- Umang Sagar
- Place, Recent article
Karnataka State

State | Karnataka |
Capital City | Bengaluru |
Founded on | 1st November (1956) |
Language | Kannada (66.46%), Urdu (10.83%), Telugu (5.84%), Tamil (3.45%) Marathi (3.29%), Tulu (2.61%), Lambadi (1.59%), Hindi (1.43%), Konkani (1.29%), Malayalam (1.22%), Others (1.99%) |
Area | 191,791 km² |
Governor | Shri Thawar Chand Gehlot |
Chief Minister | Shri Basavaraj Bommai |
Districts | 31 |
Population | 7.05 Crore |
Karnataka is famous for | Sandalwood products, Mysore silk, Channapatna wooden toys, Coorg coffee powder, Mysore Pak, Dharwad peda, Masala cashew nuts, Spices, and south Indian masalas. |
Introduction
Karnataka is a state in the southwestern region located in India. It was formed on 1st November 1956, under the State’s Reorganisation Act. Initially, it was known as the State of Mysore and it was renamed Karnataka in 1973.
The people living in Karnataka are the Kannada-speaking people who are referred to as Kannadigaa’s.
Kannada Language And Its History
Kannada was the court language of some of south and central India’s most powerful dynasties, including the Kadambas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Hoysalas, and the Vijayanagara empire. It is one of the scheduled languages of India and it is the official and administrative language of the state of Karnataka.
Kannada is a branch of the Dravidian family of languages, a collection of south Indian languages with many regional dialectical differences. At this time, there are at least three distinct regional dialects: Mysore-Kannada, Dharwad-Kannada, and Mangalore-Kannada. Kannada is spoken in Karnataka’s three cultural centers: Mysore, Dharwad, and Mangalore. There are other dialectical subdivisions within these primary divisions, such as Havyaka, Badaga, Nadava, Koosa, and others, which are local dialects mixed with other language types.
The language’s written characters are derived from the Brahmi script, which is the parent script for all current Indian languages and was originally popularised throughout India through Asoka’s edicts. The Halmidi inscription from 450 A.D. contains the earliest form of Kannada script.
This script is used in many of the Badami Chalukyan Sanskrit records. The Kannada script has been evolving for over 2,000 years, and the current Kannada script is the product of these evolutionary changes. After the invention of printing, in which letterforms are mechanically duplicated with unchanging regularity, the current script was established.
Because Kannada, Tamil, and Telugu are all Dravidian languages, their structures are similar. The technical, scientific, and philosophical vocabulary was fostered by the Sanskrit language, which went through several stages of development from being a dialect of the Dravidian stock to the status of a cultured language with its script.
The earliest form of the language is known as Halegannada (which means Old Kannada) and Nadugannada (which means Middle Kannada) of later stages paved the way for Hosagannada (Modern Kannada). Halegannada nurtured literature and most of the popular literature belongs to either Nadugannada or Hosagannada.
History Of Karnataka
- As per early history, Karnataka was ruled by various kingdoms, including the Maurya Empire, Satavahana dynasty, Kadamba dynasty, and Western Ganga Dynasty. The Chalukyas, Rasthtrakutas, Hoysalas, and Vijayanagara Empires governed this state during the medieval period. The Wodeyars of Mysore, Hyder Ali, and Tipu Sultan ruled this state during the modern era, which was succeeded by the British. The state of Mysore was founded in 1956 after India gained independence from the British, and the state was renamed Karnataka in 1973.
