- Umang Sagar
- Recent article
Integrated Plant Nutrition Management (IPNM) Bill
Introduction
The term IPNM is used in these guidelines to refer to “land husbandry” in a much broader and more holistic sense. Thus, it encompasses soil, nutrient, water, crop, and vegetation management strategies that are adapted to a specific cropping and agricultural system and are used to increase and sustain soil fertility and land production while also lowering environmental degradation.
Integrated Plant Nutrient Management strives to improve the physical, chemical, biological, and hydrological aspects of the soil to increase agricultural productivity while avoiding land degradation. There is now a growing understanding that IPNM can not only deliver concrete benefits in terms of higher yields but also conserve the soil resource itself in an almost imperceptible way.
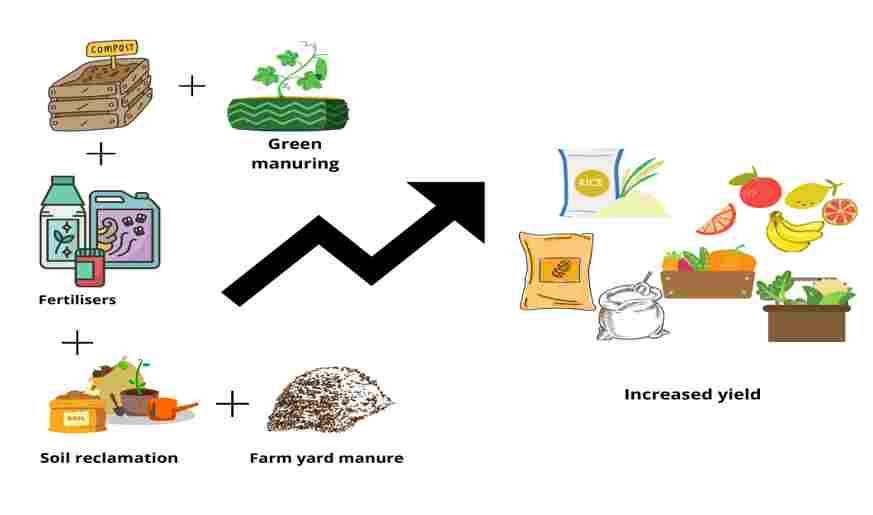
The field-level management practices considered under the heading of IPNM would include the use of farmyard manure, natural and mineral fertilizers, soil amendments, crop residues and farm wastes, agroforestry and tillage practices, green manures, cover crops, legumes, intercropping, crop rotations, fallows, irrigation, drainage, plus a variety of other agronomic, vegetative and structural measures designed to conserve both water and soil.
History
- Many of the requirements in the Integrated Plant Nutrition Management Bill, 2022 come from the current Fertilizer Control Order, 1985, and the Fertilizer Movement Control Order, 1973.
1. Fertilizer Control Order (1985):
The Central Government may set maximum prices or rates at which any fertilizer may be sold by a dealer, manufacturer, importer, or agency to regulate equitable fertilizer distribution and make fertilizers available at fair pricing.
2. Fertilizer Movement Control Order(1973):
The Fertilizer Movement Control Order, signed in 1973, regulates the movement of fertilizers in which No one may export, seek to export, or aid with the export of fertilizer from any state.
Objectives
The bill aims to encourage the development and long-term usage of balanced fertilizers to ensure India’s food and nutritional security while also protecting the environment and soil health.
It also intends to “simplify the process of fertilizer manufacturing, production, distribution, and price management,” with the declared goal of “increasing the ease of doing business” while improving outcomes.
A sectoral regulator, the Integrated Plant Nutrition Management Authority of India, will be established to give effect to the rules. States can also designate State Fertiliser Controllers and Fertiliser Inspectors, who can perform spontaneous inspections of industry and trade and have the authority to search, seize, and confiscate.
Government Policies
1. New Pricing Scheme (NPS) of 2010: The subsidy is given to the industry equivalent to a differential amount of COC (Cost of Cultivation) and selling price to farmers.
2. Nutrient Based Subsidy(NBS) policy, 2010: Subsidy fixed on the weight of different macro/micronutrients (N, P, K, S, etc) contained in the fertilizer.
Manufacturers and Marketers are allowed to fix the Maximum Retail Price (MRP) at a reasonable rate.
3. Neem Coated Urea Policy, 2015: It mandates fertilizer manufacturers for neem coating, to address the issue of black marketing and overuse of the fertilizers.
4. Gas Pooling Policy, 2015: All units will get uniform prices of gas. Which also includes all the selling attributes of Compost.
5. New Urea Policy, 2015: Free transportation of Phosphorus and Potassium fertilizer according to industrial demand for 4 financial years.
