
It was the empire that had dazzled the contemporary world with its extensive territories, military might, and cultural achievements. Ruling as large a territory as the Indian subcontinent with such a diversity of people and cultures was an extremely difficult task for any ruler to accomplish in the Middle Ages.
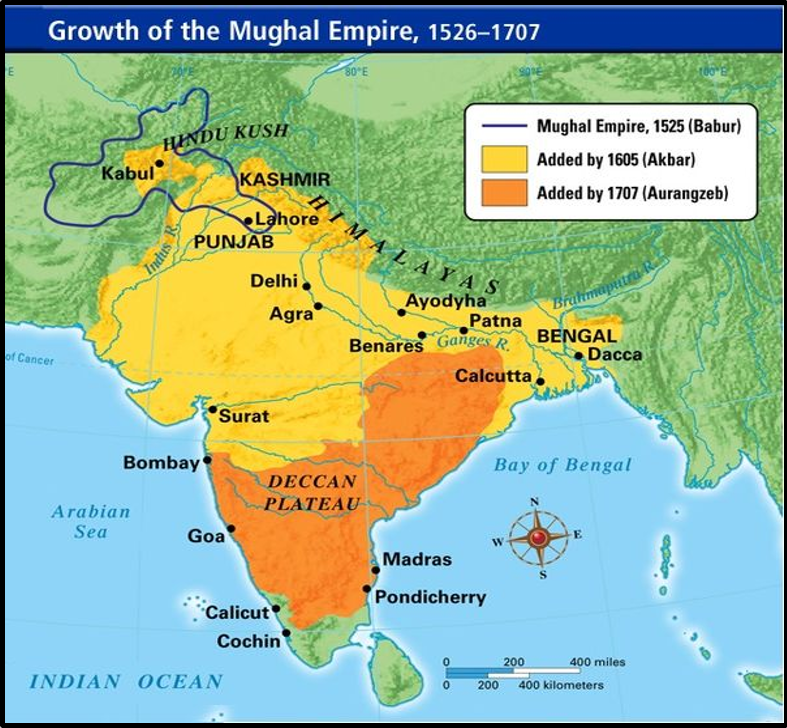
The Mughal Rulers had built up so strong central structure that this dynasty ruled for more than two centuries. The Mughal Empire was stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to Assam & Bangladesh in the east also Deccan plateau in South India.
- They imposed structures of administration and ideas of governance that outlasted their rule, leaving a political legacy that succeeding rulers of the subcontinent could not ignore.
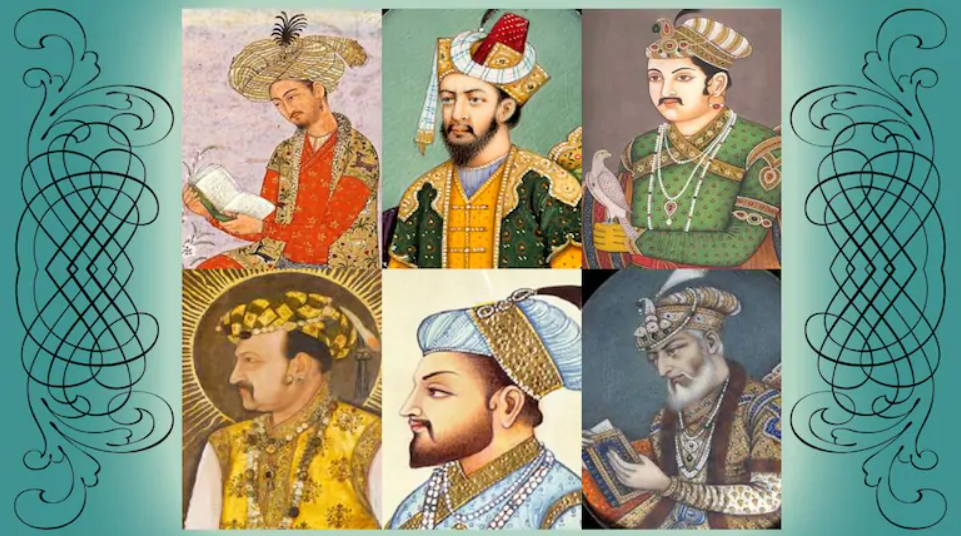
Mughal Emperors
Babur (1526-1530) - The Founder Of The Great Empire:-

