
Introduction
State Police Services (SPS) stand as a resolute bastion of law and order, entrusted with the sacred duty of safeguarding the harmony and security of their respective states in the vibrant tapestry of India. Empowered by the state governments and driven by an unwavering commitment to justice, these dedicated law enforcement officers play a commendable and vital role in upholding the fabric of society.
With a clear mandate to preserve the sanctity of law and order, SPS officers emerge through a rigorous and diligent appointment process conducted by the State Public Service Commission (PSC). It is through this gateway of merit and dedication that they assume their essential roles and responsibilities.
As guiding figures for their fellow law enforcement brethren and other personnel, SPS officers embody the embodiment of valour and virtue. Their hearts resonate with the noble purpose of ensuring the safety and security of the public they serve while holding high the torch of justice in every action they take.
Each state boasts its distinctive State Police Service, bearing names like Tamil Nadu Police Service (TPS), Andhra Pradesh Police Service (APPS), Assam Police Service (APS), Bihar Police Service (BPS), and a multitude of others. Yet, united in their commitment, these diverse names collectively refer to a force dedicated to shielding public safety and upholding the principles of righteousness within their respective jurisdictions.
Entrusted with considerable authority and responsibility, these gazetted officers of the state government epitomize the embodiment of service and selflessness. They operate solely within the boundaries of their states, humbly aware of their place in the hierarchical order, standing beneath the esteemed Indian Police Service (IPS) officers, yet commanding the reverence of those in the State Police Subordinate Service.
The dutiful SPS officers bear the mantle of overseeing the work of their subordinate service officers and other law enforcement personnel at lower echelons. Elevated to the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police (DySP) upon appointment, they embrace the mantle of leadership and embrace a myriad of crucial roles. Whether as Circle Officers (COs)/ Sub-divisional Police Officers (SDPOs), Deputy Superintendents of Police (DySPs), Additional Superintendents of Police (Addl. SPs), or Superintendents of Police (SPs), the specific responsibilities assigned to them are woven into the fabric of their rank and the invaluable experience they possess.
State Police Services harmonize with the communities they serve, forging bonds of trust and confidence. They stand as a beacon of hope, reminding us all that in a world where chaos may seek to disrupt, there will always be those willing to rise, to protect, and to serve—the selfless guardians of peace and the true sentinels of society.
Recruitment Process For State Police Services (SPS)

The recruitment process for State Police Services (SPS) in India is a rigorous and multifaceted journey that seeks to identify individuals with the passion, commitment, and integrity to uphold law and order within their respective states. It presents aspiring candidates with two distinct paths to embark on—the direct recruitment process and the promotion-based system. Both pathways hold their unique challenges and opportunities, shaping officers who will stand as the guardians of justice and protectors of society.
- Direct Recruitment Process:
In several states, the road to becoming an SPS officer commences with the direct recruitment process, overseen by the respective State Governments in conjunction with the State Public Service Commissions. This process seeks to identify and select the most deserving and capable individuals to join the esteemed ranks of the State Police Services.
The journey begins with a comprehensive written examination that evaluates candidates’ knowledge of the law, general awareness, and reasoning abilities. The examination serves as the initial filtering stage, setting the bar high for those aspiring to serve as law enforcement officers. Candidates who excel in the written test proceed to face the challenges of the physical fitness test. This test measures their physical strength, endurance, and overall fitness, ensuring that only those capable of meeting the rigorous demands of law enforcement move forward.
Following the physical fitness test, shortlisted candidates undergo a personal interview, where they are evaluated on their character, communication skills, and suitability for the demanding role of an SPS officer. This interview delves into the ethical and moral aspects of the candidates’ personalities, seeking individuals who exemplify the values of integrity, empathy, and dedication to service.
Once the selection process is complete, the chosen candidates embark on an intensive training program at prestigious police academies. During this training period, they undergo a transformative experience, sharpening their skills in law enforcement, learning crisis management, and developing leadership qualities. The training also emphasizes the importance of community-oriented policing and building strong bonds of trust with the people they serve.
Upon successfully completing their training, these officers are appointed as SPS officers and entrusted with the immense responsibility of maintaining law and order within their designated state. They become the frontline warriors, tasked with protecting society, safeguarding the innocent, and upholding the principles of justice.
