- Umang Sagar
- 2 Comments
- Education, Recent article
The Gurukul System Of Education

Introduction
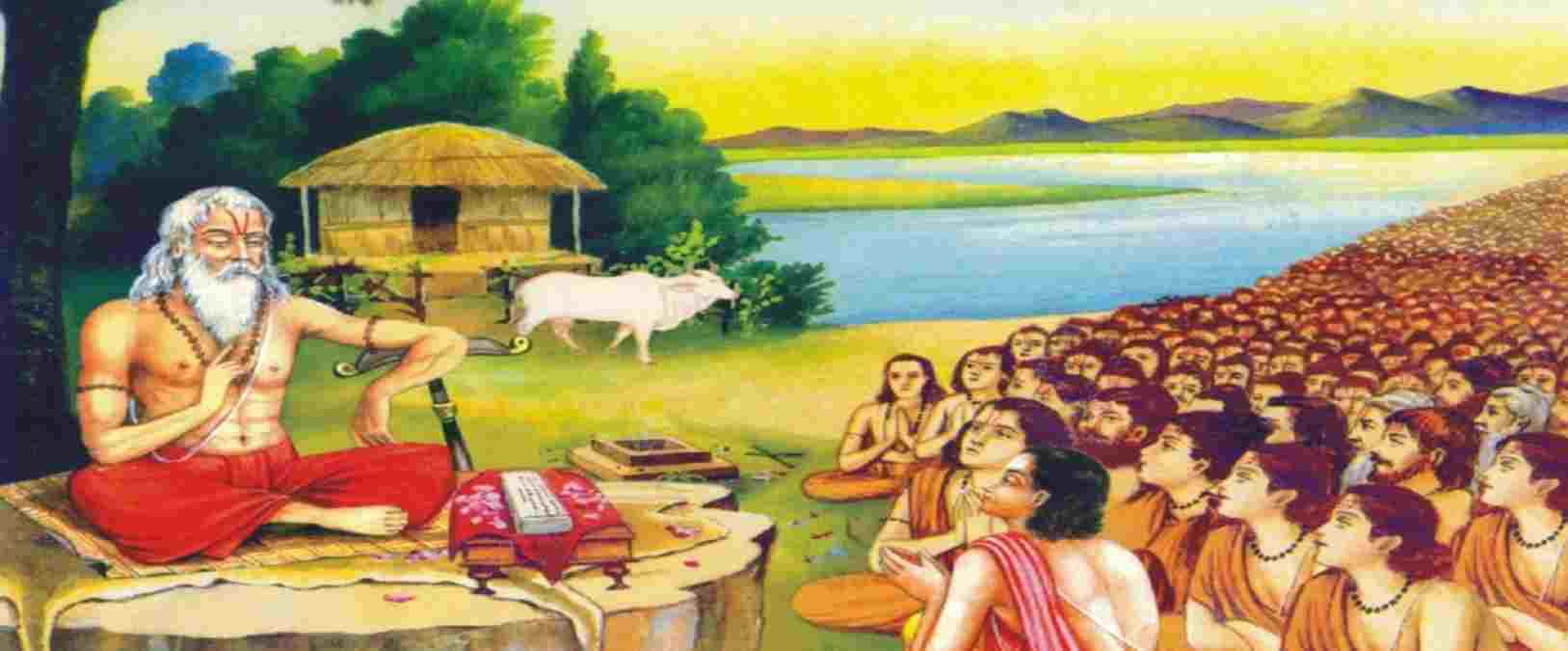
The ancient history of India has the essence of the rich traditional and cultural heritage of the country. One of the best-known traditions of the past was the unique Gurukul System of Education.
From time immemorial, education continues to be the most integral aspect of any civilization. Over the years, it has adapted itself to the changing needs of time and to keep abreast with evolutionary changes and steering towards becoming a meaningful process and promoting lifelong learning. An education system that originated in the eastern world and continues to be a source of inspiration is the ancient Gurukul Education system.
The Gurukul education system was a form of residential education system where the students lived in a Gurukul which was the home of the teacher or ‘Acharya’ and served to be the center of education. The kernel of this education system lies in the principles of discipline and hard work. Students were expected to learn from their gurus and use their knowledge in practical life. The relationship that existed between the student and teacher is sacred and it often didn’t involve any formal payments, but a Gurudakshina that the student offered the teacher as a homage to their relentless support. This education system began in ancient times during the Vedic age when there was no form of formal education, but the learning was skill-based and religiously rooted in Vedas, Puranas, and holy texts which were the imperative guide for students to expand their horizons of knowledge.
