- Umang Sagar
- History, Recent article
Maya Civilization & Its Enduring Cultural Legacy In Mesoamerica

Introduction
The Maya civilization was an ancient civilization that existed in Mesoamerica, primarily in what is now modern-day Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador. It is known for its highly advanced culture, art, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, and writing system.
It is believed to have originated around 2000 BCE and continued to thrive until the arrival of the Spanish in the 16th century. During this time, the Maya civilization went through several periods of development, including the Pre-classic (2000 BCE – 250 CE), Classic (250 CE – 900 CE), and Postclassic (900 CE – 1521 CE) periods.
It was composed of many independent city-states, each with its own ruler and governing structure. These city-states were linked by a common language, culture, and trade routes. It was known for its impressive architectural achievements, including pyramids, temples, palaces, and public plazas. Many of these structures were adorned with intricate carvings, murals, and sculptures.
They had a sophisticated writing system that included hieroglyphs and a calendar system that was more accurate than the one used in Europe at the time. And had a deep understanding of astronomy, which they used to develop their calendar and for religious purposes.
The decline of the Maya civilization is still not fully understood, but it is believed to have been caused by a combination of factors, including environmental degradation, warfare, disease, and political instability. Despite their decline, the Maya civilization has left a lasting impact on Mesoamerican culture and continues to be studied and admired today for their contributions to art, science, and civilization.
Etymology
The word “Maya” is believed to have multiple possible origins, but the most widely accepted theory is that it comes from the Yucatec Maya word “Mayab,” which means “flat land.” The name “Maya” was given to the civilization by modern scholars and historians, and it is not clear what the Maya people called themselves.
It was composed of many different city-states, each with its own unique culture, language, and history. These city-states were linked by trade, religion, and a shared cultural heritage. Some of the most well-known Maya city-states include Tikal, Palenque, Copán, and Chichén Itzá.
The word “Maya” was first used in the 16th century by Spanish conquistadors and missionaries who encountered the remnants of the Maya civilization in what is now modern-day Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador. They had already been in decline for several centuries by the time the Spanish arrived, but their influence and legacy were still evident in the region.
Today, the term “Maya” is used to refer to both the ancient civilization and the modern-day descendants of the Maya people who continue to live in Mesoamerica. The Maya people have faced many challenges throughout history, including colonization, displacement, and discrimination, but they continue to celebrate their cultural heritage and maintain a strong sense of identity and community.
Maya Civilization & Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica was a region of significant cultural and economic exchange, with trade networks connecting distant cities and regions. The region was also marked by a shared cultural heritage, as many of the civilizations in Mesoamerica shared common religious beliefs, artistic styles, and cultural practices.
The Maya civilization was one of the most prominent and influential civilizations in Mesoamerica, and their cultural and artistic achievements continue to be studied and admired today.
They also had a complex political system, with each city-state ruled by a king who was believed to have divine authority. The Maya engaged in warfare with neighbouring city-states, and there is evidence of political alliances and conflicts between different Maya groups.
Despite their impressive achievements, they faced numerous challenges, including environmental degradation, political instability, and disease. By the time the Spanish arrived in Mesoamerica in the 16th century, they had already declined significantly, but their cultural legacy continues to be celebrated and studied today.
Geography
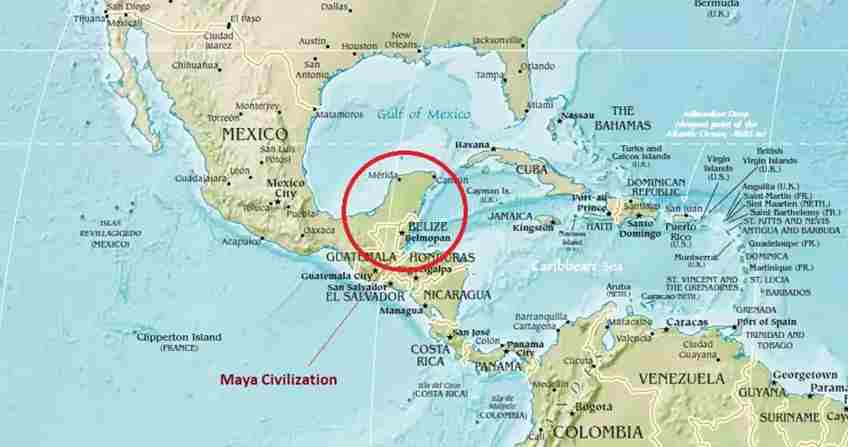
The Maya civilization was in Mesoamerica, a region that includes modern-day Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador. The geography of the region varied widely, with mountain ranges, forests, jungles, deserts, and coastlines all present.
The heartland of the Maya civilization was in the Yucatan Peninsula, which includes the modern-day Mexican states of Yucatan, Quintana Roo, and Campeche, as well as parts of Belize and Guatemala. The Yucatan Peninsula is characterized by a flat and dry landscape, with little surface water and few natural resources.
Despite these challenges, the Maya civilization was able to thrive in the region by developing sophisticated agricultural techniques, including terraced fields, irrigation systems, and the use of chinampas, or floating gardens. The Maya also built elaborate systems of roads and trade routes, which connected different cities and regions.
The Maya civilization was composed of many different city-states, each with its own unique geography and environment. Some cities were in dense jungles, while others were situated near rivers or on coastal plains. These cities were linked by trade networks and shared cultural practices, such as the worship of common deities and the practice of human sacrifice.
They also had a deep connection to the natural world, and their religious beliefs and practices were closely tied to the cycles of the sun, moon, and stars and developed a sophisticated understanding of astronomy, which they used to create a highly accurate calendar and to predict celestial events.
Today, the geography of the region continues to influence the culture and way of life of the Maya people, who continue to live in Mesoamerica and maintain a strong connection to their cultural heritage and natural environment.
History