His original name was “Zahir-ud-din Muhammad Babur”. His name was derived from the Persian word ‘Babr’, which means Tiger. He was born on 14 February 1483 in Andijan in the Fergana Valley (in present-day Uzbekistan).
He was the eldest son of Umar Sheikh Mirza, a descendant of Turk-Mongol conqueror Timur. His mother was a descendant of Asia’s conqueror Genghis Khan.
He ascended the throne of Fergana in 1494 at the age of 12.
He was invited by Dault Khan Lodi (Subedar of Punjab), Alam Khan (Uncle of Ibrahim Lodhi) to invade North India.
In the year 1526, Babur won the First Battle of Panipat against Ibrahim Lodi, the Lodi King.
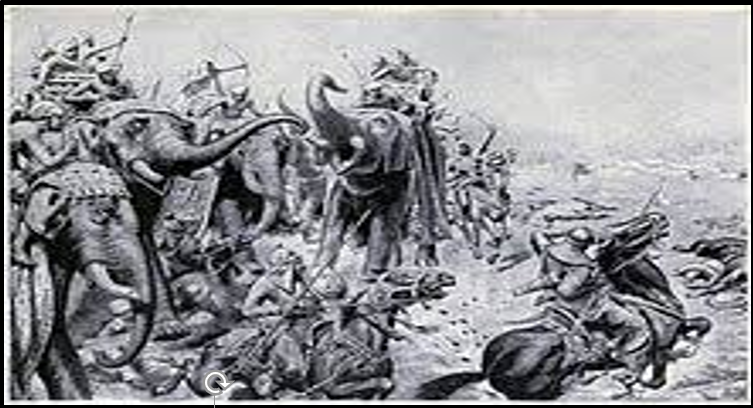

He captured Delhi and founded the greatest empire – the Mughal Empire.
He also defeated the Sangram Singh (Rana Sanga) ruler of Mewar in the Battle of Khanwa in the year 1527.

This weakened the Rajput confederacy and strengthened Babur’s position. Babur took the title of “Ghazi” after that war.
He also defeated the Medini Rai ruler of Chanderi in the year 1528 in the Battle of Chanderi.
Babur had also defeated the Afghan chiefs (under Mahmud Lodhi brother of Ibrahim Lodhi) in the Battle of Ghagra in the year 1529.
Babur wrote the Tuzuk-I-Baburi in Turki language is a classic of world literature, which was later translated in the Persian named Baburnama by Abdul Rahim Khan-I-Khana.

It shows his humane outlook and sensitivity to the beauty of nature.
He was the first Mughal emperor who declared Jihad.
He was the emperor who bought Gunpowder India.
He died in the year 1530 at the age of 48 & was buried at Aram Bagh (Agra). Late, his body was taken to Bagh-e-Babun (Kabul).

- Even today, he is considered a national hero in Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan.
Humayun (1530-40 And 1555-56):-

He was the eldest son out of four sons of Babur. The throne inherited by Nasir-Ud-Din Muhammad, better known by his regnal name, Humayun was not a bed of roses.
Humayun means “fortune” but he remained the most unfortunate ruler of the Mughal Empire. Before Babur could put the whole country on a stable basis, he died. Humayun had three brothers- Kamran, Hindal and Askari.
Humayun divided the empire among his brothers but this proved to be a great blunder on his part.
Kamran was given Kabul and Kandahar. He had a rivalry with Humayun.
Sambhal and Alwar were given to Askari and Hindal respectively.
Humayun captured Gujarat from Bahadur Shah and appointed Askari as its governor. But soon Bahadur Shah recovered Gujarat from Askari who fled from there.
Sher Shah Suri gradually gained power during his In the year 1539, Humayun was attacked by Sher Shah in the Battle of Chausa on the banks of the Ganges, near Buxar. The war was won by Shah Shah.

- Again, in the Battle of Bilgrama in the year 1540, Humayun was defeated by Sher Shah and had to flee from India. He had passed nearly 15 years (1540-1555) in exile.

- In the exile year, during his wanderings in the desert of Sindh, Humayun married Hamida Banu Begum, daughter of Sheikh Ali Amber Jaini, who had been the preceptor of Humayun’s brother Hindal.

- On 23 November 1542, Humayun’s wife Hamida Banu Begum gave birth to the successor of this prestigious dynasty and greatest leader of this dynasty Jalaluddin Muhammad Akbar.
Humayun had a chance to return in 1555. Sher Shah, the victor of Kannauj, died in 1545. He was succeeded by his son Islam Shah, who ruled 1553. He was succeeded by Muhammad Adil Shah. He was very fond of pleasures and left the affairs of his government in the hands of Hemu, his minister.
His authority was challenged by Ibrahim Shah and Sikander Shah. There was a large number of bloody battles among the various rivals. The net result of all this was that the Suri Empire was broken up. Bairam Khan, Humayun’s most faithful officer, helped Humayun in this.

- Humayun-Nama was written by his half-sister Gulbadan Begum.