- Promotion-Based Recruitment:
In certain states, the recruitment process for SPS officers takes a promotion-based route, acknowledging and rewarding the dedication and exceptional service of officers already within the state police force. This pathway values experience, tenure, and proven performance as the essential criteria for elevation to the ranks of SPS officers.
Aspirants for SPS positions through a promotion must demonstrate a remarkable track record of commitment, valour, and responsibility throughout their service. Their journey towards leadership begins with exemplary performance in their roles as police officers, displaying a deep understanding of the complexities of law enforcement and the ability to navigate diverse challenges.
Candidates selected for promotion undergo a vigorous probationary training program, which serves as a bridge between their existing roles and the higher responsibilities they will assume as SPS officers. This training equips them with the necessary skills and knowledge to lead their teams effectively, make crucial decisions, and act as agents of positive change in their communities.
Upon successful completion of the probationary training, these officers are promoted to the esteemed rank of Assistant Commissioner of Police (ACP) or Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP). Their promotion stands not merely as a career advancement but as a recognition of their leadership potential, their commitment to the greater good, and their ability to inspire and guide their fellow officers.
The recruitment process for State Police Services in India reflects the nation’s commitment to ensuring the highest standards of law enforcement and public safety. Whether through the direct recruitment process or the promotion-based system, these pathways lead to the same destination—an assembly of selfless and dedicated officers, embodying the values of courage, integrity, and compassion. As they take their place as the guardians of society, the men and women of the State Police Services stand as beacons of hope and symbols of service, embracing the responsibility to create a safer, fairer, and more just society for all.
The Hierarchical Structure Of SPS
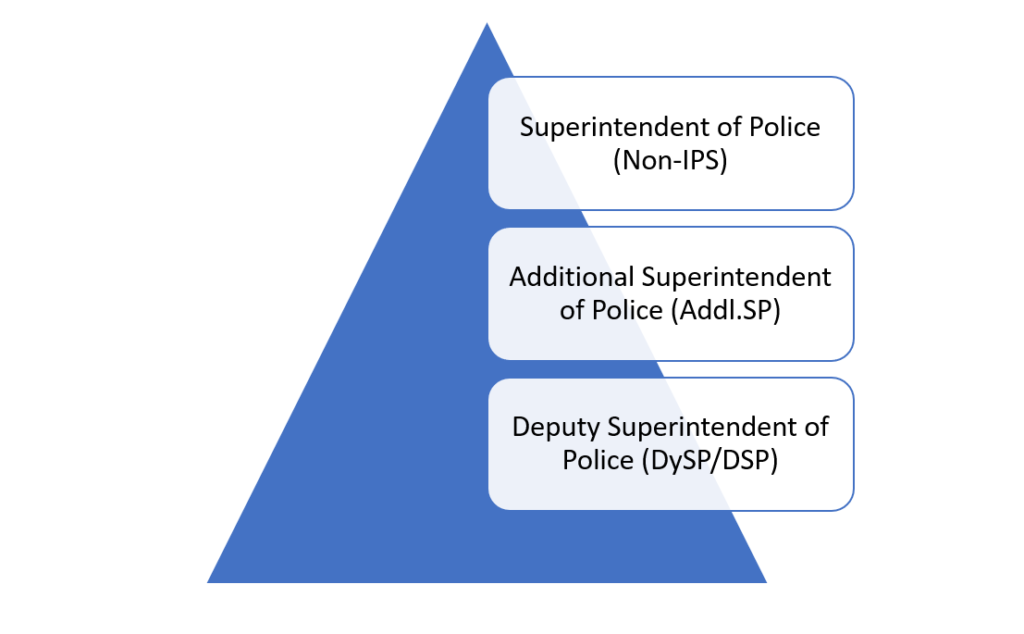
Ranks & Insignia Of Gazetted Officers From SPS
Gazetted officers include all the state police service officers: –
National Emblem above two stars (same insignia and pay band as a brigadier in the Indian Army)
- Deputy Inspector General of Police (DIG) or Additional Commissioner of Police (ACP)
- This is the senior-most rank the State Police Service officer can attain (if joined at an early age), responsible for overseeing the overall law enforcement in a division or a specialized unit.

