
Introduction
- whenever you think about President what comes in your mind? Like he is the head of the country, the topmost authority in the country. Well, it is true to some extent only. Our Indian constitution provides a variety of provisions regarding the President.
Historical Underpinnings
- Our first President Dr. Rajendra prasad who holds the record of being elected to the office 2 times, used to travel the country for 6 months a year with Indian railways to understand the social-economic conditions and cultural and social diversity of the country. He proved the fact that the post of President is a symbol of unity, integrity, and solidarity in a nation. Since 1950 India has had 13 presidents. Current President Ram Nath Kovind, the 14th President of the country is soon to complete his tenure. The country will undergo the electoral process for the post of 15th President.
Constitutional Provisions

- Article 52-78 of the Indian constitution talks about the union executive. The Union executive doesn’t only include the President but also the Vice President, Prime Minister, Council of Ministers, and Attorney General of India. President is the head of the Indian state and is considered the first citizen of India.
Role Of President
- The primary duty of the president is to preserve, protect and defend the constitution. For this role, he is also called Guardian of the Constitution. President is the ceremonial head or constitutional head of the state like the king or queen of Britain. All executive powers are vested in him but exercised by the cabinet.
Powers Of President
- President is accorded many powers by the constitution.
1. Executive Powers:-
Some executive powers of the President of India are:-
- All executive functions of the government of India are formally taken in the name of the president.
- The most important power provided to the president is the appointment of the Prime Minister and other ministers.
- He appoints the Attorney General of India, Comptroller and Auditor General of India, Chief election commissioner, other election commissioners, chairman and members of Union Public Service Commission, Governor of states, and the chairman and members of Finance Commission.
- He appoints a Commission to investigate the conditions of SCs, STs, and other backward classes.
- He appoints interstate councils to promote center-state and inter-state cooperation.
2. Legislative Powers:-
Some legislative powers of the President of India are:-
- President is an integral part of Parliament.
- He addresses at the commencement of every session of the parliament of India.
- He issues ordinances to make law when any house of the legislature is not in session.
- He nominates 12 members who have eminent and specialized knowledge of art, literature, science, etc. from the council of states.
- He summons a joint sitting of both houses of parliament when there is a deadlock between two houses of parliament over a bill.
- He makes regulations for the peaceful functioning of UTs like Andaman and Nicobar, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman, and Diu, Lakshadweep, etc.
3. Financial Powers:-
Some financial powers of the President of India are:-
- He makes advances out of the contingency fund of India, a fund for special emergencies.
- He lays the annual financial statement means the union budget before the parliament of India.
- For the purpose of distribution of resources between the center and states, he appoints the chairman and members of the Finance Commission every 5 years.
4. Judicial Powers:-
Some Judicial powers of the President of India are:-
- He appoints the Chief justice of India and other judges of the Supreme Court of India and High Court.
- He asks for advice from the Supreme Court on any matter of law or public importance.
- He can grant pardon and convert other forms of punishment into lighter forms of punishment.
5. Diplomatic Powers:-
Some diplomatic powers of the President of India are:-
- Representation of India on other international platforms.
- International treaties and agreements are concluded on his behalf of him.
6. Military Powers:-
Some military powers of the President of India are:-
- President is the supreme commander of the armed forces.
- He appoints the chiefs of the army, navy, and air force.
7. Emergency Powers:-
Some emergency powers of the President of India are:-
- He declares different types of emergencies provided in the constitution like under article 352 national emergency for example when there is war or any disturbance, under article 356 President’s rule provision for states, and under article 360 financial emergency when there is a disturbance in financial equilibrium.
8. Presidential Veto:-
Some veto powers of the President of India are:-
- President also possesses veto powers to give his final nod to the bills passed by the parliament of India. There are different types of veto like an absolute veto, pocket veto, etc. For example, the pocket veto is exercised by the president to keep it with him indefinitely without giving any assent to the bill.
- President can also exercise his veto powers over the state legislatures also.
Process Of The Election

- As presidential elections are scheduled to take place on 18th July 2022, you might be wondering what the process of election of a president of India is? So, President is not elected directly by the people of India as is the case with Lok Sabha elections, assembly elections, and Panchayati raj elections. There is a system in place for the election process of the president which makes him representative of the union and state equally.