- Humayun died in 1556 due to his fall from the staircase of his library.

He was first buried in his palace in Purana Quila in Delhi and then at the Humayun Bomb (Maqbara-I-Humayun), Nizamuddin, New Delhi. This tomb was commissioned by Humayun’s first wife and chief consort, Empress Bega Begum in 1558 & it was designed by Mirak Mirza Ghiyas and his son, Sayyid Muhammad. It is the first garden-tomb on the Indian Subcontinent. The tomb was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1993.
Akbar (1556-1605):-

» Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar was the son of Humayun and Hamida Banu Begam. He was born on 25 October at Amarkot in the year 1542. He was one of the greatest monarchs of the Mughal dynasty.
» With a strong personality and a successful general, Akbar gradually enlarged the Mughal Empire to include much of the Indian subcontinent. His power and influence, extended over the entire subcontinent because of Mughal military, political, cultural, and economic dominance.
Bairam Khan coronated him at Kalanaur when he was 13 years and 4 months old.
Bairam Khan represented him in the Second Battle of Panipat in the year 1556 against Hemu Vikramaditya.

» Hemu, wazir of Muhammad Shah Adil of Bengal, was defeated. Hemu is considered the last Hindu king of Delhi.
Between 1556 and 1560, Akbar ruled under Bairam Khan’s regency. Bairam Khan emerged as the most powerful noble and started appointing his own supporters on important positions. This caused resentment among the nobles who managed to influence Akbar as well. Akbar gave him the option of serving at the court or anywhere outside it or retiring to Mecca. Bairam Khan chose the option of going to Mecca.
On the way to Mecca, Bairam Khan was assassinated at Patan, Gujarat. Bairam’s wife and his young child were brought to Akbar at Agra.

» Akbar married the widow and brought up Bairam’s child as his own who later became famous as Abdul Rahim Khan-I-Khanan, a Hindi poet and an influential noble.
- Akbar conquered Malwa in the year 1561 defeating Baz Bahadur. He was later made the Mansabdar to honor his skill as a musician.

» Then, defeated Garh-Katanga (ruled by Rani Durgavati) followed by Chittor and Ranthambhore.
- Akbar followed a policy of reconciliation with the Rajputs. As he was aware of the importance of the Rajput Kingdoms. Some of the Rajput princesses entered into matrimonial alliances with him. In the year 1562, he married Jodha Bai, the eldest daughter of Raja Bharmal of Jaipur.

In the year 1570, he married princesses from Bikaner and Jaisalmer. All these activities paved the way for friendship between Rajputs and Mughals (except Mewar).
- Won Gujarat in the year 1572. It was in order to commemorate his victory of Gujarat that Akbar got Buland Darwaza constructed at Fatehpur Sikri.

- Akbar defeated Mewar’s Rana Pratap Singh in the Battle of Haldighati in the year 1576.


Later, Raja Mann Singh conquered Bihar, Bengal, and Orissa for Akbar.
Akbar discouraged the practice of Sati and encouraged the widow remarriage.
Akbar was given the nickname “The Great” because of his many accomplishments, among which was his record of unbeaten military campaigns that established the Mughal rule in the Indian Subcontinent.
In the year 1563 Akbar abolished the pilgrimage tax and also, he abolished Jaziyah in 1564.
He built Ibadat Khana (Hall of prayers) at Fatehpur Sikri in the year 1575.

- Ralph Fitch (1585) was the first Englishman to visit Akbar’s court.

He believed in Sulh-I-Kul or peace to all. He had a liberal attitude towards all religions. This liberal attitude also helped him a lot in the expansion of his territory.
He formulated an order called Din-I-IIahi or Tauhid-I-IIahi in 1581. Birbal, Abul Fazl, and Fazi joined the order.
The third Mughal emperor introduce a land revenue system called Todar Mal Bandobast or Zabti system, through his finance minister Raja Todar Mal, wherein the classification of land and fixation of rent was introduced.
He regularly visited the shrine of Sheikh Muinuddin Chisti at Ajmer.

He also introduced the Mansabdari System to organize the nobility as well as the army. Mansabdar meant holder of rank.
He had nine jewels or called Navratan’s named Todar Mal, Abul Fazal, Faizi, Birbal, Tansen, Abdul Rahim Khan-I-Khana, Mullah-do-Pyaza, Raja Man Singh and Fakir Aziao-Din.