The Maya civilization is believed to have originated in the region of present-day Guatemala and Belize around 2000 BCE, with the development of agricultural techniques that allowed for the growth of maize, beans, and other crops.
Over the centuries, they developed a sophisticated system of writing, a highly accurate calendar, and impressive architectural and artistic traditions and built impressive pyramids, temples, and palaces, decorated with intricate carvings, paintings, and sculptures. Between 300 and 900 CE, the Maya civilization experienced a period of great cultural and artistic achievement, known as the Classic Period. During this time, the Maya built impressive cities such as Tikal, Palenque, and Copán, and created some of their most impressive architectural and artistic works.

However, in the 9th century, they experienced a period of decline and collapse, with many cities being abandoned and their populations dispersing. The exact reasons for this collapse are still debated by scholars but are believed to include a combination of environmental degradation, warfare, political instability, and disease. Despite the collapse of their civilization, the Maya people continued to live in the region and maintain their cultural heritage.
Today, the Maya people are still present in Mesoamerica, and their cultural traditions continue to be celebrated and studied. In recent years, new discoveries have shed light on the history and achievements of the Maya civilization, further enriching our understanding of this remarkable culture.
Society

Maya society was also marked by a strong religious tradition, with the worship of numerous gods and goddesses, each associated with different aspects of the natural world. The Maya practiced human sacrifice as part of their religious beliefs, and many of their artistic and architectural works are devoted to religious themes and iconography.
Maya society was organized into city-states, each with its own king, nobility, and commoners, and had a sophisticated political system, with each city-state ruled by a king who was believed to have divine authority. The king was responsible for ensuring the well-being of his people and was often depicted in Maya art and sculpture as a powerful and divine figure. Below the king were the nobles, who were responsible for administering the city-state and overseeing the various aspects of Maya life, including religion, agriculture, and trade. The nobles were often depicted in Maya art and sculpture as powerful and dignified figures, wearing elaborate clothing and headdresses.
Beneath the nobles were the commoners, who made up the clear majority of Maya society. Commoners were farmers, craftsmen, and traders and were responsible for producing the goods and services that supported Maya society.

