- Umang Sagar
- National Issue, Recent article
Kashmir Problem- Historical Injustice Or Misguided Geopolitics

Introduction
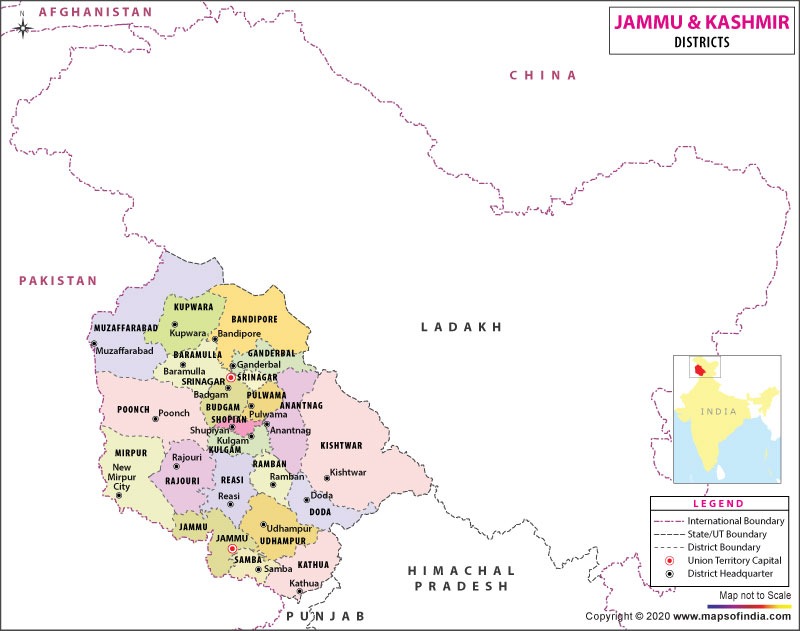
- Jammu and Kashmir lie between 32″ and 37″ North and 73″ and 80″ East. The state of Jammu and Kashmir is created by the British government in 1846. The state of Jammu and Kashmir is a mountain region. The state is confined with four natural regions, in the south lies Jammu, the winter capital of the state, in the center of the happy valley of Kashmir which contains the summer capital, Srinagar, in the north Gilgit, and between Kashmir valley and Tibet is a province of Ladakh. The State covers an area of 2, 22,200 km²and a population of around 1.54 crore. It is situated at the apex of the Indo-Pakistan Sub-continent, Kashmiris of great strategic importance because its east lies Tibet, to N-E Sinkiang, a province of China, to N-W Afghanistan, and a few miles from Afghanistan lies Russian Turkestan. This actual and potential importance of Kashmir has caused the rulers of adjoining countries to cast covetous eyes on it.
Kashmir

- The political history of Kashmir originates with King Gonanda I, but most historians begin their studies with Ashoka, who lived in the 3rd century BC. A constant flow of invasion and dynastic eruption brought to power ruling families was the central feature of the succeeding 2000 years. Shah Mir, the first Muslim ruler ascended the throne in 1342 AD.


- Gazi Khan became the first Chak ruler in 1554. The Next change of importance was the invasion of Kashmir by Emperor Akbar. This great potentate conquered the valley in 1586 by defeating Chak’s and made Srinagar his summer resort. In 1819, Maharaja Ranjit Singh of Punjab invaded Kashmir and was successful in wresting Kashmir from Pathan rulers. For nearly 25 years Kashmir was ruled by a governor appointed by Sikh Darbar at Lahore.



Jammu

- In the middle 18th century, Jammu was ruled by a Dogra chief of Rajput descent named Ranjit Deo. He died in 1780 AD and there ensued a dispute for the succession, the three grand nephews of Ranjit Deo struggling to rule Jammu.


- They were the sons of Kishore Singh’s sons allowed the Sikh Darbar of Lahore to turn Jammu into a dependency. In 1808, Jammu was annexed to the Sikh territory and the three sons of Kishore Singh took services under Raja Ranjit Singh. Pleased with the service of three brothers, Raja Ranjit Singh in 1820 conferred the principality of Jammu on Gulab Singh, the eldest of the three brothers, with the hereditary title of Raja, Bhimber, and Chibal including Poonch were given to Dhyan Singh and Ram Nagar to Suchet Singh. Both Dhyan Singh and Suchet Singh were killed and their jagirs also fell in hands of Gulab Singh. Thus, the whole province of Jammu came under a single ruler, for the first time in the history of Jammu.