Akbarnama which means ‘Book of Akbar’, is an official biographical account of Akbar, written in the Persian language. This book includes vivid and detailed descriptions of his life and times. It was commissioned by Akbar and written by Abul Fazl, one of the Nine Jewels.
The book ‘Akbarnama’ took seven years to be completed.
Akbar was the mightiest emperor of the Mughal dynasty. He stretched the Mughal empire from Sindh in the western part of India to Bengal in the eastern part of India and from present-day Afghanistan to the Godavari basin in the South.
Famous monuments during the reign of Akbar include Lahore Fort, Allahabad Fort, Agra Fort, Diwan-I-Aam, Diwan-I-Khas, Panch Mahal.


Akbar built a city, 37 km from Agra predominantly in Red Sandstone and is called Fatehpur Sikri.


Akbar fell ill on 3 October 1605, with an attack of dysentery. He is believed to have died on 27 October 1605.

- His body was buried at a mausoleum in Sikandra, Agra.
Jahangir (AD 1605-1627):-
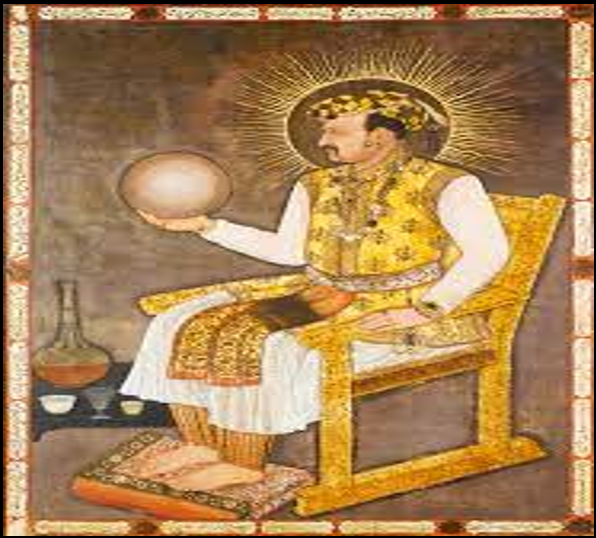

Salim was the eldest son of Akbar the Great & his favorite consort Marium-uz-Zamani daughter of Raja Bharmal. Salim assumed the title of Nur-ud-din Muhammad Jahangir. He was the fourth Mughal Emperor. His imperial name (in Persian) means ‘conqueror of the world’, ‘world-conqueror’ (Jahan: world; gir: to seize).
He mostly lived in Lahore which he adorned with gardens and buildings.
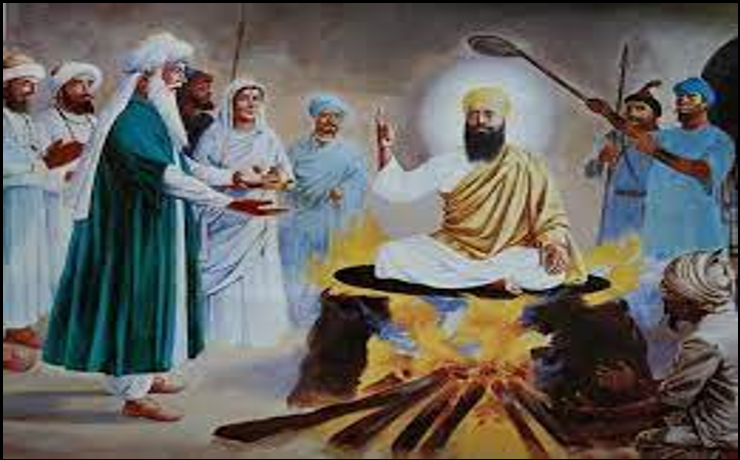
His eldest son Prince Khusrau Mirza revolted against the Jahangir; he was suppressed. As a punishment Khusrau Mirza was partially blinded and killed.

- The fifth Sikh guru, Guru Arjun Dev, had helped Khusrau. So, he was executed after 5 days of torture.

- Captain Hawkins (1608-11) and Sir Thomas Roe (1615-1619) visited the court of Jahangir.


Sir Thomas Roe was granted permission for the establishment of the East India Company Factory at Surat.
Jahangir was married to Rajput Princess, Jagat Gosain Begum, daughter of Raja Udai Singh Rathore of Mewar. Jahangir named her Taj Bibi Bilqis Makani and she gave birth to Prince Khurram, the next successor of Mughal dynasty Shah Jahan.