National Emblem above two stars (same insignia and pay band as a colonel in the Indian Army)
- Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP) or Deputy Commissioner of Police (selection grade)
- This is the senior rank in the State Police Service, responsible for overseeing the overall law enforcement in a district or a specialized unit.

National Emblem above one Star (same insignia and pay band as a lieutenant colonel in the Indian Army)
- Superintendent of police (SP) or Deputy Commissioner of Police (DCP)
- This is the senior-most rank in the State Police Service, responsible for overseeing the overall law enforcement in a district or a specialized unit.

National Emblem (same insignia and pay band as a major in the Indian Army)
- Additional superintendent of police (ASP) or Additional Deputy Commissioner of Police (Addl. DCP)
- These officers assist the Superintendent of Police in managing law and order and may be assigned to specific areas or functions.

Three Stars (same insignia as a captain in the Indian Army; pay band of a Lieutenant)
- Assistant Commissioner of Police or Deputy Superintendent of Police: In some states, hold significant responsibilities and assists higher-ranking officers in various operations.
- Circle Officer (CO) or Sub-Divisional Police Officer (SDPO): In some states like Rajasthan, Bihar, and Uttar Pradesh, officers oversee a sub-division or circle within a district.

From State Police Service To Indian Police Service (IPS)
Within the Indian Police Service (IPS), there exists a journey of aspiration and determination, leading officers to don the prestigious uniform through two distinct pathways—the DR Quota and the Promotion Quota. Aspiring officers can draw inspiration from these paths, each representing a testament to their commitment, valour, and leadership.
- Embracing the Challenge: The DR Quota
The first path to the IPS begins with the Direct Recruit (DR) Quota—a rigorous and competitive process that calls upon the nation’s best and brightest. These aspiring officers embark on a journey of preparation, readying themselves for the Civil Services Examination conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC). This examination tests not just their knowledge but also their mental acumen, ethical values, and decision-making abilities. With dedication and perseverance, they immerse themselves in the vast ocean of knowledge, honing their intellectual prowess to meet the challenges that lie ahead.
Each candidate in this ambitious pursuit grapples with the vastness of the syllabus, knowing that success is a combination of hard work, self-belief, and resilience. They confront their dreams with unwavering determination, forging ahead in the face of adversity. With numerous sleepless nights and countless sacrifices, they prepare for the examination that will determine their destiny.
The day of the examination arrives, laden with nerves and anticipation. As they sit for the gruelling test, these aspirants know that their performance in these few hours will shape their future. The pressure is immense, but their indomitable spirit keeps them going.
And then, the moment of truth arrives—results are declared. For those who succeed, an overwhelming sense of achievement and pride fills their hearts. They have earned the privilege to serve their nation as direct recruit IPS officers, a feat they wear as a badge of honour.
- Rising through Dedication: The Promotion Quota
The Promotion Quota, the second pathway to the IPS, awaits those who have already demonstrated their mettle within the State Police Services. These officers, with an illustrious track record of dedication and service, stand as living examples of leadership and integrity. Their journey towards the IPS begins when the Central Government identifies the vacancies against the promotion quota for a given state in a calendar year.
For these officers, the journey towards promotion is not just about attaining higher ranks; it is an expression of their unwavering commitment to their duties. Day in and day out, they tread the path of service, facing various challenges and adversities. Their dedication goes beyond personal gains; it is a selfless devotion to upholding the values of law and order, ensuring the safety and well-being of the people they serve.
- A Meticulous Process of Ascension
The process of appointment from the State Police Service to the IPS under the Promotion Quota involves a symphony of collaboration between three key stakeholders—the concerned State Government, the UPSC, and the Union Government. Guided by the Indian Police Service (Recruitment) Rules, 1954, Indian Police Service (Appointment by Promotion) Regulations, 1955, and IPS (Regulation of Seniority) Rules, 1988, this journey unfolds.