Ladakh

- Ladakh has been a tributary of Tibet for centuries. About the middle of the 17th century, 1687, Moghuls with the help of rulers of western Tibet, defeated Mongols and for nearly a century it remained with Moghuls. In 1834 AD Gulab Singh, the rulers of Jammu, sent Zorawar Singh with a force of about 800 to conquer Ladakh. King if Ladakh submitted, agreeing to pay a war indemnity of Rs. 50,000 so Gulab Singh became Raja of Ladakh also.
History

In November 1845, war broke out between Sikhs and the British at Sobraon. The Sikh nobles asked Gulab Singh to help and lead them. But Gulab Singh was not interested in helping Sikhs to whom his allegiance formerly belonged. On 9 March 1846, was concluded a treaty of Lahore between Maharaja Duleep Singh of Lahore and the British Government. It was provided in the treaty that Maharaja Duleep Singh, king of Lahore will cede all his property, all his forts, territories, hills, and plain, situated between river Beas and Sutlej.
Seven days after the conclusion of this treaty, another treaty was signed between the British Government and Raja Gulab Singh on March 16, 1846, at Amritsar. By this treaty of Amritsar – notoriously referred to in State of Jammu and Kashmir as the ‘Sale deed of Kashmir’- the British Government made over to Raja Gulab Singh the State of Jammu and Kashmir. By Article 1 of the Treaty, Kashmir was made over “forever and in independence possession, to Maharaja Gulab Singh and the heirs male of his body” And so, for a total sum of Rupees seventy-five lakhs was sold to Maharaja Gulab Singh, an area of 84,471 sq. miles and 2.5 million people. This transaction between the British Government and Gulab Singh has been a subject of great controversy. The British Government accepted the payment of seventy-five lakhs for transferring the state to Maharaja Gulab Singh, yet Sardar Panikkar, who has written a biography of Maharaja Gulab Singh, had mentioned that there was no sale of Kashmir at all. He bases this contention on the ground that even before this treaty was signed it has been agreed between British Government and the Lahore Darbar that area between River Beas and Sutlej was to be transferred to Raja Gulab Singh. This contention is of course, indisputable, but the treaty between Lahore and the British left it to the British Government to enter into a separate arrangement with Raja Gulab Singh, and that separate arrangement was the payment of rupees seventy-five lakhs for the territory of Kashmir.
Glancy Commission

- After the massacre of July 13, 1931, Maharaja Hari Singh appointed a commission under an Englishman, BJ Glancy, an officer of the Foreign Affairs Ministry of the British India Government, to look into the demands of Muslims. The commission under the leadership of Glancy began its sitting before the end of November in Srinagar. In the middle of January 1932, the commission left Srinagar and moved to Jammu. The commission inquired into the matter, looks into the complaints and grievances of the different communities, and submitted its report to His Highness. Briefly, its recommendations were as follows:
1. Religious:-

There should be no interference with religious observance.
Activities that tend to harass people who want to; who desire to change their religion should be strictly prohibited.
All officers concerned should make it their duty to see that the severest community to which the delinquent belongs.
2. Education:-

Primary Education should be expended and attention should be paid to the provision of a suitable building of primary schools.
Muslims of Jammu requested to have an Islamia High School in Gandoo Di Chawani.
A regular program for the construction of a middle school and high school should be drawn up.
Care should be taken towards Muslim students.
Scholarship should be granted in the name of ‘Muhammadan scholarship’, in high schools and colleges rather than in middle school, to encourage higher education among students.
In the matter of free studentship a due proportion should be allotted to all communities.
The number of Muslim employees should be increased in the teaching department.
A special Muhammadan inspector should be appointed to ‘attend the program of Muhammadan education in all grades.
3. Employment in State Services:-