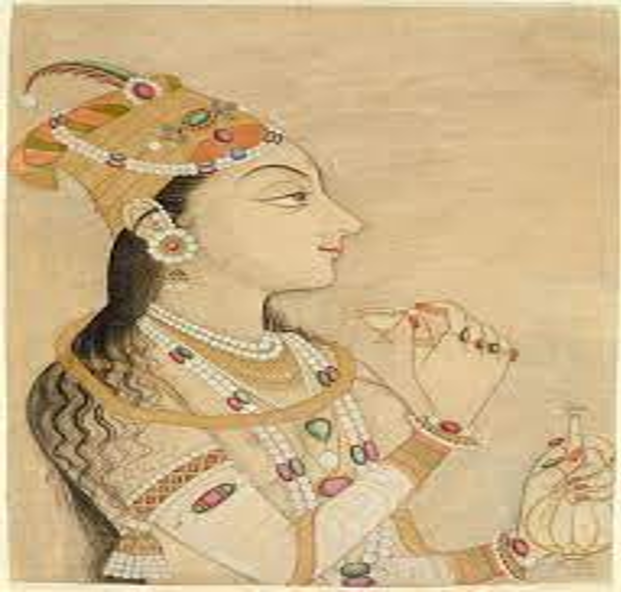
- The most important event in Jahangir’s life was his marriage to Mehr-un-Nisa, the widow of Sher Afghan, in 1611. The title of Nur Jahan was conferred on her. She had a great influence on Jahangir’s life.

- Jahangir had a chain of justice outside his palace in Agra (called Zanzir-I-Adil). He also laid a number of gardens, such as the Shalimar & Nishat gardens in Kashmir.


Painting reached its zenith in India under Jahangir. Special progress was made in portrait painting and painting of animals. The use of ‘Halo’ or Divine Lights started under Jahangir.
Jahangir died journey from Kashmir to Lahore, near Sarai Saadabad in Bhimber in the year 1627.
Shah Jahan (1628-1658):-
Shahab-Ud-din Muhammad Khurram is known by his regnal name Shah Jahan, fifth Mughal emperor of India. Shah Jahan was an able general and administrator. His childhood name was Khurram.

Shah Jahan secured Kandahar in AD 1639.
Shah Jahan annexed Ahmednagar while Bijapur and Golconda accepted him as their overlord.
Shah Jahan’s army consisted of 911,400 infantry, musketeers, and artillerymen & had 185,000 members in his cavalry regiment.
His policy of annexing the Deccan was quite successful. He made his son, Aurangzeb, the Viceroy of Deccan in 1636.
Shah Jahan’s court was visited by two Frenchmen Bernier and Tavernier.
His court was also visited by Italian adventurer Manucci.

- He was fond of architectural constructions. He had left behind a grand legacy of structures constructed during his reign. His constructions include Red Fort, large sections of Agra Fort, Jama Masjid, Wazir Khan Mosque, sections of the Lahore Fort, and the Jahangir Mausoleum.


- To celebrate his rule, he also made the Peacock Throne, Takht-e-Taus.

- His fourth wife, Mumtaz Mahal, was married to another man who was killed by Shah Jahan so that he could marry her.

- The building of love Taj Mahal was built by Shah Jahan in memory of his favorite wife Mumtaz Mahal on the bank of river Yamuna in the Indian city of Agra. The Taj Mahal was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the year 1983. Taj Mahal attracts 7-8 million visitors a year & in 2007, it was declared as the winner of the seven wonders of the World.
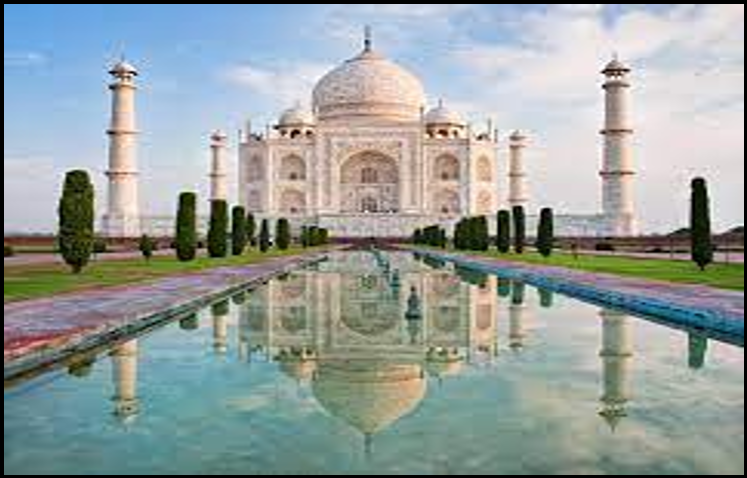