The State Government initiates the process, submitting a proposal to the UPSC with details of State Police Service officers ranked according to their seniority. The UPSC convenes a Selection Committee Meeting, where the officers’ records and performance evaluations are meticulously scrutinized. With careful consideration, the Committee records its recommendations in the form of ‘Minutes,’ a testament to the officers’ worthiness for promotion.
The ‘Minutes’ are not just pieces of paper; they carry the dreams and aspirations of these officers who have dedicated their lives to the service of the nation. Each word in these documents reflects the hard work, sacrifice, and achievements of the officers being considered for elevation to the IPS.
- A Journey of Collaboration and Approval
The ‘Minutes’ are sent to the concerned State Government and then forwarded to the Central Government, which examines and provides its concurrence. The Commission, as the cadre controlling authority for the IPS, approves the minutes, paving the way for the officers’ ascent to the IPS.
The moment when the Central Government provides its approval is a culmination of years of perseverance and commitment. It is a moment of validation, recognizing the contributions of these officers and their suitability to lead at higher echelons of the police force.
- A Testament to Leadership and Service
The journey from State Police Service to IPS is not just about wearing a new insignia; it is a testament to the officers’ leadership and service. It is a recognition of their unwavering commitment to uphold the values of justice, compassion, and duty. Whether through the DR Quota or the Promotion Quota, these officers stand tall, representing the collective spirit of service and the pursuit of excellence within the Indian Police Service.
- United in Service and Dedication
The paths to the IPS may be different, but the destination remain the same—a commitment to the service of the nation. The direct recruit officers and those who rise through the promotion quota share a common purpose—to protect and serve society with unyielding determination.
Inspired by their journeys, these officers embrace the challenges of their roles with courage and conviction. United in their quest for a safer, just, and harmonious society, they embody the spirit of courage, determination, and sacrifice that is the hallmark of the Indian Police Service.
List Of State Police Services

Andhra Pradesh Police Service (APPS): The Andhra Pradesh Police Service (APPS) is a committed law enforcement body operating under the state government of Andhra Pradesh, India. With a clear mandate to uphold law and order, APPS officers serve as guiding figures, ensuring the safety and security of the public while upholding principles of justice and law enforcement.
Arunachal Pradesh Police Service (ANPS): The Arunachal Pradesh Police Service (ANPS) diligently safeguards law and order within the state of Arunachal Pradesh. These dedicated officers bear the responsibility of overseeing the work of subordinate service officers and law enforcement personnel, striving to create a harmonious and secure environment.
Assam Police Service (APS): The Assam Police Service (APS) is a vital pillar of law enforcement within Assam, India. Endowed with considerable authority and responsibility, APS officers play a commendable role in maintaining peace and order while upholding the principles of justice and fairness.
Bihar Police Service (BPS): The Bihar Police Service (BPS) operates with a solemn commitment to protect and serve the people of Bihar. These officers, entrusted with vital roles and responsibilities, dedicate themselves to ensuring public safety and promoting lawfulness across the state.
Chhattisgarh Police (CPS): The Chhattisgarh Police Service (CPS) stands as the guardian of law and order in Chhattisgarh, India. Its officers exemplify courage and dedication in their efforts to safeguard the well-being of citizens, creating a peaceful and secure environment.
Goa Police Service (GPS): The Goa Police Service (GPS) plays a vital role in maintaining law and order within the picturesque state of Goa. These officers, guided by principles of justice and integrity, ensure the safety and security of the public and visitors alike.
Gujarat Police Service (GPS): The Gujarat Police Service (GPS) operates as the custodian of law and order in the vibrant state of Gujarat. These officers, committed to upholding the values of justice and fairness, work tirelessly to create a safe and harmonious environment for all.
Haryana Police Service (HPS): The Haryana Police Service (HPS) stands firm in its duty to protect and serve the people of Haryana. HPS officers, with their dedication and professionalism, serve as role models for maintaining law and order and ensuring the well-being of the community.
Himachal Pradesh Police Service (HPS): The Himachal Pradesh Police Service (HPS) exemplifies the spirit of service and commitment to duty within the state of Himachal Pradesh. These officers, driven by a sense of responsibility, work diligently to ensure public safety and uphold the law.
Jharkhand Police: The Jharkhand Police is a crucial force responsible for maintaining law and order within the state. Jharkhand Police officers, through their dedication and expertise, contribute significantly to the security and well-being of the people they serve.