Muslims who form the great majority of the population should be given a greater share in matters relating to State Services.
Minimum qualification for appointment should not be pitched unnecessarily high.
The policy of His Highness’s Government in the matter of reserving State appointments for State Subjects should be adhered to as far as possible.
Effective measures should be taken in the appointment process and machinery for supervising that system in such a way that no community could take due interest in any subject.
All vacancies should be effectively advertised, an equal appointment should be given to all communities and similar action should be taken as regards all scholarships intended to provide equipment for government services.
By and Large, these recommendations were accepted and a notification to the effect was signed and issued on 10th April 1932.
4. Special Provision to the State:-

- Article 370 of the Indian Constitution provides special provisions concerning the state of Jammu and Kashmir. Article 370 was the legal provision with which Kashmir was assured of autonomy. Under article 370, the president can, with the constitution (Application to Jammu and Kashmir) order 1954, decide provision of the Indian Constitution which could be applied to Jammu and Kashmir with or without modification. The key feature of article 370 was that laws passed by the central government, or central laws passed by parliament didn’t automatically apply to the erstwhile state of Jammu and Kashmir, and it was the right of the State Legislative to approve them by passing a parallel act. Article 35-A of the Indian Constitution empowers the J&K state legislative to define “permanent residents”. The provision mandates that no act of the state legislative coming under the ambit of Article 35-A can be challenged for violating the Indian Constitution or any other law of the land.

- Article 370 as evident from the title of the part, was supposed to be a temporary provision and its applicability was projected to last till the formulation and adoption of the State’s constitution. It restricts parliament’s legislative powers concerning the state of Jammu and Kashmir. Under Article 370 of the Constitution of India, the President has the power of issuing orders for the application of a provision of the constitution of India with modification, exceptions, and amendments in the provisions. The Presidential orders, broadly speaking, deal with the following subject matters:
- Enhancing the jurisdiction of parliament to enact laws in the state of Jammu and Kashmir out of the union list.
- Laws relating to increase or decrease in the areas of the State.
- Exclusion of the State list.
- Provision as regards the decision affecting the disposition of the state of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Provision for the proclamation of emergency.
- Provision for Governor and the Election Commission.
- Transfer of Judges from the High Court of J&K or to the said court.
- Provision for non-application of the amendments carried out by the Parliament of India in the Constitution of India.
- In the year 1954, the Constitution Application Order 1950 was renamed as the Constitution Application Order 1954 and the issuance was the first infringement on the constitutional autonomy of the State of J&K.
Constitution (Application To Jammu And Kashmir) Order, 2019


Constitution Order, 2019 shall come into force once, and shall thereupon supersede the constitution (Application to Jammu and Kashmir) Order, 1954 as amended from time to time.
The President’s order signed by the President of India has not scrapped Article 370. But invoking this very Article, the special status of Jammu and Kashmir has been withdrawn. The move of government gives the constitution of India full applicability over the State of Jammu and Kashmir. Earlier only limited provisions of the Indian Constitution are applicable over J&K such as foreign relations, communication, and defense. Since the Presidential order of August 5 has extended all the provisions of the Constitution to Kashmir, the Fundamental Rights chapter has now been extended and therefore some discriminatory provisions of Article 35-A may not be by prescribed rules. Therefore, the President can also declare this to be inapplicable.
| Before | Now |
| Special power exercised by J&K | No special power now |
| Dual Citizenship | Single Citizenship |
| Separate flag | No separate flag, tricolor will be the only flag |
| RTI not applicable | RTI will be applicable |
| Panchayats did not have any rights | Panchayats will have the same rights as in other states |
| The right to Education was not there | Right to Education will be applicable in the state |
| If a woman from J&K marries out of state, she would lose her citizenship of the state and can’t claim any property in the state. | If a woman marries outside the state, she will have her citizenship and can retain all her rights and property in the state. |
| Duration of Legislative Assembly is for 6 years | Duration for Legislative Assembly in Union Territory of J&K will be 5 years |
| Article 360 (Financial emergency) not applicable | Article 360 is applicable |
| Indian citizens from other states can’t buy land or property in J&K | People from other states will not able to buy land or property in the state. |
| No reservation for minorities such as Hindu and Sikhs | Minorities will be eligible for a 16% reservation |
Jammu And Kashmir Reorganization Act, 2019