Symbol Of Karnataka
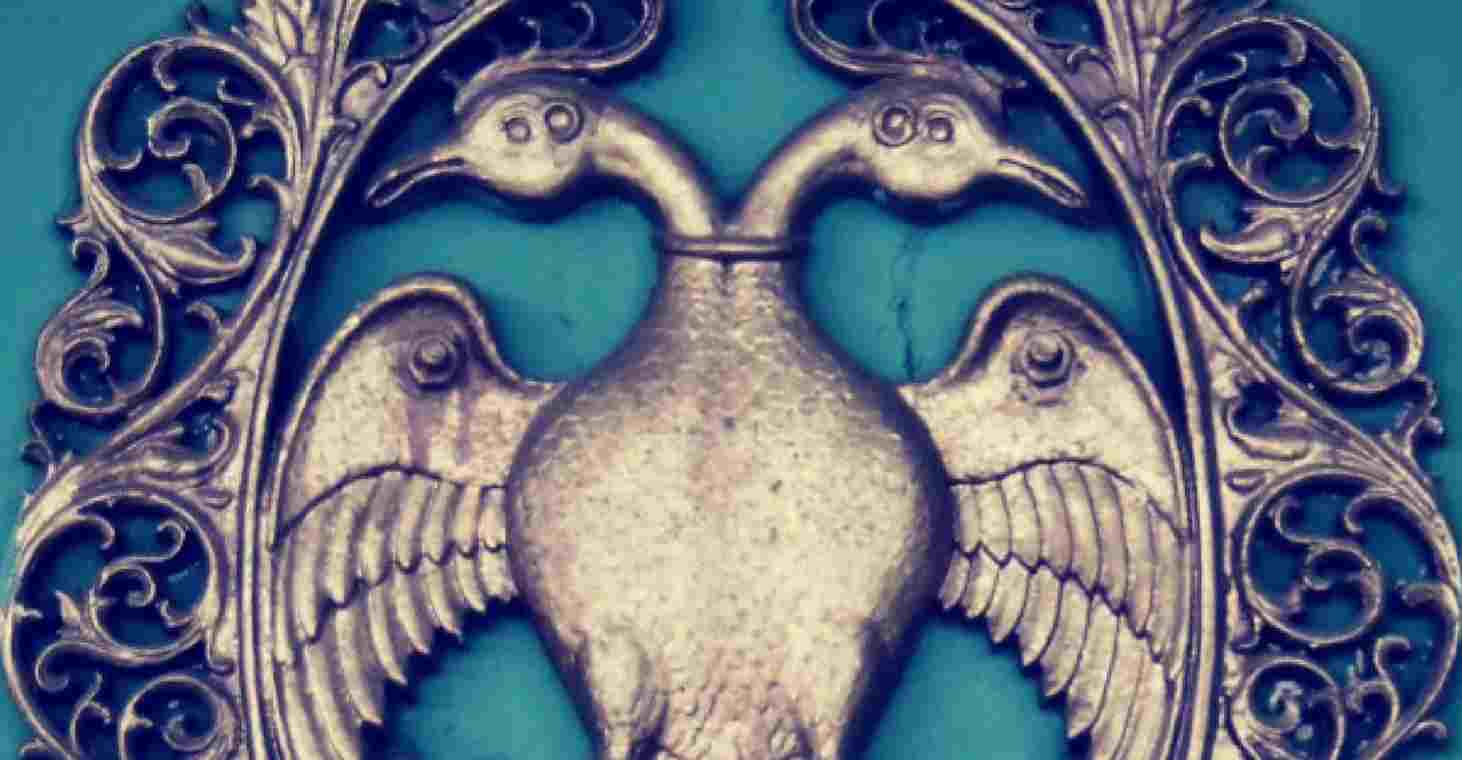

A symbol of Karnataka is “The Gandaberunda” it is an imaginary two-headed bird that resembles a mythical creature in Hindu mythology.
The Gandaberunda was used by the Wodeyar dynasty that ruled the Kingdom of Mysore as the Royal emblem. The Karnataka Government adopted this as the state symbol and can be found on bus terminals and tickets issued by Karnataka State Road Transport Corporation.
Government Of Karnataka (GOK)

The current Hon’ble Governor of Karnataka is Shri Thawar Chand Gehlot.
The current Chief Minister of Karnataka is Shri Basavaraj Bommai.
Departments
- Department of agriculture.
- Department of animal husbandry and fisheries.
- Department of backward class welfare.
- Department of commerce and industries.
- Department of co-operation.
- Department of personnel and administrative reforms (dpar).
- Dpar (administrative reforms)
- Dpar (e-governance)
- Dpar (janaspandana)
- Department of higher education.
- Department of primary and secondary education.
- Department of energy.
- Department of finance.
- Department of food and civil supplies.
- Department of forest, ecology, and environment.
- Department of health and family welfare.
- Department of women and child welfare.
- Department of housing.
- Department of infrastructure development, ports, and inland water transport.
- Department of information technology and biotechnology.
- Department of Kannada and culture.
- Department of labour.
- Department of law.
- Department of medical education.
- Department of minor irrigation.
- Department of minority welfare.
- Department of parliamentary affairs.
- Department of planning.
- Department of public enterprises.
- Department of public works.
- Department of rural development and panchayat raj.
- Department of revenue.
- Department of horticulture and sericulture.