Karnataka State Police Service (KSPS): The Karnataka State Police Service (KSPS) serves as the vanguard of law enforcement in Karnataka, India. With a deep sense of responsibility, KSPS officers work tirelessly to maintain peace and order, ensuring the safety and security of the state’s residents.
Kerala Police Service (KPS): The Kerala Police Service (KPS) is renowned for its professionalism and commitment to duty. KPS officers, known for their sense of service and integrity, play a crucial role in upholding law and order and protecting the rights of the citizens of Kerala.
Madhya Pradesh Police Service (MPS): The Madhya Pradesh Police Service (MPS) stands as a symbol of dedication and valour in the state of Madhya Pradesh. With their unwavering commitment, MPS officers work relentlessly to create a secure and harmonious environment for the people they serve.
Maharashtra Police Service (MPS): The Maharashtra Police Service (MPS) is a key law enforcement agency in the state of Maharashtra. MPS officers, armed with the values of justice and duty, strive to safeguard the interests of the public, making Maharashtra a safe place to live and thrive.
Manipur Police: The Manipur Police play a pivotal role in maintaining peace and order in the state of Manipur. With a strong sense of duty, Manipur Police officers work diligently to foster a sense of security and justice for the people of the region.
Meghalaya Police: The Meghalaya Police is the stalwart of law enforcement in Meghalaya, India. Meghalaya Police officers, driven by a commitment to service, work with dedication and courage to ensure the well-being of the state’s residents.
Mizoram Police: The Mizoram Police serves as the guardian of law and order in the state of Mizoram. Mizoram Police officers, motivated by their sense of responsibility, strive to maintain harmony and safety, earning the trust of the local community.
Nagaland Police: The Nagaland Police stands as a beacon of justice and security in the state of Nagaland. With their devotion to duty, Nagaland Police officers diligently work to uphold law and order, creating an atmosphere of peace and stability.
Odisha Police: The Odisha Police is a stalwart in maintaining law and order in the state of Odisha. With their commitment to the welfare of the people, Odisha Police officers work tirelessly to ensure public safety and uphold the principles of justice.
Punjab Police: The Punjab Police stands as a symbol of strength and dedication in the state of Punjab. Punjab Police officers, with their unwavering sense of duty, work diligently to protect the interests of the public and maintain peace and order.
Rajasthan Police: The Rajasthan Police plays a crucial role in maintaining law and order in the state of Rajasthan. With their unyielding commitment, Rajasthan Police officers work diligently to safeguard the rights and safety of the state’s residents.
Sikkim Police: The Sikkim Police stands tall as a guardian of justice and security in the state of Sikkim. Sikkim Police officers, guided by principles of integrity and responsibility, ensure the welfare and well-being of the local community.
Tamil Nadu Police Service (TPS): The Tamil Nadu Police Service (TPS) exemplifies the spirit of dedication and service in Tamil Nadu, India. TPS officers, through their unwavering sense of duty, work tirelessly to create a secure and harmonious environment for the state’s residents.
Telangana State Police Service (TSPS): The Telangana State Police Service (TSPS) plays a crucial role in maintaining law and order in Telangana. TSPS officers, driven by a commitment to public safety, work diligently to protect the rights and interests of the state’s residents.
Tripura Police: The Tripura Police serves as the vanguard of law enforcement in the state of Tripura. With their dedication and professionalism, Tripura Police officers work diligently to maintain peace and order and ensure the security of the local community.
Provincial Police Service (PPS) UP Police: The Provincial Police Service (PPS) UP Police is dedicated to upholding law and order within the state of Uttar Pradesh. PPS officers, with their unwavering commitment, work to create a safe and secure environment for the state’s residents.
Uttarakhand Police: The Uttarakhand Police stands as a symbol of duty and service in the state of Uttarakhand. Uttarakhand Police officers, driven by a commitment to protect the public, work tirelessly to maintain peace and order in the region.
West Bengal Police Service (WBPS): The West Bengal Police Service (WBPS) plays a crucial role in maintaining law and order in West Bengal, India. WBPS officers, with their dedication and professionalism, ensure the safety and security of the state’s residents.