- Jammu and Kashmir Reorganization Act, 2019, is an act by the Indian Parliament where the state of J&K was bifurcated into two union territories – Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh. The Union Territory of J&K has a legislative assembly, whereas the Union Territory of Ladakh doesn’t have a Legislative assembly and is administered by the Lieutenant Governor alone.
Geography
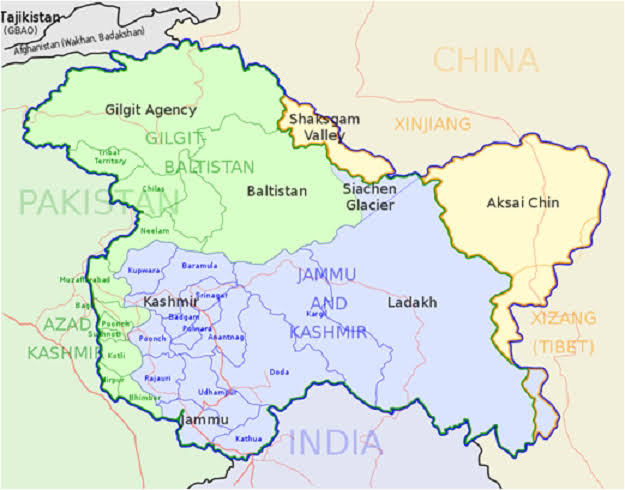
- India and Pakistan both claim ownership over this disputed territory. India and Pakistan were formed as a result of the split of the Indian subcontinent along religious lines. It is also well known that India and Pakistan have very different perspectives on what constitutes a conflict. Pakistan sees it as an unfinished agenda item from the 1947 Partition of the Subcontinent, as well as a matter of allowing Kashmiris the right to self-determination, a principle endorsed by UN Security Council resolutions. On the other hand, India sees it as a territorial dispute. It claims that Jammu and Kashmir are a part of India and that Pakistan is seizing Indian land. Due to the standoff, India now controls two-thirds of Jammu and Kashmir, while Pakistan administers the other third, separated by an UN-recognized ceasefire line. Shaksam Valley and Aksai Chin were both in China. India, Pakistan, China, and the people of Kashmir are the parties to the conflict. India claims the entire old Dogra princely state of Jammu and Kashmir, and currently administers around 43% of the territory, including the majority of Jammu, the Kashmir Valley, Ladakh, and the Siachen Glacier. Pakistan, which controls about 37% of Kashmir, including Azad Kashmir and the northern territories of Gilgit and Baltistan, disputes India’s claim. Furthermore, China holds 20% of Kashmir, including Aksai Chin, which it conquered after the 1962 Sino-Indian War, and the Trans-Karakoram Tract, popularly known as the Shaksam Valley, which Pakistan relinquished in 1963. Today we have a Line of Control (LOC) with Pakistan and a Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China.
LOC & POK