- Department of information and public relations.
- Department of skill development entrepreneurship and livelihood.
- Department of social welfare.
- Department of tourism.
- Department of transport.
- Department of urban development.
- Department of water resources.
- Department of home.
- Department of youth empowerment and sports.
Services Provided By GOK
e-services: – Sakala, Seva Sindhu, e-Gazette, Online RTI, e-Spandana, Mahiti Kanaja.
Apps: – Anjanwadi, Antharjala, Apthamitra, AranyaBhoomii, Bele darshak 2022, Bidding App, BMTC mobile App, CA App, CESC apps, Crime location, Crop cutting experiments mobile app, Damini-lightning alert, DULT – Data collector, Crop survey, BBMP Apps, etc, through which Government provides services.
List Of Chief Ministers Of Karnataka
| Sl. No | Name | constituency | From | To | Party |
| 1. | C. M. Poonacha | Berriath Nad | 27 March 1952 | 31 October 1956 | Indian National Congress |
| 2. | S. Nijalingappa | Molakalmuru | 1 November 1956 | 16 May 1958 | Indian National Congress |
| 3. | B. D. Jatti | Jamkhandi | 16 May 1958 | 14 March 1962 | Indian National Congress |
| 4. | S. R. Kanthi | Hungud | 14 March 1962 | 21 June 1962 | Indian National Congress |
| 5. | S. Nijalingappa | Shiggaon Bagalkot | 21 June 1962 | 29 May 1968 | Indian National Congress |
| 6. | Veerendra Patil | Chincholi | 29 May 1968 | 18 March 1971 | Indian National Congress (O) |
| 7. | Vacant (President’s rule) | N/A | 19 March 1971 | 20 March 1972 | N/A |
| 8. | D. Devaraj Urs | Hunasuru | 20 March 1972 | 31 December 1977 | Indian National Congress |
| 9. | Vacant (President’s rule) | N/A | 31 December 1977 | 28 February 1978 | N/A |
| 10. | D. Devaraj Urs | Hunasuru | 28 February 1978 | 12 January 1980 | Indian National Congress |
| 11. | R. Gundu Rao | Somwarpet | 12 January 1980 | 10 January 1983 | Indian National Congress |
| 12. | Ramakrishna Hegde | Kanakpura Basavanagudi | 10 January 1983 8 March 1985 | 7 March 1985 13 August 1988 | Janata Party |
| 13. | S. R. Bommai | Hubli Rural | 13 August 1988 | 21 April 1989 | Janata Party |
| 14. | Vacant (President’s rule) | N/A | 21 April 1989 | 30 November 1989 | N/A |
| 15. | Veerendra Patil | Chincholi | 30 November 1989 | 10 October 1990 | Indian National Congress |
| 16. | Vacant (President’s rule) | N/A | 10 October 1990 | 17 October 1990 | N/A |
| 17. | S. Bangarappa | Soraba | 17 October 1990 | 19 November 1992 | Indian National Congress |
| 18. | M. Veerappa Moily | Karkala | 19 November 1992 | 11 December 1994 | Indian National Congress |
| 19. | H. D. Deve Gowda | Ramanagara | 11 December 1994 | 31 May 1996 | Janata Dal |
| 20. | J. H. Patel | Channagiri | 31 May 1996 | 11 October 1999 | Janata Dal |
| 21. | S. M. Krishna | Maddur | 11 October 1999 | 28 May 2004 | Indian National Congress |
| 22. | Dharam Singh | Jevargi | 28 May 2004 | 3 February 2006 | Indian National Congress |
| 23. | H. D. Kumaraswamy | Ramanagara | 3 February 2006 | 8 October 2007 | Janata Dal (Secular) |
| 24. | Vacant (President’s rule) | N/A | 8 October 2007 | 12 November 2007 | N/A |
| 25. | B. S. Yediyurappa | Shikaripura | 12 November 2007 | 19 November 2007 | Bharatiya Janata Party |
| 26. | Vacant (President’s rule) | N/A | 20 November 2007 | 29 May 2008 | N/A |
| 27. | B. S. Yediyurappa | Shikaripura | 30 May 2008 | 5 August 2011 | Bharatiya Janata Party |
| 28. | D. V. Sadananda Gowda | MLC | 5 August 2011 | 12 July 2012 | Bharatiya Janata Party |
| 29. | Jagadish Shettar | Hubli-Dharwad-Central | 12 July 2012 | 13 May 2013 | Bharatiya Janata Party |
| 30. | Siddaramaiah | Varuna | 13 May 2013 | 17 May 2018 | Indian National Congress |
| 31. | B. S. Yediyurappa | Shikaripura | 17 May 2018 | 23 May 2018 | Bharatiya Janata Party |
| 32. | H. D. Kumaraswamy | Channapatna | 23 May 2018 | 26 July 2019 | Janata Dal (Secular) |
| 33. | B. S. Yediyurappa | Shikaripura | 26 July 2019 | 28 July 2021 | Bharatiya Janata Party |
| 34. | Basavaraj Bommai | Shiggaon | 28 July 2021 | Incumbent | Bharatiya Janata Party |
Law And Order Situation In Karnataka
- The Chief Minister of Karnataka said we adhere to strict rules. It is our responsibility to preserve law and order and keep the peace. If any group tries to take over control of law and order, we will immediately take action against them and wherever we had to take action, we didn’t think twice, stated CM.