It is believed that Shah Jahan got the hands of the workers chopped off to prevent them from constructing an imitation of the Taj Mahal. It is a myth.
Shah Jahan’s reign is considered the Golden Age of the Mughal Empire.
The last 8 years of Shah Jahan’s life were very painful, as there was a brutal war of succession among his four sons- Dara, Shuja, Aurangzeb, & Murad.
Aurangzeb was made prisoner in the Agra Fort, being looked after by his daughter, Jahan Ara, till his death in 1666.
Aurangzeb (1658-1707):-
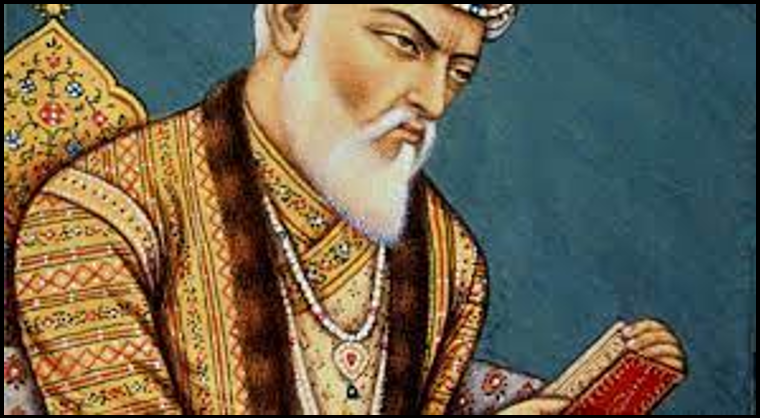

Muhi-Ud-Din Muhammad Aurangzeb commonly known by the sobriquet Aurangzeb (meaning ‘Ornament of the Throne’) was the sixth Mughal emperor, who ruled over almost the entire Indian subcontinent for a period of 49 years. At the time of Shah Jahan’s illness, Dara was in Delhi and the other brothers were in different places- Shuja in Bengal, Murad in Gujarat, and Aurangzeb in Deccan.
- Aurangzeb first defeated the Imperial army in the Battle of Dharmatt and then defeated a force led by Dara in the Battle of Samugarh. Thereafter, he entered Agra and crowned himself with the title of ‘Alamgir’ which means “Conqueror of the World.”

He reintroduced the Jizya tax and other policies based on Islamic ethics.
It is said that he led the demolition of Hindu temples.
He executed the Sikh Guru Tegh Bahadur after his refusal to convert to Islam.

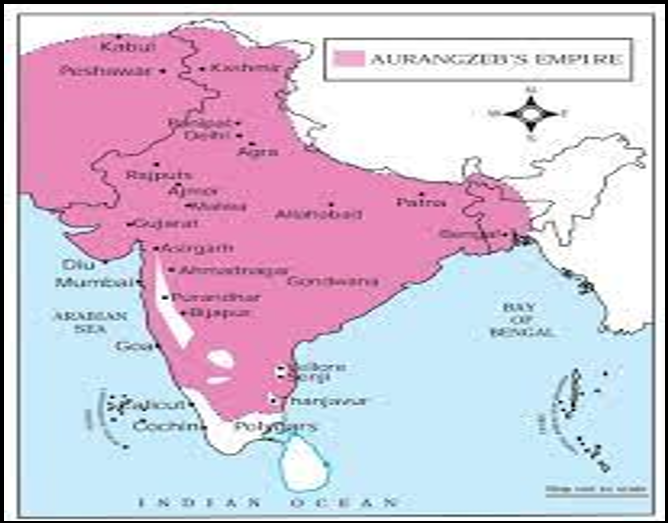
Under Aurangzeb, the Mughal Empire reached its greatest extent. The Mughal conquests reached the territorial climax during his reign, as Bijapur (1686) and Golconda (1687) were annexed to the Mughal Empire.
His reign can be broadly divided into two 25year periods. First in the affairs of North India when the Maratha power under Shivaji emerged and second marked by his preoccupations about the affairs of Deccan.
- Aurangzeb issued an order against Sati practice (in AD 1664 or 1666) and also gave the death penalty to those who forced widows to be burnt.

- Aurangzeb built Bibi Ka Makbara on the tomb of his queen Rabaud-Durani at Aurangzeb, Moti Mahal within Red Fort at Delhi, and the Jami or Badshahi Mosque at Lahore.


- Aurangzeb died on 3 March 1707, Bhingar, Ahmednagar.
Decline And Disintegration Of The Mughal Empire
After the death of Aurangzeb, the mightiest Mughal dynasty started declining. The reign of Aurangzeb was the swan-song of the Mughal rule in India. After his reign, the complex disease struck the heart of the empire and gradually spread to different parts. After Aurangzeb, there was a series of weak rulers due to which this Great dynasty come to end.
Bahadur Shah I (1707-1712):-