- The Line of Control (LOC) is the demarcation line that separates Kashmir’s two halves. India controls the territory on one side of the border, while Pakistan controls the area on the other which is known by the name Pakistan occupied Kashmir (POK). It is the effective border between the two countries, not a formal international border. Between 1947 and 1948, India and Pakistan fought over Kashmir. When the two countries announced a truce on 1/2 January 1949, the line originally marked the military front. The fronts eventually solidified into a solid barrier. After the Simla Agreement, which was signed on July 3, 1972, it was formally dubbed the Line of Control. Pakistan Occupied Kashmir (POK) is the part of India’s Jammu and Kashmir that Pakistan occupied in 1947. The POK has separated administratively into two parts, known in official languages as Jammu and Kashmir, and Gilgit-Baltistan. In Pakistan, ‘Azad Jammu and Kashmir’ is also known as Azad Kashmir. The President of Pakistan-occupied Kashmir is the Chief Executive Officer, while the Prime Minister is assisted by a Council of Ministers. Pakistan claims to have a self-governing legislature in Occupied Kashmir (POK); however, it is controlled by Pakistan. Pakistan Occupied Kashmir (POK) is a portion of Kashmir that borders Pakistan’s Punjab province in the northwest, Afghanistan’s Wakhan corridor, China’s Xinjiang region, and Indian Kashmir in the east. If Gilgit-Baltistan is removed, Azad Kashmir covers 13,300 square kilometers (about three times the size of Indian Kashmir) and has a population of 52 lacs. Muzaffarabad is the capital of Azad Kashmir, which contains 10 districts, 33 tehsils, and 182 federal councils. Mirpur, Bhimbar, Kotli, Muzaffarabad, Bagh, Neelam, Rawalakot, and Sudhanoti are the eight districts in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir’s southern region. Pakistan gave up a portion of Pakistan-occupied Kashmir’s Hunza-Gilgit, the Shaksgam Valley, the Raksam region, and Baltistan to China in 1963. This territory is known as the Trans-Karakoram Tract or ceded area.
LAC & Aksai Chin
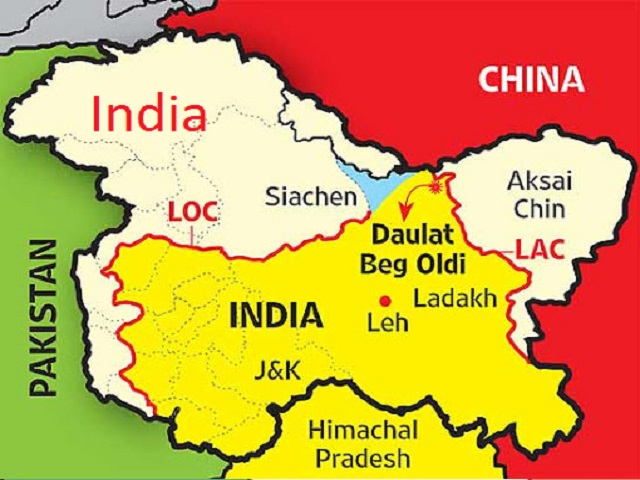
- Another distinct cease-fire line divides the Indian-controlled sector of Kashmir from the Chinese-controlled Aksai Chin region. This is known as the Line of Actual Control (LAC) and is located further east. Although India controls the other side, China considers this line to be part of its Pakistani border. China and Pakistan have reached an agreement on a border, but India has yet to do so. It subsequently referred to the line formed after the 1962 Sino-Indian war and is part of the Sino-Indian border disputes. In the Sino-Indian boundary dispute, it differs from the borders claimed by each country. Indian claims encompass the entire Aksai Chin region, whereas Chinese claims encompass Arunachal Pradesh. The term “actual control” does not apply to these claims.
In general, the LAC is divided into three sectors:
- the western section, which runs between India’s Ladakh and China’s Tibet and Xinjiang autonomous areas. The 2020 China–India conflicts took place in this sector.
- Between Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh on the Indian side and the Tibet autonomous area on the Chinese side is a midway, generally undisputed sector.
- Arunachal Pradesh on the Indian side and Tibet Autonomous Region on the Chinese side make up the eastern sector. The McMahon Line is frequently followed in this sector.
After the 1962 Sino-Indian War, the term “Line of Actual Control” was limited to the western sector’s boundaries, but by the 1990s, it had expanded to include the entire de facto border.
Role Of India