Despite their hierarchical society, the Maya civilization was also marked by social mobility, with individuals able to rise through the ranks of society based on their abilities and achievements. It was also characterized by a strong sense of community and cooperation, with the people of each city-state working together to ensure the well-being of their community. It was renowned for its rich and diverse cultural traditions, including art, architecture, literature, music, and dance. Maya art and culture developed over several millennia and were influenced by a wide range of regional and historical factors.
Maya art was characterized by its intricate and detailed style, which was used to create a wide range of works, including pottery, sculpture, murals, and textiles. It often depicted religious and mythological themes and was created using a wide range of materials, including clay, stone, shell, bone, and precious metals. Their architecture was also highly developed, with the construction of massive pyramids, temples, and palaces that showcased the artistic and engineering skills of the Maya. Maya architecture was often decorated with intricate carvings, paintings, and sculptures that depicted religious and historical themes.
Maya literature was also highly developed, with a rich tradition of hieroglyphic writing that was used to record historical events, religious beliefs, and cultural traditions. It was often created on bark paper or other materials and decorated with elaborate drawings and paintings.
Maya music and dance were also an important part of their cultural traditions, with a wide range of musical instruments and dance styles used to celebrate religious and cultural events. Maya music was often created using drums, flutes, and other traditional instruments, while Maya dance was marked by intricate movements and costumes that reflected the complex cultural heritage of the Maya.
The art and culture of the Maya civilization were characterized by intricate detail, a deep connection to the natural world, and the celebration of religious and cultural themes. Today, the artistic and cultural traditions of the Maya continue to be celebrated and studied and have had a profound impact on the cultural heritage of Mesoamerica and beyond.
Architecture
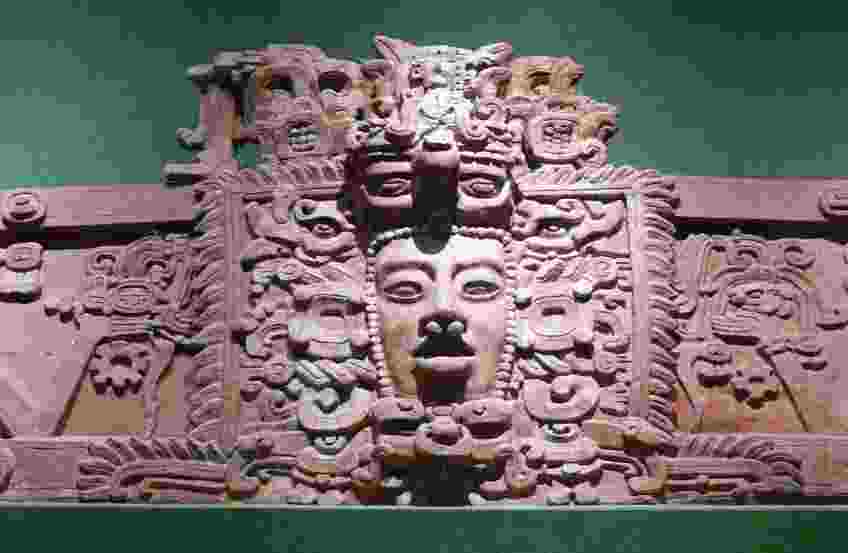

Maya architecture was highly developed and sophisticated, with the construction of massive pyramids, temples, palaces, and other structures that showcased the artistic and engineering skills of the Maya. Maya architecture developed over several millennia and was influenced by a wide range of cultural and historical factors.
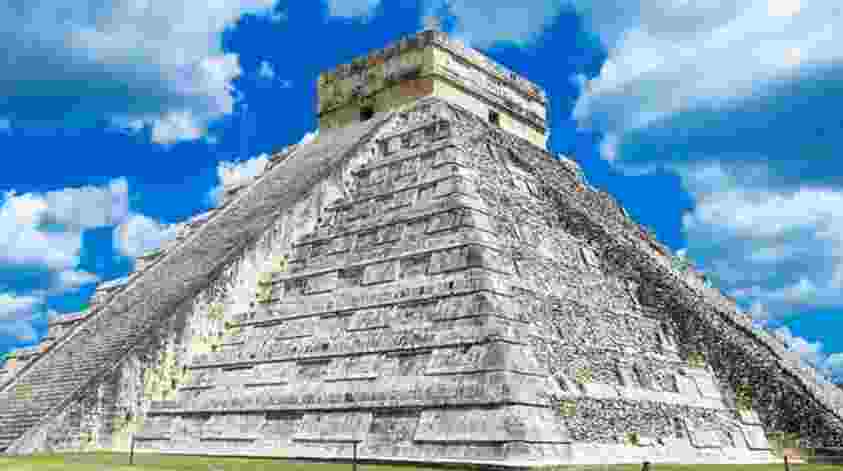

- One of the most iconic forms of Maya architecture is the pyramid, which was used for religious and ceremonial purposes. Maya pyramids were typically built in a stepped shape with multiple levels and platforms that were decorated with intricate carvings and sculptures. The largest and most impressive Maya pyramid is the Pyramid of Kukulcan at Chichen Itza, which stands over 30 meters tall and features intricate carvings of snakes, jaguars, and other animals.