Economy Of Karnataka
| Sl. No | Sector | GVA (Rupees in Lakh) at current prices (2020-21) | % Share |
| 1 | Primary Sector | 20,438,651 | 13.68 |
| 1.1 | Agriculture, forestry & fishing | 19,655,955 | 13.15 |
| 1.11 | Crops | 12,804,541 | 8.57 |
| 1.12 | Livestock | 5,268,755 | 3.53 |
| 1.13 | Forestry & logging | 997,948 | 0.67 |
| 1.14 | Fishing and aquaculture | 584,711 | 0.39 |
| 1.2 | Mining & quarrying | 782,696 | 0.52 |
| 2 | Secondary Sector | 29,578,388 | 19.79 |
| 2.1 | Manufacturing | 19,598,850 | 13.11 |
| 2.2 | Electricity, gas, water supply & other utility services | 2,182,925 | 1.46 |
| 2.3 | Construction | 7,796,613 | 5.22 |
| 3 | Tertiary Sector | 99,442,804 | 66.53 |
| 3.1 | Trade, repair, hotels, and restaurants | 17,919,883 | 11.99 |
| 3.11 | Trade & repair services | 15,509,059 | 10.38 |
| 3.12 | Hotels & restaurants | 2,410,825 | 1.61 |
| 3.2 | Transport, storage, communication & services related to broadcasting | 8,024,850 | 5.37 |
| 3.21 | Railways | 282,017 | 0.19 |
| 3.22 | Road transport | 5,962,730 | 3.99 |
| 3.23 | Water transport | 40,151 | 0.03 |
| 3.24 | Air transport | 151,605 | 0.10 |
| 3.25 | Services incidental to transport | 101,931 | 0.07 |
| 3.26 | Storage | 40,654 | 0.03 |
| 3.27 | Communication & services related to broadcasting | 1,445,763 | 0.97 |
| 3.3 | Financial services | 7,313,593 | 4.89 |
| 3.4 | Real estate, ownership of dwelling & professional services | 50,004,960 | 33.46 |
| 3.5 | Public administration & defense | 4,598,984 | 3.08 |
| 3.6 | Other services | 11,580,533 | 7.75 |
| Total | GVA at basic prices | 149,459,843 |
Geographical Information
Karnataka is situated between 11°30′ and 18°30′ north latitudes and 74° and 78°30′ east longitudes in India. It is located on a tableland in the western section of India’s Deccan Peninsular region, where the Western and Eastern Ghats intersect to form the complex. The state is bordered on the north and northwest by Maharashtra and Goa States; on the west by the Arabian Sea; on the south and southeast by Kerala and Tamil Nadu, and on the north and east by Andhra Pradesh and Telangana. Karnataka stretches for around 750 kilometers north to south and 400 kilometers east to west.
The Mullayanagiri hill in Chikkamagaluru district is the highest elevation in Karnataka which has an altitude of 1,929 meters (6,329 ft) above sea level.
1. Land:-
Eleven groups of soil orders are present in Karnataka.
- Entisols
- Inceptisols
- Mollisols
- Spodosols
- Alfisols
- Ultisols
- Oxisols
- Aridisols
- Vertisols
- Andisols
- Histosols.