History

The gurukul system of education has been in existence since ancient times. The Upanishads (1000-800 BCE) mention multiple gurukulam, including that of guru Drona at Gurgaon. The Bhrigu Valli (a discourse on the Brahman) is said to have taken place in Guru Varuni’s gurukula. The Vedic school of thought prescribes the gurukul (sacred rite of passage) to all individuals before the age of 8 at least by 12. From initiation until the age of 25 all individuals are prescribed to be students and to remain unmarried, a celibate.
The students were admitted to the Gurukul at a specific stage depending on the caste they belonged to. The Brahmins, the Kshatriyas, and the Vaishya students were admitted to the Gurukul at the age of 6,8, and 11 respectively. It was called Yajnopavita, Upanayana, or Upavita then and sacrificial rituals were performed before the students were allowed in. They sat near their Guru and studied as Brahmachari.
It was the duty of the Guru to impart knowledge to his pupil about all intellectual rites, scriptures, and all useful disciplines and finally initiate and marry him to send him back to perform various household duties.
Main Objectives Of Gurukul
- The key goals of the gurukul system are as follows:
- Self-control
- Development of the mind
- Personality development and social awareness
- Creating a character development
- Knowledge and cultural preservation Spiritual
- Spiritual growth and development
- The students in Gurukuls were required to recite the Vedas and other ancient books daily to learn well. This was to ensure that they remember the crucial parts of the texts. Apart from performances, Gurukuls provided students with hands-on learning opportunities. They would cook, clean, and perform other tasks. There were regular debates and discussions on certain subjects as well. Pupils were required to analyze and apply critical thinking to a variety of topics.
Teachings Of Gurukul

It is a myth that in the gurukul system of education, only the Vedas and Upanishads were taught as topics. This was a comprehensive and all-encompassing educational system where a student’s overall growth was included. The pupils’ moral, physical, and spiritual well-being was prioritized. Gurukul’s teachings include all parts of life, both physical and mental. Students were taught to live in harmony with nature.
The following are some of the subjects that were taught in the gurukul system of education:-
- Languages of Science and Astronomy
- Medicine in its early stages
- Mathematics and mathematics fundamentals
- Vedas, Upanishads, Brahmanas, Dharma sutras
- Yogic sciences
- Martial arts and sports as well.
- The sources of knowledge were the writings of eminent academics such as Aryabhatta and Patanjali. In ancient times, the teacher’s inherent knowledge and experiences also were some of the sources of learning. The Shishyas were taught yoga, exercises, physical labor, games, archery, martial arts, and sports in addition to mathematics and many disciplines. Students were also taught about the responsibilities of social responsibilities. As a result, it is to conclude that the ancient gurukul educational system was a way of life.
Classes In The Gurukul
The method of teaching involved the Guru testing students before every lesson. It was a routine that 10-15 minutes before the starting of any class, the teacher used to take an oral revision test of the students to analyze their learning.
The students used to learn the Samhitas as per their intelligence along with the Guru. This way the students with better intelligence were able to memorize faster than others and were moved on to another lesson by the Guru.
It was not a system that exists today where the children need to wait for others in their class to memorize the lesson so that the whole class can be shifted to the next one. The students who were capable of progressing were never hindered due to the nonperformers.
Administration Of The Gurukul
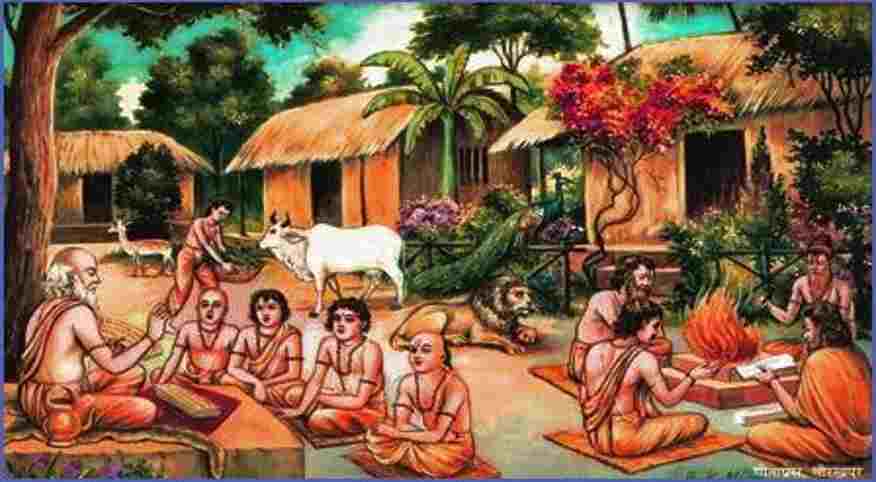
Basically, it was the Brahmin households that used to run Gurukuls. They were situated inside and outside the villages or towns. Even the clergy back then used to attract the students and word of mouth was used as a method of promotion. There was never any discrimination between rich and poor in Gurukul which was a plus point of the Indian education system of that time. The doors were always open for various deserving students.
