Introduction
- Alcohol is a beverage that is consumed by many people that contains ethanol. The person who drinks alcohol is referred to as a drinker or alcoholic. Alcohol is a substance to which drinking repeatedly easily causes addiction. Though they know it’s dangerous to health, despite their age many people are consuming it. This drink may give you pleasure on starting but finally end you and your family in severe physical and mental damage on addiction to it. Alcohol abuse has been destroying many families’ peace, happiness, joy, and dreams. Family members of alcoholics are experiencing a lot of mental suffering due to their loved one’s alcohol abuse. Few alcoholics’ actions are leading to violent abuse of their families, breaking many relationships, spooling their children’s education and future, financial problems, physical and emotional issues, and sometimes even the death of a person. Alcohol consumption contributes to 3 million deaths each year globally as well as to the disabilities and poor health of millions of people. Overall, the harmful use of alcohol is responsible for 5.1% of the global burden of disease. WHO is currently developing an action plan (2022–2030) to effectively implement the global strategy to reduce the harmful use of alcohol as a public health priority.
Types Of Alcholic Beverages

- Based on their method of preparation alcohols are usually classified into 3 categories. They include:
- Malted liquors
- Wines
- Spirits
1. Malted liquors:
- These are prepared by the fermentation of the germinating cereals.
- These are in undistilled form.
- The percentage of alcohol ranges between 3-6%, but nowadays strong beers are available up to 10%.
- Examples are beer, stout.
2. Wines:
- These are prepared by the fermentation of the natural sugars in grapes and other fruits.
- These are in undistilled form.
- The percentage of alcohol ranges between 9-22%.
- Examples are lighter wines (9-12%) are Claret and cider. Effervescent wines (12-16%) are Champagne. Fortified wines (16-22%) are port, sherry.
3. Spirits:
- These are distilled after fermentation.
- These are in distilled form.
- The percentage of alcohol ranges between 40-50%.
- Examples are rum, gin, whiskey, vodka, etc.
Alcohol Consumption In The World And India

1. Alcohol consumption in India
- Alcohol consumption in India has slightly gone up among men and women in the last decades.
- According to 2021 Alcohol consumption in India; Arunachal Pradesh ranks the 1st in the population who drinks alcohol most.
- Next followed by Sikkim in 2nd place, Telangana in 3rd place, Jharkhand in 4th place and Chhattisgarh in 5th The alcoholics are less in Gujarat and Jammu and Kashmir.
2. Alcohol consumption in the world
Looking at the amount of alcohol consumed per person aged 15 years or older, Seychelles is in first place with around 20.5 litres of alcohol drunk per person per year, followed by Uganda with Second place at about 15 litres per year, followed by the Czech Republic with third place about 14.45 litres, Lithuania in fourth place with 13.22 litres and Luxembourg with the fifth place with about 12.94 litres per year.
3. Top 10 Countries’ Alcohol Consumption
- Seychelles: 50 litres
- Uganda: 09 litres
- Czech Republic: 45 litres
- Lithuania: 22 litres
- Luxembourg: 94 litres
- Germany: 91 litres
- Ireland: 88 litres
- Latvia: 77 litres
- Spain: 72 litres
- Bulgaria: 65 litres.
Legal Age For Alcohol Consumption In Different States Of India

- There is a fixed age for drinking alcohol and below that age comes under crime. The age that is required to drink alcohol is known as the Legal drinking age. The legal drinking age differs from one state to another state. For the majority of the states, 21 years is the legal drinking age and for a few it’s 18,23,25 and it’s banned in few states.
1. States with Legal drinking age – of 21 years
- Uttarakhand
- Haryana
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- Odisha
- Jharkhand
- West Bengal
- Meghalaya
- Assam
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Manipur
- Telangana
- Andhra Pradesh
- Tamilnadu
2. States with Legal drinking age – 18 years
- Ladakh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Himachal Pradesh
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Karnataka
3. States with Legal drinking age – 21 years
- Uttarakhand
- Haryana
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- Odisha
- Jharkhand
- West Bengal
- Meghalaya
- Assam
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Manipur
- Telangana
- Andhra Pradesh
- Tamilnadu
4. States with Legal drinking age – 23 years
- Kerala
5. States with Legal drinking age – 25 years
- Punjab
- Maharashtra (but for beer it’s 21)
6. States where alcohol is banned legally
- Mizoram
- Bihar
- Nagaland
- Gujarat
Effects Of Alcohol On Different Organs
Central Nervous System (brain and spinal cord):
Alcohol depresses various functions of the central nervous system. mainly it depresses the Inhibitory mechanisms in the brain – so the person becomes more talkative and hyperactive.
- Depending on the amount of alcohol, a person drinks and the amount of alcohol concentration in the blood, the person’s effects depend in the central nervous system; Hangover on the next day.