Aurangzeb had three sons, Prince Muazzam, Muhammad Azam & Kam Bakhsh. The eldest brother got the better of the other two and defeated and Killed Muhammad Azam and Kam Bakhsh.
Muazzam assumed the title of Bahadur Shah I.
He was 63 years old of age when he ascended the throne.
He released the Maratha prince, Shahu who had been in the Mughal captivity since 1689 and was allowed to return to Maharashtra.
He was forced to take action against the Sikhs whose new leader Banda had become a terror for Muslims in Punjab.
Bahadur Shah, I died on 27 February 1712.
Jahandar Shah (1712-1713):-

The usual war of succession broke out again in 1712 amongst the four sons of Bahadur Shah- Jahandar Shah, Azim-us-Shan, Rafi-us-Shan, and Jahan Shah.
Jahandar Shah came out successful with the help of Zulfikar Khan, a prominent leader of the Irani party.
His position was challenged by Farrukhsiyar (son of Azim-us-Shan) & with the help of the Sayyid brothers he defeated and killed Jahandar Shah.
Farrukhsiyar (1713-1719):-

He killed Jahandar Shah and took the throne.
He was the son of Azim-us-Shan.
Farrukhsiyar’s reign saw a victory for Mughal arms over the Sikhs whose leader Banda Bahadur was a prisoner at Gurdaspur and later executed at Delhi (19 June 1716).
He granted many trading privileges to East India Company including exemption of customs duties for its trade through Bengal.
He was killed in the year 1719.
Rafi-ud-Darajat (28 February - 4 June 1719):-
- He was the 10th Mughal emperor raised by Sayyid’s brothers who were playing the role of kingmaker at those time.
Rafi-ud-Daula (6 June - 17 September 1719):-
- He was emperor for a very brief period of time.
Muhammad Shah (September 1719 - April 1748):-

He was also called Rangeela.
He was able to get rid of the Sayyid brothers.
He suffered the invasion of Nadir Shah of Persia in the year 1739.
Ahmad Shah Bahadur (1748-1754):-

He was son of Muhammad Shah.
His minister Safdarjung was responsible for Mughal Civil War.
Ahmad Shah Abdali from the northwest raided India several times in 1748, 1749, 1752.
He was defeated at Sikandarabad by the Maratha Confederacy.
Alamgir II (1754-1759):-

Ahmad Shah Abdali from the northwest raided India in years 1756-57 & 1759 during his reign.
He was murdered by a conspiracy of Imad-Ul-Mulk and his Maratha associate Sadashivrao Bhau.
Shah Jahan III (1759-1760):-
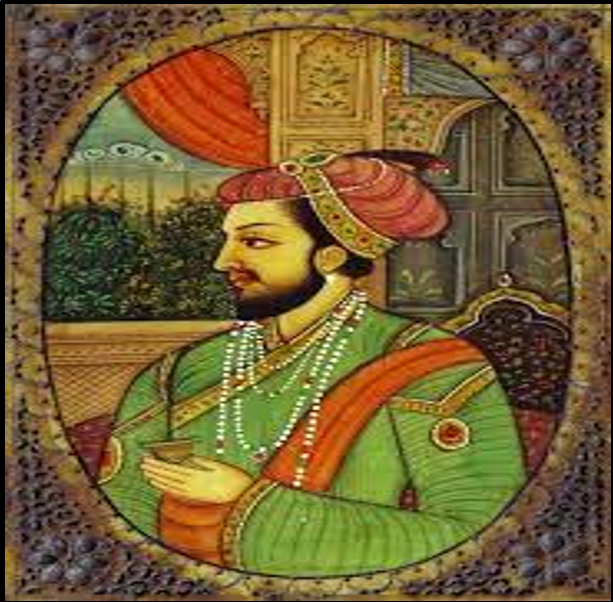

- He was overthrown after the Third Battle of Panipat by Prince Mirza Jawan Bakht.
Shah Alam II (1760-1806):-
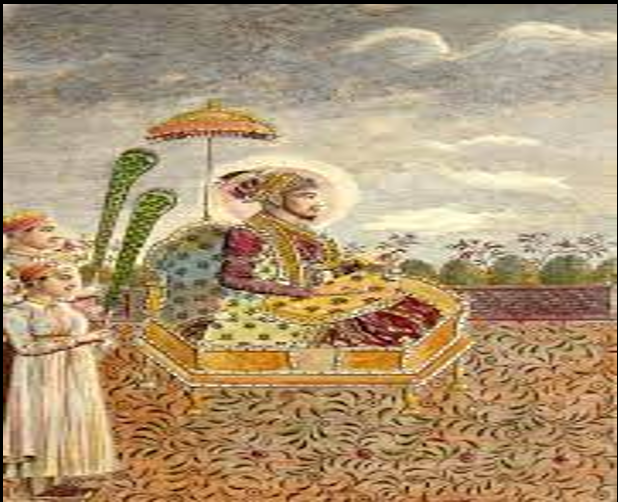