The fee of the Guru or Acharya was called ‘Dakshina’. It can be given by the celibate student to the Gurukul or the family of the Guru through his services or through payment of a fee after the completion of his course. However, any monetary reward was given only after the initiation and initiation of Guru Vidya. The students also went as a routine practice to ask for alms or Madhukari. Begging was an important part of the celibacy fast thus being compulsory for all to follow. This helped the Guru run the Kul. Also, subsidies from the kings and the government, along with generous donations from the people around helped the financial administration of the Gurukul.
How students were divided in Gurukul
Students were divided into three categories:
- Vasu – Those who get education till the age of 24 years.
- Rudra – Those who get education till the age of 36 years.
- Aditya – Those who get education till the age of 48 years.
Features Of Gurukul Teachings
The emphasis was on holistic learning with an incremental focus on professional, social, religious, and spiritual education.
The education given was profusely influenced by the culture and religion which were incremental elements of the ancient Indian society.
The basis of being selected by a gurukul was an impeccable attitude and moral strength that could be displayed through impeachable conduct.
The gurukul education system resulted in the all-around development of the individual and emphasized a psychological method of teaching.
Alongside knowledge of the art, literature scriptures, and philosophy, students were also taught practical skills and trained for different tasks.
Why Is The Gurukul System Valuable?
- The Gurukul system has been very valuable for the students. Modern-day education is different from the Gurukul education system especially because it focused on quality and holistic education:
Applied Knowledge: Gurukul focused on applied knowledge and offered an education that prepares them for all fields of life. Today, it can be done by combining academics and extracurricular activities along with mindful and spiritual awareness.
Value-based Learning: Gurukul offered value-based learning where learning happens as per the uniqueness of the child. This offers healthy competition and reduces stress levels amongst children.
- Student-teacher relationship: Gurukul creates a teacher and student relationship that creates a secure learning environment. This way students have trust in their caregivers.
Objectives Of Gurukul System
Students are spiritually elevated which gives them an optimistic, calm, and composed personality.
Every student is given proper attention as the student-teacher ratio is properly planned, unlike other schools where students aren’t given individual attention.
Gurukul emphasizes practical knowledge which is quite beneficial to building the concepts of the students.
Students are taught to follow the principle of “simple living and high thinking” which is a great lesson for life.
The students of gurukul are more disciplined and organized. They are taught to follow a well-planned schedule in a gurukul.
The students are more focused and possess more concentration power than normal students. This is because they are trained through techniques such as meditation which enhances their focusing power.
In a gurukul, students are taught to respect everyone irrespective of their caste, creed, ethnicity, culture, religion, and perspective. So, such students grow up as people with strong character and values.
The ‘guru – shishya Parampara’ is an integral part of Gurukul. Here, the students highly respect their teachers and share a good bond with them. They are molded under the guidance of their mentors.
In a gurukul, ‘Gurus’ also take complete responsibility for their Shishyas. They share their experiences, inculcate good habits, and mold the character of the students in a positive direction.
The students are developed into strong individuals. They are taught to stay firm and face any adverse situation in the outside world.
Gurukul students are taught to value nature. So, they are very close to nature. They worship nature and learn a lot of things from it.
The Importance Of The Gurukul System In Present Times

- The focus of Gurukuls was on imparting learning to the students in natural surroundings where the Shisyas lived with each other with brotherhood, humanity, love, and discipline. The essential teachings were in subjects like language, science, and mathematics through group discussions, self-learning, etc. Not only this but the focus was also given to arts, sports, crafts, and singing which developed their intelligence and critical thinking. Activities such as yoga, meditation, mantra chanting, etc generated positivity and peace of mind and made them fit. It was also mandatory to do daily chores on their own with a motive to impart practical skills to them. All of these helped in their personality development and increased their confidence, sense of discipline, intellect, and mindfulness which is necessary even today to face the world that lay ahead.