Alcohol concentration in blood | Effects |
20mg% | Relaxed |
30 mg% | Excessive talking |
50 mg% | Besides talking excessively, but in controlled |
50-100 mg% | Careless and freer |
100-200 mg% | Uncoordinated movements with slurred speech |
200-300 mg% | Intoxicated (fully drunk) but still mobile |
300-400 mg% | Stupor |
Greater than 400 mg% | Comma and sometimes death |
1. Cardio Vascular System (Heart and blood vessels):
When alcohol is taken in a moderate amounts, it causes an increase in BP (hypertension) and tachycardia (increased heart rate).
- When alcohol is taken in large amounts, it causes a fall in BP (hypotension).
2. Respiratory System:
- When alcohol is consumed in large doses it directly depresses the respiratory center causing difficulty in breathing, increased respiratory rate, and the person is unable to breathe properly.
3. Liver:-
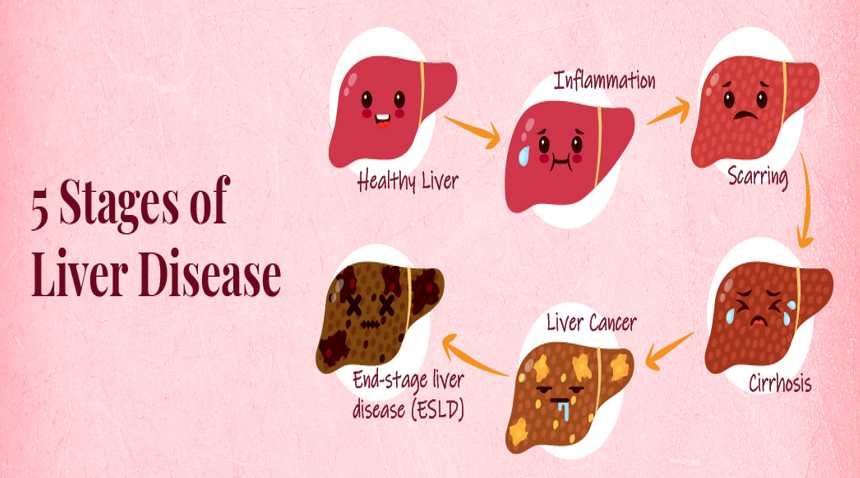
The liver is the most affected organ in the body due to alcohol consumption.
When the alcohol enters the liver; Alcohol is converted into Acetaldehyde (toxic product) by the alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme, alcohol dehydrogenase is present in sufficient amounts in the body so that it can easily convert alcohol to acetaldehyde.
The Acetaldehyde is converted into Acetate, water, and carbon dioxide in the presence of the enzyme Aldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme. but the Aldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme is present in fewer amounts in our body so it’s ok when the person drinks in small amounts and when the person drinks in a large amount the acetaldehyde cannot be converted into Acetate, water, and carbon dioxide and remains as acetaldehyde in the cells of the liver.
The acetaldehyde presents in the liver cells, damages each and every cell of the liver and causes inflammation and scarring of the liver leading to Liver Cirrhosis and in cases of more and more alcohol consumption leads to complete Liver damage.
Alcohol
⇓ (Alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme)
Acetaldehyde (toxic product)
⇓ (Aldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme)
Acetate + water+ carbon dioxide
- The alcohol moves the fat present in the peripheral body parts into the liver. This leads to more and more fat accumulation in the liver causing Fatty Liver.