He is known to have fought against the British East India Company during the Battle of Buxar and reformed the Mughal army under the command of Mirza Najaf Khan.
He was also known as one of the last effective Mughal emperors.
Akbar Shah II (1806-1837):-
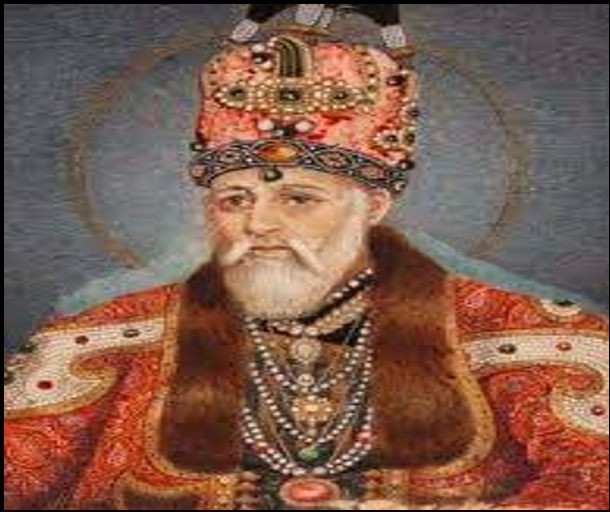

He designated Mir Fateh Ali Khan Talpur as the new Nawab of Sindh.
He was emperor in name only, he was the puppet of the East India Company.
Bahadur Shah II (1837-1857):-
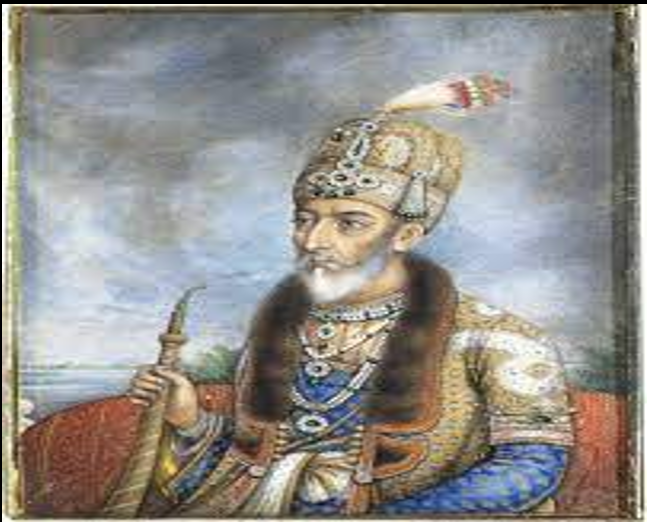

He was the last Mughal emperor.
He was deposed by the British and exiled to Rangoon due to the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
Top 13 Interesting Facts Of The Great Mughal Dynasty
The Mughal Empire was stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to Assam & Bangladesh in the east also Deccan plateau in South India.
Babur defeated the Sangram Singh (Rana Sanga) ruler of Mewar in the Battle of Khanwa in the year 1527. Babur took the title of “Ghazi” after that war.
Humayun means “fortune” but he remained the most unfortunate ruler of the Mughal Empire.
Humayun-Nama was written by Humayun’s half-sister Gulbadan Begum.
Akbar Won Gujarat in the year 1572. It was in order to commemorate his victory of Gujarat that Akbar got Buland Darwaza constructed at Fatehpur Sikri.
Akbar formulated an order called Din-I-IIahi or Tauhid-I-IIahi in 1581. Birbal, Abul Fazl, and Fazi joined the order.
Akbar had nine jewels or called Navratan’s in his court named Todar Mal, Abul Fazal, Faizi, Birbal, Tansen, Abdul Rahim Khan-I-Khana, Mullah-do-Pyaza, Raja Man Singh, and Fakir Aziao-Din.
The fifth Sikh guru, Guru Arjun Dev, had helped Khusrau. So, Jahangir was executed after 5 days of torture.
Sir Thomas Roe was granted permission by Jahangir for the establishment of the East India Company Factory at Surat.
Shah Jahan’s reign is considered the Golden Age of the Mughal Empire.
The building of love Taj Mahal was built by Shah Jahan in memory of his favorite wife Mumtaz Mahal on the bank of river Yamuna in the Indian city of Agra. The Taj Mahal was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the year 1983. Taj Mahal attracts 7-8 million visitors a year & in 2007, it was declared as the winner of the seven wonders of the World.
Aurangzeb executed the Sikh Guru Tegh Bahadur after his refusal to convert to islam.
Bahadur Shah Jafar was deposed by the British and exiled to Rangoon due to the Indian Rebellion of 1857.