Union Territories
Andaman and Nicobar Islands Police Service: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands Police Service is entrusted with the responsibility of ensuring the safety and security of the islands’ residents and visitors. With a focus on maintaining law and order, the officers of this service work diligently to create a peaceful environment for all.
Chandigarh Police: The Chandigarh Police is dedicated to upholding law and order in the union territory of Chandigarh. Chandigarh Police officers, with their commitment to duty and justice, strive to protect the rights and well-being of the local community.
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu Police: The Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu Police serve as the guardians of law and order in this unique union territory. With a focus on community safety, the officers of this police force work diligently to ensure peace and harmony.
Delhi Police: The Delhi Police is a formidable force responsible for maintaining law and order in the national capital territory of Delhi. With their dedication and bravery, Delhi Police officers strive to protect the interests and safety of the city’s residents.
Jammu and Kashmir Police: The Jammu and Kashmir Police stands tall as a symbol of courage and dedication in the union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. J&K Police officers, with their unwavering sense of duty, work tirelessly to protect the region’s people and maintain peace.
Ladakh Police: The Ladakh Police is entrusted with the vital responsibility of ensuring law and order in the union territory of Ladakh. With their commitment to service, Ladakh Police officers strive to create a secure and harmonious environment for the residents.
Lakshadweep Police: The Lakshadweep Police is a guardian of justice and security in the union territory of Lakshadweep. With their focus on community welfare, Lakshadweep Police officers work diligently to maintain peace and harmony in this unique island territory.
Puducherry Police: The Puducherry Police plays a crucial role in maintaining law and order in the union territory of Puducherry. With their unwavering commitment, Puducherry Police officers work diligently to protect the rights and well-being of the local community.
How To Become A Gazetted Police Officer Through State Public Service Commission (State PSC)?
Becoming a gazetted police officer through State Public Service Commission (State PSC) involves a competitive and rigorous selection process. The steps to become a gazetted police officer are as follows:
Educational Qualification: The first requirement is to have a bachelor’s degree from a recognized university. Some states may specify additional educational qualifications, so it’s essential to check the specific eligibility criteria for the State PSC you are interested in.
Age Limit: There is an upper age limit for candidates applying to become gazetted police officers through State PSC exams. The age limit may vary from state to state and can be relaxed for certain categories as per government norms.
State PSC Exam: The State PSC conducts competitive exams for various administrative services, including the State Police Service. Interested candidates need to apply for the State PSC exam when the notification is released.
Preliminary Examination: The State PSC exam usually consists of two stages: the preliminary examination and the main examination. The preliminary exam tests candidates on general awareness, aptitude, and reasoning.
Main Examination: Candidates who qualify in the preliminary exam move on to the main examination, which is more comprehensive and includes subjects like general studies, language papers, and optional subjects.
Interview: Those who perform well in the main examination are called for a personal interview or personality test. The interview assesses the candidate’s suitability for the role of a police officer.
Medical and Physical Fitness Test: Successful candidates in the interview may have to undergo a medical examination and a physical fitness test to ensure they meet the necessary health and fitness standards required for police service.
Merit List and Final Selection: The final selection is based on the combined performance in the main examination, interview, medical test, and physical fitness test. A merit list is prepared, and candidates at the top of the list are offered gazetted police officer positions based on the number of vacancies available.
Training: After selection, candidates undergo comprehensive training at police academies to equip them with the necessary skills and knowledge for their roles as gazetted police officers.
It’s important to note that the selection process and eligibility criteria may differ slightly for each state’s State PSC. Aspiring candidates should regularly check the official State PSC websites or notifications for the latest updates and detailed information about the examination process and eligibility requirements. Additionally, thorough preparation, dedication, and hard work are crucial to succeed in the competitive State PSC exams and becoming a gazetted police officer.
Perks And Facilities Enjoyed By SPS Officers
List of facilities and benefits that DSPs (Deputy Superintendents of Police) recruited through state public service exams receive:
Well-Furnished Bungalow: DSPs are provided with a comfortable and well-equipped official residence, ensuring a conducive living environment.