Debate In Constituent Assembly About The Method Of The Election
- How the presidential election will take place and what will be the process were also a matter of debate in the constituent assembly. But being a ceremonial head, the process of Indirect election was found more suitable for a country like India which was newly independent.
Electoral College
- The process for the election of the president is complex. The electoral college means who can take part in the process of election of President of India. In the election only elected members of both houses of parliament, state legislatures, and the union territory of Delhi and Puducherry take part. Nominated members of any house do not take part in the process of the election of the president of India. The election process is done by proportional representation by means of a single transferable vote. Voting is done through a secret ballot.
Electoral Quota And Value Of Vote
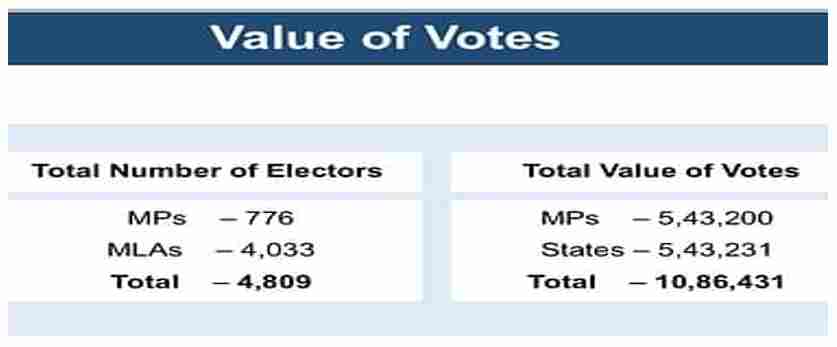
- To be elected successfully to the office of the president there is a fixed quota of votes which determines who will get elected to the post. There is a value provided to the vote of every member of parliament and the members of the state legislative assembly.
Qualifications For Becoming A President
There are essential qualifications for the post of President which makes a person eligible to contest for the office of President.
- He/she should be a citizen of India.
- He/she should have completed 35 years of age.
- He/she should be qualified to become a member of parliament.
- He/she should not have any office of profit under any of the government offices be it a union, state, or any other local authorities.
- For the nomination of a candidate to the election, there must be at least 50 electors as proposers and 50 electors as seconders.
Oath
- After being elected to the office of President, he must take oath before entering his office. The oath is administered by the Chief Justice of India. President takes an oath to defend, protect and preserve the constitution. In case of violation of the Constitution, he can be removed from his office.
Term Of The President
- President holds office for a tenure of 5 years. If he wants to resign before completing his tenure, he gives his resignation to the vice president of India.
Impeachment
- If the president is removed by the parliament before completing his tenure this process is called Impeachment.
Presidential Candidates For The Upcoming Elections
- NDA alliance has chosen Draupadi Murmu as its candidate, who is a former governor of Jharkhand and if chosen will become 1st tribal and second women president of India. 13 party section of opposition led by Indian national congress has chosen Yashwant Sinha, who is a former union minister, a retired bureaucrat, and former BJP leader. Fate will be decided on 18th July over the post of President.
Top 13 Interesting Facts About President
Dr. Rajendra Prasad became the first President to serve for the longest time and for 2 terms.
Dr. Sarvapalli Radhakrishnan became the first person to have acted as president and vice president.
Dr. Zakir Hussain was the first President to have died in office.
Mohammed Hidayatullah was the first Chief Justice to hold the office of President.
V.V Giri became the first acting president.
Nilam Sanjeev Reddy became the youngest president and wrote a book called “without fear or favor- reminiscence and reflections of the president”.
Fakruddin Ali Ahmed was the president of India when the emergency was declared by Prime Minister Indira Gandhi.
Dr. A.P.J Abdul Kalam, also known as missile man, was known as the ‘president of people’.
Pratibha Patil became the first women president of India.
President’s bodyguard is an elite household cavalry regiment of the Indian army.
The residence of the president is called Rashtrapati Bhawan, which is one of the largest Presidential houses in the world.
The salary, pension, and allowance of the president of India are determined by parliament.
President acts on the aid and advice of the council of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister.







