than four times the amount in 1999.
With these ideas in mind, a few government projects have been launched. One of them is the Jal Shakti Abhiyan.
The National Water Mission was launched and managed under the Ministry of Jal Shakti, Department of Water Resources, RD & GR. Described by the NAPCC (The National Action Plan on Climate Change) as the means through which many of India’s goals of studying the water consumption of groundwater and the surrounding water resources will be studied, documented and new ideas would be put forward to prevent water pollution that is mainly caused by waste not being managed ideally or properly.
3. The World Bank

The World Bank has, in a recent article, underlined that lack of proper Waste Management is also a reason for poverty in underdeveloped countries and developed countries alike. They have given the context that while developed countries do have established methods and practices for proper waste management, most of the waste dumped in the lands of the underdeveloped countries is not treated, and if treated, then not done completely right, which leads to a lot of health problems and other consequences, which serves to emphasize how proper waste management practices and campaigns are important for human society development.
The World Bank states that this problem is on the rise because ‘effective waste management is expensive, comprising up to 45% to 50% of the municipal budget.’ But by highlighting this problem, they have also made clear that they are willing to help any countries that need to adopt these measures and would provide them with capital and advisors who can help the departments.
Why Should We Manage Waste Ideally?
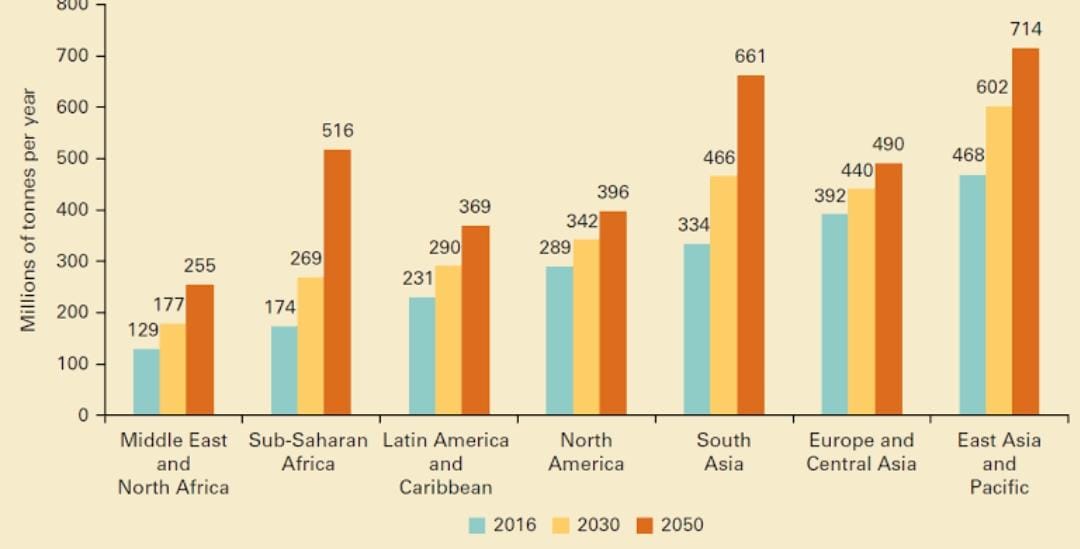
There are multiple ways to manage waste, some of which have been mentioned earlier, like recycling and reusing/repurposing. But alongside these, first knowing what you can promote by managing waste appropriately entails for us as individuals and humanity as a whole. It might also create a drive within our dear readers to actually follow through and come up with their own schemes to help in this issue that is threatening the harmony of our planet.
The biggest changes with effective waste management would be the reduction in two of the most deadly environmental problems that we are facing as humanity, (not COVID, people) which are, as mentioned before, pollution and global warming.
Effective waste management would mean less release of methane and other greenhouse gases which contribute to global warming, as well as treated garbage and sludge from factories and industries would be properly treated, leading to less soil pollution and start promoting more land which can be cultivated for different purposes. Not to mention, garbage would start filling up in the landfills and decomposing, which would lead to far less amount of rancid, rotting smell in the air, again reducing air pollution and making the air more breathable and helpful for all living creatures.
Additionally, landfills, or more appropriately, large spaces where garbage is dumped also produce inflammable liquids and gases, which make them equivalent to large explosives, just waiting for destruction. Just a small mistake, a small nick of fire can set off these sites and lead to heavy destruction of resources and life in the vicinity of these areas.
Recycling has one very common method, which is to conserve energy. It means exactly what it says. Recycling can help in conserving energy and resources that would instead be used by industries for the production and manufacturing of products. This also leads to an increase in the status of employment, as all industries involved in waste management require a lot of labor work.
Getting to know these advantages, now we can look forward to how we can bring them about.
And the way we can do it is by following some common methods of waste management that can be carried out on a large scale but also on a community as well as individual level.
How To Manage Waste Ideally: Methods And Ways
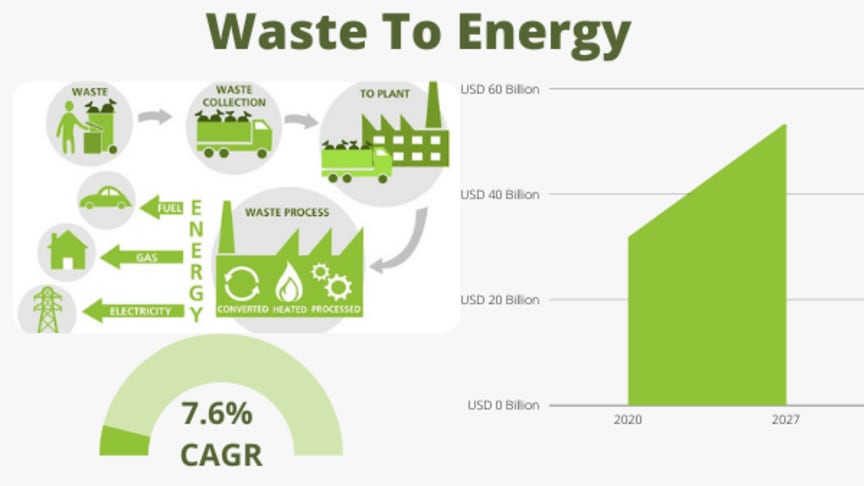
- The most common form of waste management we are seeing right now is Landfill. But landfills are actually becoming a problem right now instead of a solution, because the waste that is dumped on landfill sites is just…there. They are not recycled, nor are any methods adopted to help this problem. Well, there are now some ideas being presented, one of which is the Waste-to-Energy (WtE) strategy that even India is adopting.