Another important form of Maya architecture is the temple, which was used for religious and ceremonial purposes. Maya temples were often decorated with intricate carvings and sculptures and were designed to align with the movements of the sun, moon, and stars. Many Maya temples were built on top of pyramids and were accessed via a series of steep steps or ramps.
Maya palaces were also an important form of architecture and were used by the ruling elite for administrative and residential purposes. Maya palaces were often decorated with intricate carvings and murals that depicted scenes from everyday life and featured courtyards, gardens, and other amenities.
The Maya also developed advanced engineering techniques, including the use of corbeled arches, which allowed them to construct vaulted ceilings and other complex structures without the use of mortar or cement. The Maya also developed sophisticated water management systems, including the construction of underground cisterns and reservoirs that allowed them to collect and store water for use during the dry season.
Maya architecture was marked by its impressive scale, intricate detail, and advanced engineering techniques. Today, the architectural achievements of the Maya continue to be celebrated and studied and have had a profound impact on the architectural traditions of Mesoamerica and beyond.
Calendar

The Maya calendar was based on a combination of astronomical observations and mathematical calculations and was used to track time and predict important events such as the arrival of the rainy season, the planting and harvesting of crops, and the occurrence of religious festivals and ceremonies.

The Maya calendar system consisted of three main components:
(a) The Long Count: It was used to track the passage of time over long periods and was based on a series of cycles that began on a specific date in the distant past (known as the “Creation Date”). The Tzolk’in and Haab’ calendars were used to track shorter periods of time and were based on a combination of astronomical observations and mathematical calculations.
It was used to track the passage of time over longer periods and was based on a series of cycles that began on a specific date in the distant past (known as the “Creation Date”) and it was based on a system of units that included the kin (1 day), uinal (20 days), tun (360 days), Katun (7,200 days), and b’ak’tun (144,000 days). Each cycle of the Long Count calendar was believed to have its own unique energy and significance and was associated with important historical and religious events.
(b) The Tzolk’in calendar: It consisted of a 260-day cycle that was divided into 20 “day signs” (represented by various animals, objects, and supernatural beings) and 13 “day numbers” (represented by the numbers 1-13). Each day in the Tzolk’in calendar was identified by a unique combination of a day sign and a day number and was believed to have its own unique energy and significance.
(c) The Haab calendar: It consisted of a 365-day cycle that was divided into 18 “months” of 20 days each, plus a final period of 5 “unlucky” days known as Wayeb’. The Haab calendar was used for agricultural and seasonal purposes and was based on the observation of the solar year and the movement of the sun through the sky.
The Maya calendar system was highly sophisticated and played a central role in the religious and cultural traditions of the Maya civilization. Today, the Maya calendar continues to be studied and celebrated and has had a profound impact on the calendar traditions of Mesoamerica and beyond.
The Maya People Today Facing Modern Challenges

- The Maya people are an indigenous group that inhabits parts of southern Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, and Honduras. They are descendants of the ancient Maya civilization, which was one of the most advanced civilizations in pre-Columbian America. Today, the Maya people face a range of challenges, including poverty, discrimination, environmental degradation, and cultural assimilation. However, they are also working to preserve their cultural heritage and traditions.
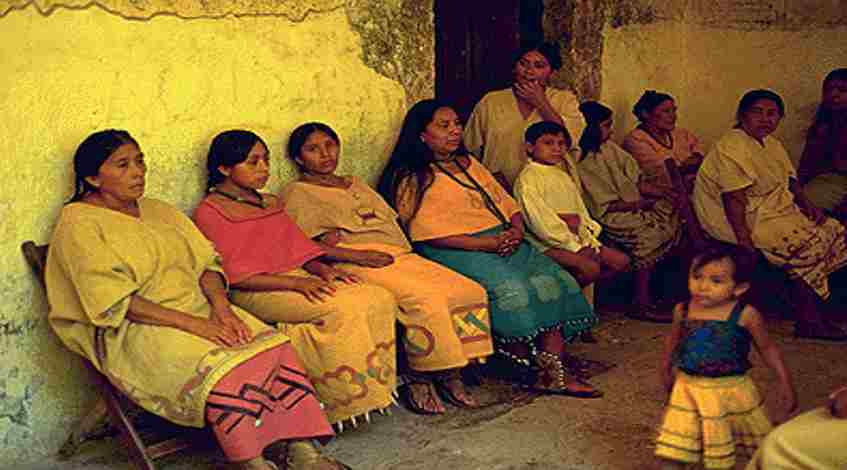