Flaws In The Present Education System
- Unfortunately, the above concept has disappeared, and the modern system of education brought to India in the year 1835 by Lord Macauley is all about a rat race to be ahead of others. There is a total absence of personality development, the creation of moral conscience, and ethical training. One of the biggest flaws of this education is that it is more commercial in nature rather than an institutional concept that should impart holistic learning to the students. It devotes very less time to physical activity and the development of other skill sets that can assist a student to become a better human being.
Gurukul System in Later Vedic Period
The advent of the Britishers changed the education scene in the country. The Gurukul system ended. The Britishers introduced their centralized system of education. However, realizing the steep decline in the Gurukul system of education and its importance in modern education, the pioneers Dayanand Saraswathi and Swami Shradhanand spearheaded the revival of the modern Gurukul system of education. In 1886 they founded the Dayanand Anglo-Vedic Public Schools and Universities.
The school revived the almost forgotten ancient system of education. Slowly but surely, the school spread its wings to various parts of the country and even the rest of the world. The relevance of the ancient gurukul system of education in today’s educational setup cannot be forgotten. Though the concept has undergone significant changes to keep up with modernization, the basic theme of the gurukul system still stands today.
Even today, the concept of teaching students moral values has remained an integral part of the education system like the ancient times.
Do We Need A Gurukul System Back In India?

Many individuals think of the gurukul system as an unstructured and strange concept. People may worry about how a child will learn anything if he or she lives with a teacher if there is no curriculum or fixed schedule.
Modern educationalists, on the other hand, have taken a step back and discovered that there are numerous teaching methodologies from the Gurukul system that can be incorporated into today’s educational system.
- The relation between teacher and student– The need of present times is to ensure that teachers and students share a friendly relationship and respect. This is because when the children feel secure and have trust in the caregiver then they are most likely to emulate the same. This was present in the Gurukul system which can be inculcated today using activities, and training workshops to bond with the students.
- Modern infrastructure – Robust learning of the students can only take place when focusing on given on practical knowledge. But alas our present-day education just believes in bookish knowledge and cramming which is not sufficient. The Gurukul system focused on applied knowledge that prepared the students in all fields of life. In present times it can be done by creating a perfect combination of academics and extracurricular activities along with teaching in mindfulness and spiritual awareness to make the students better individuals.
- Holistic education – Current education mainly focuses on a rank-based system driven by hostility towards one’s peers. More fuel is added by over-ambitious parents who judge students’ knowledge only by academic performance. Instead, the application of the Gurukul system can work on a value-based system where the uniqueness of the children can be taken care of so that they can excel in their areas of interest. It will also build a good character that shuns fierce competition and increased stress levels that usually lead to depression.
- Overall, the goal of incorporating a Gurukul system into Indian education is to help pupils grasp the concept of living a balanced life. This balance idea should be instilled in children at a young age so that they can make informed decisions regarding employment, food, exercise, and how they want to live their lives. A gurukul school is clearly the ideal option for a child’s entire development. It produces people who have a distinct point of view.
Top 13 Facts About The Gurukul System Of Education
The schools were known as Gurukuls. These schools were attended by various rulers of India like the Pandavas, the Kauravas, Chandragupta Maurya, and even Lord Rama and Lord Krishna.
The best part about Gurukuls was that they followed the concept of hostels.
The term is derived from Guru meaning teacher and Kula meaning clan or family.
Gurukuls had three basic pillars- the Acharya or the teacher, the Shishya or the student, and the ashram or the place where they interacted.
The extended part of Gurukuls was what we would call the modern-day universities.
Famous universities like Taxila, Nalanda, and Vikramshila. These served as centers for advanced learning.
One of the famous pupils of Taxila was the noted grammarian Panini. He became an expert in language and grammar and wrote the famous book Ashtadhyayi.
The ruins of Taxila were excavated in the mid-19th century in the North-Western part of Pakistan. It is now a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Education during ancient times was sacred. It was a venerated and revered field. Due to its adulation, no fixed fee was charged to students.
In return for the knowledge acquired from the teacher, the pupils paid Guru Dakshina teacher. It was a token of respect from a student to the teacher, on completing the period of study.
Realizing the steep decline in the Gurukul system of education and its importance in modern education, the pioneers Dayanand Saraswathi and Swami Shradhanand spearheaded the revival of the modern Gurukul system of education.
In 1886 they founded the Dayanand Anglo-Vedic Public Schools and Universities. The school revived the almost forgotten ancient system of education.
The significant relevance of the gurukul system in today’s education is the concept of Guru Dakshina.




good
ok