A few other methods include thermal treatment of waste, special procedures for biomedical and nuclear, radioactive waste, and composting.
Thermal treatment includes procedures like incineration, which means burning all waste to ash and gaseous materials. Incinerators are mostly used in countries where no more landfill space is available, but it also has an additional value of reducing the size of landfills to a small fraction of the original size, less than 40% in volume of the original.


Special Procedures are followed for treating bio-medical or radioactive wastes because treating these types of waste properly is a requisite and this waste, if not treated properly, can be highly toxic and cause pollution as well as a lot of problems in the living creatures that would be exposed to them.
Composting is a form of waste management that can be done on an individual level too. Generally, what is done is to segregate the waste in our homes and then further find what waste can be composted and which should not be. In this way, the segregation of waste makes it easier to find which waste has to be incinerated and which are or can be recycled or reused. Composting also would make your gardening an experience to be cherished, which is just an additional benefit.
World’s Most Well Managed Countries In Terms Of Waste Managed And What Practices India Can Adopt From Them
According to NS Packaging, Germany is the first country in terms of waste management, with the country being able to manage upto 55% of their annual waste generated. Following it are Austria, South Korea, and Wales, all of whom show a waste management rate of higher than 50% and not far behind them is Switzerland, with a management rate of more than 49%.
All of these countries have one thing in common. And it is that they have devised ways to manage waste ideally in a way that the rest of the citizens are also able to do easily and actually want to do it instead of being forced to. The reason behind this adequate education and appropriate means for the public to follow to help in the waste management schemes.
India can also apply some ideological methods of waste management. One of them is composting, which has been explained earlier. Another is the wonderful invention in the USA, a machine that uses solar energy to operate and removes waste from the harbour.
One of the ideas also being followed are smart bins, which can check and let you know what waste you can throw in it and which should be thrown in a different one. Some countries have even started a scheme, where for every recyclable they enter in the machine, they get some reward. This should be followed in India too, as India is one of highest producers of plastic waste.
Top 13 Interesting Facts
A single recycled plastic bottle saves enough energy to run a 100-watt bulb for 4 hours. It also creates 20% less air pollution and 50% less water pollution than would be created when making a new bottle.
Research shows that if India continues to dump untreated garbage at its current rate, then we will need a landfill of size 66,000 hectares which are 10 metres high and can hold 20 years’ worth of waste. That is almost 90% of Bengaluru’s area.
One ton of recycled plastic saves around 2595 gallons of oil.
Waste management can include over 20 different industries.
Glass can be recycled and re-manufactured an infinite number of times and never wear out.
Making paper from recycled paper reduces the related contribution to air pollution by 95%.
According to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) report, Maharashtra tops by generating 26,820 tonnes of solid waste per day. That is equivalent to the weight of about 12,000 Mercedes-Benz GLE.
Deonar dumping site, which is the biggest landfill in India and one of the oldest in the world is finally getting waste to energy plant set up. The last recorded height shows that the landfill is almost or maybe even more than 200 ft tall.
If every garbage truck we filled annually was placed end-to-end, it would cover half the distance to the moon which is almost 2,00,000 kilometres.
The only relatively “clean” place on Earth is Antarctica. It is protected by the Antarctic Treaty, which prohibits military activities, mineral mining, nuclear explosions and nuclear waste disposal. In other words, humans need to draw up a treaty and declare a place prohibiting nuclear explosions for the place to not be in as bad a condition as the rest of the world.
Every year, over 45,35,92,37,000 kg of electronic waste (i.e., cell phones, computers, TVs, etc.) is created. That is almost the same as the number of potatoes we Indians consume in a year on average.
Landfills are among the biggest contributors to soil pollution even though roughly 80% of the items buried in landfills could be recycled.
A ton of recycled cardboard can free up to 9 cubic metres of landfill area. When you compare this to how much landfills are overshooting their limit in most areas, we can probably clear 8% of landfills just by recycling cardboard.
Some FAQs Or Also Ask Question
What are the 5 types of waste management & Disposal?
=> Different Types of Waste Management and Disposal are as follows:-
- Refuse
- Reduce
- Reuse
- Repurpose
- Recycling
What is meant by waste management?
Waste management refers to the collection, transportation, and handling, and disposal process collectively dealing with the removal of human waste.
Why is waste management so important?
Waste management minimizes the impact of waste on the environment, health etc. It can also help in reusing or recycling resources, such as; paper, cans, glass, and so on.
How do you manage waste properly?
There are some steps for better waste management such as measuring your own waste, Recycling. Waste segregation, etc.
What is the future of waste management in India?
As per the reports released by the Government of India, it is estimated that by the year 2031, MSW production will increase to 165 million tonnes and by 2050 to 436 million tonnes (Planning Commission Report 2014).