One of the most significant challenges facing the Maya people today is poverty. Many Maya communities are in rural areas, where access to basic services such as healthcare, education, and clean water is limited. Additionally, the agricultural practices of many Maya farmers are often inefficient, which leads to low crop yields and food insecurity. As a result, poverty is endemic in many Maya communities, with high rates of malnutrition, illiteracy, and infant mortality.
Discrimination against the Maya people is also a significant challenge. Historically, the Maya have faced discrimination based on their indigenous identity, language, and culture. This discrimination has led to social and economic marginalization, as well as a loss of land and resources. In recent years, however, there have been efforts to address this discrimination, including legal reforms, community organizing, and cultural revitalization.
Another challenge facing the Maya people is environmental degradation. The Maya have a deep connection to their natural environment, which has sustained them for centuries. However, deforestation, climate change, and resource extraction have all had a negative impact on the environment, threatening the livelihoods of Maya farmers and exacerbating poverty and food insecurity.
Despite these challenges, the Maya people are also working to celebrate and preserve their cultural heritage. Maya traditions and practices, including their language, religion, art, and cuisine, are an important part of their identity and are deeply rooted in their history and culture. In recent years, there has been a renewed interest in Maya culture, both within the Maya communities and among non-Maya people. This has led to a revival of traditional arts and crafts, as well as the creation of new forms of cultural expression.
Maya people today face a range of challenges, including poverty, discrimination, and environmental degradation. However, they are also working to celebrate and preserve their cultural heritage and traditions. By addressing these challenges and working to preserve their cultural identity, the Maya people are building a more sustainable and just future for themselves and their communities.
Top 13 Interesting Facts About The Maya Civilization
The Maya civilization developed a complex writing system that used hieroglyphs to represent words and concepts. This writing system was one of the few independent writing systems in the world and has helped scholars to understand the history and culture of the Maya.
The Maya were skilled astronomers and developed a sophisticated system for observing and tracking the movements of the stars and planets. They used this knowledge to create accurate calendars and to predict astronomical events.
The Maya civilization developed a complex system of mathematics that included the use of a positional numbering system, zero, and a base-20 counting system.
Maya cities were often built around central plazas or squares, which were used for religious and ceremonial purposes.
The Maya civilization was highly stratified, with a ruling class of nobles and priests who controlled the political and religious institutions of society.
The Maya practiced a wide range of religious and ceremonial rituals, including human sacrifice, bloodletting, and the use of hallucinogenic drugs.
The Maya civilization developed a complex system of trade and commerce and established extensive networks of trade routes that connected different regions of Mesoamerica.
Maya women had a high status in society and were involved in many aspects of daily life, including agriculture, trade, and even warfare.
The Maya civilization produced a wide range of artistic and cultural achievements, including intricate carvings, sculptures, and ceramics.
The Maya civilization collapsed around the 9th century CE for reasons that are still debated by scholars but may have included environmental factors such as drought, warfare, and political instability.
The Maya civilization had a complex and unique form of the ball game, which was played using a rubber ball and a narrow court. The game had both religious and sporting significance and was often accompanied by music and ritual performances.
The Maya civilization developed a complex system of water management, which included the construction of reservoirs, cisterns, and canals to collect and store water for agricultural and domestic use.
The Maya civilization left behind a rich legacy of cultural and historical artefacts, including impressive architectural structures, intricate artwork, and sophisticated calendar systems that continue to inspire and fascinate people around the world today.