The common types of soil types present in Karnataka are:
- Red soils: Red gravelly loam soil, Red loam soil, Red gravelly clay soil, Red clay soil
- Black soil: gravelly soil, loose, black soil, basalt deposits
- Lateritic soils: Lateritic gravelly soil, Lateritic soil
- Black soils: Deep black soil, Medium deep black soil, Shallow black soil
- Alluvio-Colluvial Soils: Non-saline, saline and sodic
- Forest soil: Brown Forest soil
- Coastal soil: Coastal laterite soil, Coastal alluvial soil
2. Water:-
Approximately102 km of water surface including waterfalls, rivers, lakes, reservoirs, etc are found in Karnataka.
Around 60% of the water surface is covered by west-flowing wing rivers, remaining 40% of the water surface is covered by east-flowing rivers.
3. Climate:-
Karnataka has the following four seasons in the year:-
- Winter season (from January to February)
- Summer season (from March to May)
- Monsoon season (from June to September)
- Post-monsoon season (from October to December)
4. Rainfall:-
Coastal Karnataka: The districts of Uttara Kannada, Udupi, and receive an average rainfall of 3638.5 mm per annum.
North Interior Karnataka: The arid districts like Belgaum, Bidar, Bagalkot, Haveri, Gadag, Dharwad, Gulbarga, Koppal, Bellary, and receive only 711.5 mm of average rainfall per annum.
South Interior Karnataka: The rest of the districts of Karnataka falls into this zone. This zone receives 1064.8 mm of average rainfall per annum.
Culture Of Karnataka
Karnataka has a diverse cultural heritage. The lineages of Indian emperors such as the Mauryas, Chalukyas, and Hoysalas have left their imprints on numerous aspects of Karnataka culture. The indigenes’ diverse religions and languages had contributed to its ethnic grandeur.
The famous rock editcs of King Ashoka, epitomizing regal artistry and aestheticism, are landmarks, thus making the region familiar to the people of the world.
Karnataka is home to many tribes, including the Kodavas, Konkanis, Tuluvas (Tuluva Dynasty), and Tibetan Buddhists and Siddhi people. Karnataka’s art forms include a diverse range of magnificent festivals, music, theatre, and regal cuisine.
Lion Of Karnataka
- Gangadharrao Balkrishna Deshpande (31 March 1871 to 30 July 1960) is known as Lion of Karnataka, Khadi Bhageeratha of Karnataka. He was the leader in the Indian independence movement against British colonial rule from Belgaum and he was also the right-hand man of both Lokamanya Tilak and Mahatma Gandhi.
About Bengaluru (The IT Hub Of The Country)
Bengaluru (Bangalore) is known as India’s Silicon Valley and as a significant technology or information technolcenterntre or IT hub in India.
For nearly three decades, it has functioned as India’s technological capital.
Electronic City, Whitefield, Outer Ring Road (between KR Puram and Sarjapur Road), Domlur, Bannerghatta Road, Mysore Road, Koramangala, and others are some of the prominent areas in Bangalore where most of the IT businesses are located.
Bangalore is home to tech empires such as Infosys, Wipro, and Google, as well as unicorn startups such as Byju’s, Swiggy, Ola Cabs, InMobi, and others. Bangalore’s IT and software companies are a dream come true for anyone wishing to start a career in technology.
Bengaluru is one of the most desirable locations for companies involved in the IT industry these days namely;
- Infosys
- SAP Labs India
- Amazon
- Cisco
- Trigent Software Limited
- Global Edge Software
- Tech Mahindra
- Mphasis
- IBM
- Dell EMC
- ITC Infotech India Ltd
- Wipro Technologies Ltd
- Mindtree Ltd
- Intuit
Historical Places To Visit In Karnataka
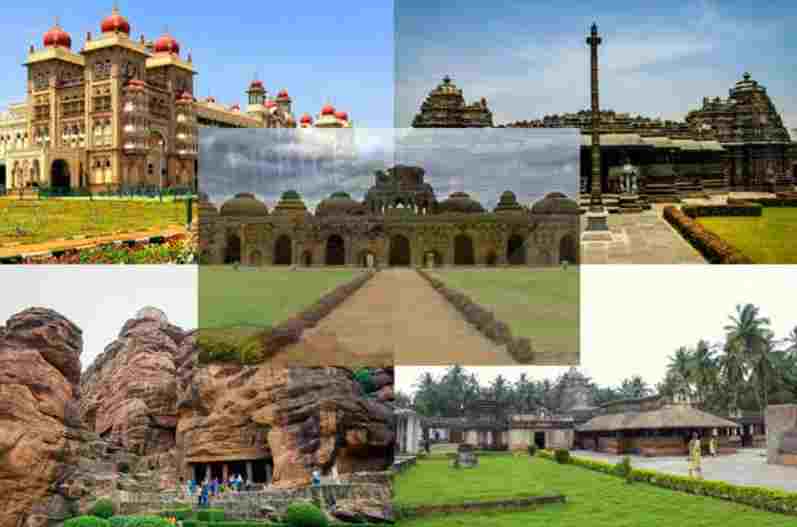

Places | Description |
Hampi
Mysore
Bijapur
Shimoga
Bangalore
Badami
Halebidu
Srirangapatna
Aihole
Dandeli
Ramanagaram
Hassan
Bidar
Talakadu
Melukote
Somnathpur
Mirjan Fort
Madikeri Fort
Sringeri
Pattadakal
Karkala | It is the city of ruins.