IPNM Include
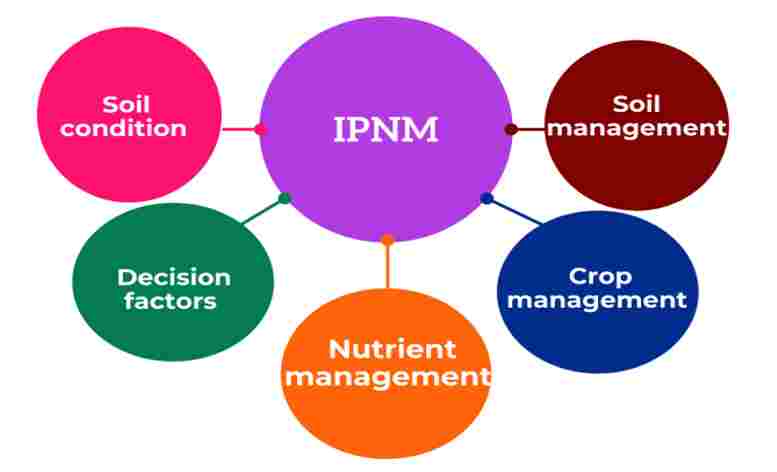
Soil conditions include soil texture and structure, soil PH, loss of organic matter, soil erosion, nutrient availability, micronutrient availability, etc.
Decision factors include market access, labor availability, social conditions, natural resources, traditional knowledge/skills, etc.
Nutrient management includes the use of FYM / compost / green manure. And also includes organic matter and crop residue management, stabilizing microbial population, chemical fertilizer, household waste
Crop management includes crop rotation, estimation of yield, Intercropping system, planting time and methods, moisture condition, and management of weeds, insects/pests efficiently.
Soil management includes decreasing leaching loss, balancing the soil, increasing availability of nutrients, tillage management, etc.
1. Integrated plant nutrition management bill
The central government has proposed a law to empower it to fix the maximum selling price of fertilizers and control their quality and distribution.
2. The state of the Indian fertilizer industry
There are many small and marginal farmers in India. However, it is frequently plagued by poor quality and productivity. Crops are mainly rain-fed and are cultivated on a single piece of land over time. Thus, it decreases soil fertility in many regions. As a result, increasing quantities of nitrogen fertilizers have been used across India. Because of this, the Indian government has brought economic reforms and ensured that fertilizers are available at affordable prices to increase productivity.
Conclusion
- The Bill proposes to set up an Integrated Plant Nutrition Management Authority. The main objective of the law is to ensure good quality fertilizers at low rates. There are many government schemes and policies to facilitate the ease buy of farmers. The central government has wanted suggestions from the public regarding this bill. The bill includes measures that would make it illegal to manufacture and distribute fertilizers that do not have a valid registration and the misleading marketing shall be prohibited. Those who sell counterfeit fertilizer products will be punished.
Top 13 Interesting Facts About IPNM
This is a draft bill proposed by the central government, which is open to public suggestions.
The Centre has proposed a law that empowers it to fix the maximum selling price of fertilizers and control their quality as well as distribution in the country.
Because of the variable nature of international raw material pricing, the fertilizer industry has struggled to stay stable. As a result, farmers face severe fertilizer shortages, to help the industry grow quicker and facilitate fertilizer needs, the government has proposed the Integrated Plant Nutrition Management Bill, 2022.
The Alliance for Sustainable and Holistic Agriculture (ASHA) has opposed some provisions in the Draft Integrated Plant Nutrition Management Bill, 2022 declaring that they take away the rights of States and farmers.
India is self-sufficient in the case of Nitrogen-based fertilizers.
India is the 2nd largest consumer of Urea fertilizers after China.
India ranks 2nd in the production of nitrogenous fertilizers and 3rd in phosphatic fertilizers.
Apart from importing crude and manufactured fertilizers, the country is heavily dependent on importing raw materials such as rock phosphate, ammonia, and phosphoric acid.
The bill also focuses on tightening the government’s existing considerable restrictions over the fertilizers industry by establishing an extensive Inspector Raj to oversee it.
The Bill gives the Centre broad authority to set maximum selling prices for fertilizers while also allowing it to set various pricing for different regions and customers.
The Centre will have the authority to impose restrictions on the movement of fertilizers between states and to set limits on the amount of fertilizer a company can sell in each state.
The sectoral regulator has been given broad powers to search, seize, and confiscate in the shape of the Integrated Plant Nutrition Management Authority of India, State Controllers of Fertilisers, and Fertiliser Inspectors.
The fertilizer industry understands that the complicated inspector Raj will encourage rent-seeking and make managing business more difficult.