4. Digestive system:
- Low concentrations of alcohol stimulate the overproduction of gastric secretions leading to gastritis.
- High concentrations of alcohol inhibit gastric secretions causing indigestion, nausea, and vomiting.

5. Muscles:
- On taking alcohol in low doses causes fatigue.
- On taking alcohol in high doses and long-term alcohol consumption causes decreased synthesis of muscle protein thereby leading to weakness, muscle pain and myopathy.
6. Kidneys:
- Alcohol consumption causes Diuresis (more urine excretion) by inhibiting ADH hormone secretions.
- More alcohol consumption leads to more urine excretion which further may cause dehydration, fluid and electrolyte distribution.
7. Male sex organ:
- Alcohol is an Aphrodisiac (stimulates sex drive) substance.
- Alcohol may provoke sex drive but it will decrease both erection and ejection.
- Chronic drinkers may develop erectile dysfunction, impotence, and infertility.
8. Bone marrow:
- Bone marrow produces red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells.
- Alcohol on chronic use, suppress the bone marrow.
- Thereby reducing the production of Red Blood Cells causing Anaemia, reducing White Blood Cells causing immune deficiency, and decreasing Platelets having bleeding diseases.
9. Pregnancy:
- Alcohol consumption during pregnancy is very hazardous and alcohol should strictly avoid during pregnancy.
- Alcohol produces Foetal alcohol syndrome.
- Foetal alcohol syndrome in mental retardation, slow growth of baby, small head, facial abnormalities.

Types Of Alcohol Poisonings
Alcohol poisoning is an overdose of alcohol or too much alcohol concentration in the blood.
Alcohol poisoning is of two types:
1. Acute Alcohol poisoning:
- It is due to sudden and excessive drinking of alcohol within a short period of time.
- The signs and symptoms noticed are a fall in BP, gastritis, fall in sugar, collapse, respiratory depression, coma and sometimes death.
2. Chronic Alcohol poisoning:
- It is due to long-term, gradual and excessive drinking of alcohol within a long period of time like for many years.
- Tolerance, physical and mental dependence on alcohol.
- It has many signs and symptoms like Whole body: blackout, dizziness, shakiness, craving, or sweating; Behavioural: aggression, agitation, compulsive behaviour, self-destructive behaviour, or lack of restraint; Mood: anxiety, euphoria, general discontent, guilt, or loneliness; Gastrointestinal: nausea or vomiting; Psychological: delirium or fear.
Treatment For Alcohol Poisonings

The treatment options differ for acute alcohol poisoning and chronic alcohol poisoning.
1. Treatment options in Acute Alcohol Poisoning:
- The first choice of drug in acute poisoning is Fomepizole it blocks the alcohol dehydrogenase which blocks the conversion of Alcohol into Acetaldehyde.
- Check for Airways, Breathing, and circulation, and in case of any problems, correct them.
- Treat Acidosis with sodium bicarbonate.
- Induce vomiting to bring out the alcohol present in the digestive tract.
- Gastric larvage.
- Dialysis, if necessary, in severe cases.
2. Treatment options in Acute Alcohol Poisoning:
- Treating chronic drinkers is the toughest task. The main aim of the treatment is to decrease the tolerance, dependence, and cravings for alcohol.
- Naltrexone will reduce the craving for alcohol by blocking the opioid receptors.
- Substitutional therapy; giving a controlled dose of diazepam will produce sedation and depression the same as alcohol.
- Acamprosate also reduces the pleasuring effect of alcohol.
- Finally, Disulfiram drug is given as Aversion therapy causes many side effects and the person suffers a lot and becomes totally afraid of drinking alcohol.
- Besides this motivational, emotional, and psychological counseling plays a key role in changing the person to stop drinking.
Strictly Avoid Alcohol Consmuption In These Diseases