Official Vehicle: They are allocated a dedicated vehicle with a blue beacon, showcasing their authority and facilitating efficient transportation during official duties.
Enhanced Job Security: DSPs enjoy a high level of job security, instilling confidence in their career path and fostering a steadfast commitment to public service.
Security Guard: They are accompanied by security guards, ensuring their safety and aiding them in dealing with challenging situations.
Medical Facilities: As government officials, DSPs have access to state-provided medical facilities, addressing their healthcare needs and ensuring their well-being.
Attractive Gross Salary: The gross salary of a DSP typically ranges from 55,000 to 80,000 per month (also depending on many factors like the area of postings, etc), providing a substantial financial reward for their service.
Additional Allowances: DSPs may be eligible for various allowances such as housing allowance, travel allowance, and others, further enhancing their overall compensation.
Access to Government Resources: They have access to resources and support from other government departments, enabling efficient execution of their duties.
Training and Professional Development: DSPs often receive specialized training and opportunities for professional development, enhancing their skills and expertise.
Recognition and Prestige: Serving as a DSP brings recognition and prestige within the community and the law enforcement fraternity.
Scope for Advancement: The position of DSP serves as a stepping stone for higher ranks and responsibilities in the police department.
Community Impact: DSPs have the opportunity to make a significant impact on society by maintaining law and order and ensuring public safety.
Networking Opportunities: They get to interact with influential individuals and leaders, creating networking opportunities for personal and professional growth.
Access to Information: DSPs have access to sensitive information and intelligence, enabling them to combat crime effectively.
Social Status: Their position as a DSP confers a respected social status, garnering admiration and appreciation from the community they serve.
The role of a DSP comes with a range of facilities and benefits that go beyond monetary compensation. These provisions are aimed at supporting and motivating them to fulfill their duties with dedication and excellence, making a positive impact on the community and upholding the principles of justice and security.
Top 13 Facts About The State Police Service
State Police Services (SPS) constitute an essential law enforcement body governed by the respective state governments in India, responsible for maintaining law and order within their designated states and union territories.
SPS officers are appointed through a diligent process conducted by the State Public Service Commission (PSC), ensuring that only the most dedicated and capable individuals assume crucial roles and responsibilities.
Each state has its distinct State Police Service, such as the Andhra Pradesh Police Service (APPS), Tamil Nadu Police Service (TPS), and Kerala Police Service (KPS), among others, which collectively work to safeguard public safety and uphold the principles of justice and law enforcement.
The recruitment process for SPS officers varies from state to state, with some states having a direct recruitment process through state-level competitive exams, while others follow a promotion-based system.
SPS officers are gazetted officers of the state government, entrusted with considerable authority and responsibility to maintain law and order within their respective jurisdictions.
The ranks and insignia of SPS officers follow a hierarchical structure, with various designations like Superintendent of Police (SP), Additional Superintendent of Police, Assistant Commissioner of Police (ACP), and more, signifying their roles and responsibilities.
The Indian Police Service (IPS) has two components—DR Quota and Promotion Quota. Direct recruit IPS officers come through the Civil Services Exam conducted by the UPSC, while State Police Service officers can be inducted into the IPS through the Promotion Quota.
The process of appointment from the State Police Service to the IPS under the Promotion Quota involves collaboration between the concerned State Government, the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC), and the Union Government, adhering to defined rules and regulations.
SPS officers operate solely within the boundaries of their respective states in India, maintaining a rank below the esteemed Indian Police Service (IPS) officers but standing above the State Police Subordinate Service officers in the hierarchy.
The training and probationary period for SPS officers are rigorous, equipping them with the necessary skills and knowledge to handle diverse challenges and serve as leaders in their police departments.
Each state and union territory’s police force reflect the cultural diversity and ethos of the region, promoting community-centric policing to build trust and harmonious relationships with the public.
SPS officers undertake diverse roles, from patrolling the streets and investigating crimes to providing assistance during emergencies and fostering community engagement to address social issues effectively.
State Police Services play a crucial role in upholding the rule of law, ensuring public safety, and protecting the fundamental rights of citizens, exemplifying the commitment and dedication of the officers who serve as the guardians of justice and peace in the nation.