Jammu and Kashmir, a Union Territory of India caught in the cross-fire of civil strife for several years, has witnessed tremendous development in the last year with new highways, state of art hospital facilities, educational institutions, and resorts coming up in different parts. These high-profile projects will remain to be completed, but surety is shown from the government that these projects will be completed soon and after the completion of these development projects, they will link far-flung villages with the mainstream, connect millions of people to better opportunities, and prosperity and transform Kashmir into a destination for tourists as well as entrepreneurs. The region is witnessing rapid growth a year after the government of India revoked special provisions of the state and also announced its division into two Union Territories – Ladakh and Jammu &Kashmir. A statement is released by the Indian Government said that the changes which are made in Jammu and Kashmir have taken place with the extraordinary participation of people. Indian Government had released many programs which focus on youth development and their growth and the Economic Status of Jammu and Kashmir.
The statement said that the discriminatory and unjust laws were either repealed or modified and more than 170 central laws were made applicable which include progressive laws like the right to protect scheduled castes, scheduled tribes, forest dwellers, juveniles, and the ages. The Indian Government is also focusing on schemes counts for individual development such as scholarships or houses, in the Union Territory of J&K and Ladakh, is an effort for the development on an individual basis. Similarly, the government is providing people with houses and a total target of around 37,000 is already achieved by the government. The Government has also been decided that the schemes such as scholarships, gas connections under the Ujjwala program, and housing for the poor must start with a 100 percent offtake with complete enrolment and funding. The situation in Jammu and Kashmir is calm and has returned to normalcy as the Indian Government has been extending all support to help the people with new welfare projects and plans. A statement released by the Indian Ministry of Foreign Affairs said that “lives of hundreds of thousands of men and women across the Kashmir valley have been transforming for the better by innovative and diligently implemented programs adopted by the new union territory”. These include schemes for the old-age pension, merit scholarships for students, supplementary nutrition for lactating mothers and pregnant women, and for keeping thousands of children safe and healthy staying at public and private orphanages,” said the statement. There is in addition to a free health insurance cover of rupees 5 lakh per family per year on a floater basis and there would be no restriction on family size, age, or gender.

- During the COVID 19 pandemic, local authorities have been quick to procure masks, sanitizers, and hand wash items for children with special grants. A special committee has also been set up to monitor the health of children and ensure easy access to medical care and healthy nutrition.

The Government of Indian assists every Indian state using loans and grants, Jammu and Kashmir get 905 of the money as a grant and 10% as a loan. The rest of it was 70% grants and 30% as a loan. In the year 2001, the GDP of India was $494 Billion. In this GDP the contribution from Kashmir Valley was less than 1%. The Central Government has funded a sum of Rs 25,000 Crore for the development project in the valley. Excluding this, the state of Jammu and Kashmir receives grants from the Central amounting to Rs 1.51.321 Crore. This amount excludes the expenditure done on railways, roads, and power projects. J7K annual income is Rs6,500 Crore while the state’s annual liability on staff salaries is Rs 13,500 Crore. During the 2014 Kashmir Floods. Rs 1900 Crore aid was provided to the state.
The Government of Dubai, one of the UAE’s seven emirates, linked an agreement with Indian to ramp up infrastructure investment in Jammu and Kashmir. Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s government said the deal will see Dubai building infrastructure in the troubled region including industrial parks, IT towers, multi-purpose towers, logistics centres, a medical college, and a specialized hospital. Sultan Ahmed Bin Sulayem, chairman, and CEO of DP world Dubai told the media in Srinagar. “We are committed to connecting J&K to the rest of India. We know how to do that, we know the obstacles.”
The state of Jammu and Kashmir is defined as it existed on or before the invasion of Pakistan on 22nd October 1947. This includes the present territory of Pak-occupied Kashmir, Gilgit, Baltistan, Jammu, Ladakh, and Kashmir valley. As nearly one-third of the state of Jammu and Kashmir is still under the occupation of Pakistan, it is noncompliance of conditions leading to the plebiscite.
Kashmir’s first political party, the Muslim Conference, was formed in 1925, with Sheikh Abdullah as president. Later, in 1938, it was renamed as National Conference. The National Conference was a secular organization and had a long association with Congress. After Maharaja Hari Singh signed an ‘Instrument of Accession’ with the Government of India, Sheikh Abdullah took over as the Prime Minister of the state of J&K in March 1948. Sheikh Abdullah was against J&K joining Pakistan. The pro-Indian authorities dismissed the state government and arrested Prime Minister Sheikh Abdullah. The new Jammu and Kashmir government was satisfied and agreed to the accession to India. In 1957, Kashmir was formally incorporated into the Indian Union.
When Sheikh Abdulla takes over as Prime Minister, he initiated major land reforms and other policies which benefited ordinary people. But there was a growing difference between him and the Central Government about his position on Kashmir’s status. He was dismissed in 1953 and kept in detention for several years. During most of the period between 1953 and 1974, the congress party exercised a lot of influence on the politics of the state. Congress gained direct control over the government in the state. In the meanwhile, there were several attempts to reach an agreement between Sheikh Abdullah and the Government of India. Finally, in 1974 Indira Gandhi reached an agreement with Sheikh Abdullah and he became the Chief Minister of the State
Ever since 1947, Kashmir remained a major issue of conflict between India and Pakistan. Pakistan always attempts to occupy Kashmir. Pakistan always says that Kashmir is their territory and had taken many attempts to occupy Kashmir. The conflict resulted in three main wars between India and Pakistan – 1947, 1965, and 1971. Pakistan was not only the illegal occupant of the Kashmir region. China too started claiming parts of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir. By the 1950s, China started to gradually occupy eastern Kashmir (Aksai Chin). In 1962, India fought a war with China over its encroachments, however, China defeated India.
Conclusion