- Strictly avoid alcohol in the following conditions:
- In Pregnancy because it causes birth defects and anomalies.
- Peptic ulcer because it further worsens the disease by increasing the gastric secretion and making the ulcer more and more severe.
- In Heart burn or GERD, it further worsens the disease by increasing gastric secretion.
- Epilepsy (fids) because it causes fids.
- In Liver diseases becomes liver is the first most affected organ and alcohol consumption during liver diseases will completely destroy each and every cell of the liver leading to complete Liver Failure.
- Hyperglycaemia, because it further increases the glucose level and produces complications like Retinopathy, Neuropathy, and Nephropathy.
Strictly Avoid Alcohol While Using These Medications
Strictly avoid alcohol while using the following medications:
- When you are using medicines to treat anxiety (Anxiolytics drugs).
- When you are using medicines to treat depression (Anti-depressants drugs).
- When you are using medicines to treat sleep diseases (hypnotic drugs and opioid drugs).
- When you are using medicines to treat allergic conditions (Anti-histamines).
- When you are using medicines to treat infections or diseases caused by bacteria (Antibiotics like Cephalosporins, cefeotan, cefoperazine.
- When you are using medicines to treat diabetes (Anti-diabetic drugs like Sulfonylureas like Gliclazide, glipizide, glibenclamide and glimepiride).
- When you are using medicines to treat fungal diseases (anti-fungal drug like Griseofulvin).
- When you are using medicines to treat cancer (Anti-cancer drugs like procarbazine).
- Disulfiram drug to treat chronic alcoholism.
Clinical Use Of Alcohol
- Alcohol is used as disinfectant.
- Alcohol is used as Anti-sceptic.
- Alcohol is used as antidote in methyl poisoning.
- Alcohol is used in mouthwashes.
- Alcohol sponging is used to wipe the body of a fever.
- Alcohol is used in scents.
Guidelines For Safe Drinking
The common question to all doctors by all alcoholics is to advise them on safe ways of drinking. To answer this many official agencies, Physician organisations, and alcoholism experts came up with Safe Drinking Guidelines.
They are:
- On an average 1-2 drinks per day is usually safe.
- Not more than 3 drinks on occasions.
- Consumption with greater than 3 drinks is associated with adverse health effects.
- Don’t engage or drive into hazardous activates after drinking.
- Don’t drink if an interacting drug has been taken.
- Avoid strictly in case of contraindications.
1 drink= 400ml of beer
=150ml of wine
= 50ml of spirit
One And Only Benefit Of Drinking Alcohol
“Regular intake of small doses of alcohol i.e.; 1-2 drinks have been found to increase good cholesterol (HDL) levels thereby acting as Cardiac protectant by lowering the risk of heart diseases.”
But alcohol is not the one and only choice to increase good cholesterol levels, there are many foods like almonds, walnuts, egg, olive oil, fatty fish, grapes, dark chocolate, oats, fresh green leafy vegetables, soya foods, etc can increase HDL levels and act as a cardiac protectant.
Regular intake of alcohol will be associated with addiction to it and can cause many adverse effects on different organs.
So, by measuring the risk-to-benefit ratio – Alcohol consumption is having many risks besides a single benefit. So, it’s better to off alcohol consumption for a healthier and happier life.
Top 13 Interesting Facts About Alcohol
Alcohol consumption contributes to 3 million deaths each year globally.
Alcohol is the leading risk factor for premature mortality.
The harmful use of alcohol is a causal factor for more than 200 diseases.
Alcohol is not digested by the body; instead, it gets absorbed directly into the bloodstream.
Approximately 600 grapes are utilized in the production of one bottle of wine.
Did you know that there is more alcohol in mouthwash than in wine?
Alcohol consumption for kids over 5 years is legal in the UK as long as they are drinking at home or on other private premises.
Belarus country drinks the most liters of pure alcohol than any other country in the world.
Raising awareness of the health and social problems for individuals and society caused by alcohol can change at least a few people.
WHO is currently developing an action plan (2022–2030) to effectively implement the global strategy to reduce the harmful use of alcohol as a public health priority.
Moderate alcohol consumption can increase your HDL level and acts as a cardiac protectant.
Having red wine in moderation is a healthier choice than other alcoholic drinks.
Alcohol in low doses shows more effective in women because of the presence of low Alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme in women when compared to men.