- Jammu and Kashmir is a beautiful state, great tourist gathering place. No doubt in the fact that apart from having so beautiful in nature, the state and its people and gone through really bad time, they had faced many difficulties in their life, some of them struggle every day to leave. But apart from all this many people leave very happy and fruitful life over there. Jammu and Kashmir is a tourists attraction place which can generate a lot of revenue and after removing Article 370 and declaring the state as equal as other states are, the growth process in the state developed lot and attracted many big investors over there, which will provide employment, great opportunities to the people of Jammu and Kashmir. Both Central and State government is working in the development process of the state. Government is launching many new schemes and policies to help the people of Jammu and Kashmir to leave a better and healthy life. Even though Article 370 is removed from the constitution and there is no special rights provided to the state of Jammu and Kashmir, still there are people who want special right for the people of the state and wants themselves to be treated differently from others people. Now Jammu and Kashmir is part of India and will be treated as equal to other states, people of Jammu and Kashmir and people of other states will be free to move throughout the state and can easily explore the state.
Top 13 Interesting Facts
There are seven Union Territories specified under part 2 of the First Schedule to the Constitution of India, viz. Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Lakshadweep, Delhi, and Puducherry. Except for Delhi and Puducherry, UTs did not have their own legislative until now. But now the state of Jammu and Kashmir has also been added along with Delhi and Puducherry to be a UT with a legislature.
Srinagar was founded was emperor Ashoka and not the Mughal emperor Jahangir.
The Pir Panjal railway tunnel, or the Banihal railway tunnel, located in Jammu and Kashmir, is India’s longest railway tunnel. It is 11,215 km long, 8.4m wide and 7.39m tall.
Kawa, traditional green tea with spices and almonds, is consumed all through the day in Kashmir. Apart from Kawa or Kehwa, sheer chai or gulabi chai is the traditional beverage of Kashmir. It is pink in color and salty in taste.
Amarnath cave in Jammu and Kashmir has natural Shiv Lingam made of ice which is over 5000 years old. According to a popular legend, the Amarnath cave was discovered by a Muslim shepherd, Buta Malik.
India’s first floating post office was built on a household at the western edge of Dal Lake in Srinagar.
Houseboats first appeared in the 1800s in Dal Lake by Pandit Naraindas to house English visitors.
Vaishno Devi Temple in Katra, Jammu which is visited by over 81 lakh pilgrims every year, has been awarded the cleanest religious place award.
Wular Lake is located in Jammu and Kashmir, is one of the largest freshwater lakes in Asia.
The library in Raghunath Temple in Jammu house over 6000 manuscripts in several Indian Languages.
Turtuk village, Located in Ladakh, is the last village in India where tourism is permitted.
The famous Bollywood movie, 3 idiots, was shot at Pangong Tso. Others parts of Ladakh have also been the site of the shooting of several Bollywood movies.
13. While traveling in Ladakh, you will come across a lot of quirky road signs like,” Don’t be a Gama in the land of Lama”, “Darling I like you but not so fast”, “Love the neighbor but not while driving”, “After whisky driving risky”.