It is the city of palaces.
This city has the biggest domes in India.
Ancient Rulers and Dynasties were ruled.
It is the Silicon Valley.
The unique rock-cut temples are present in this city.
The history of the Hoysala empire.
Magnificent architectural masterpieces can be seen.
This place is the temple complex of Karnataka.
Ancient limestone caves are there.
Age-old silk trade.
It has an elegant hasanamba temple.
It is the seat of ancient kingdoms.
Temples buried in the sand.
The religious land.
It is the land of the Vaishnava temple.
Holding the historical ruins.
The gem of the 17th century.
It is also called a hill town and explores ancient relics.
The UNESCO heritage site.
Home to Jain temples. |
Holy Places In Karnataka
1. Hindu Temples In Karnataka

- Virupaksha Temple
- Hampi OmkareshwaraTemple
- Madikeri Shrikantheshwara Temple
- Mysore Virupaksha Temple
- Dharmasthala
- Shree Kotilingeshwara Temple
- Pattadakal Shri Kadri Manjunatha Temple
- Mangaluru Shri Kadri Manjunatha Temple
- Mangaluru Marikamba Temple
- Sagar Shri Kadri Manjunatha Temple
- Mangaluru Someshwara Temple
- Someshwara Ranganatha Swamy Temple
- Kukke Subrahmanya
- Temple Mangalore Kollur Mookambika Temple
- Murudeshwar
- Kudalasangama
2. Gurudwara In Karnataka

- Gurudwara Nanak Jhira (Bidar)
- Gurdwara Guru Nanak Prachar Sabha
3. Mosque In Karnataka
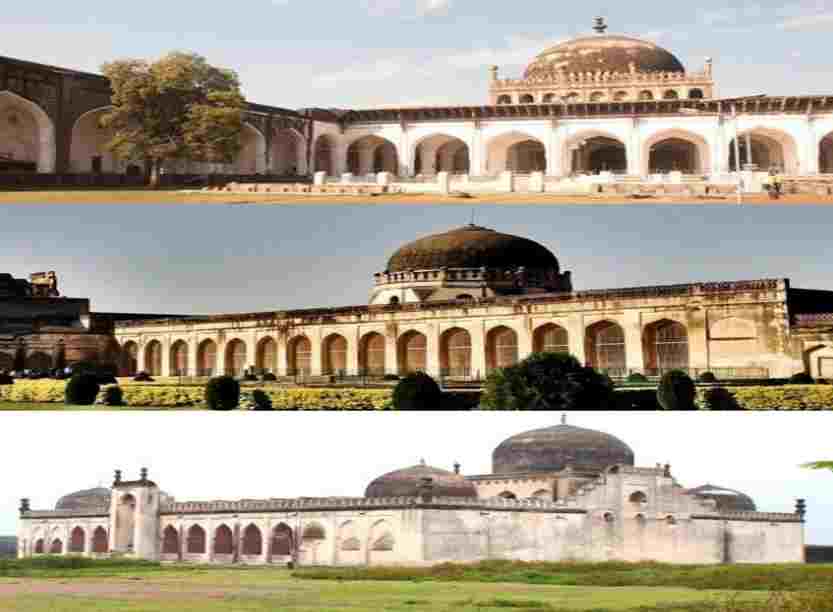

- Ek Minar Mosque in Raichur
- Solah-Khamba Mosque in Bidar
- Jamia Masjid in Bhatkal
- Jama Masjid in Bijapur
- Jama Masjid in Gulbarga
- Zanana Masjid in Bidar
4. Churches In Karnataka
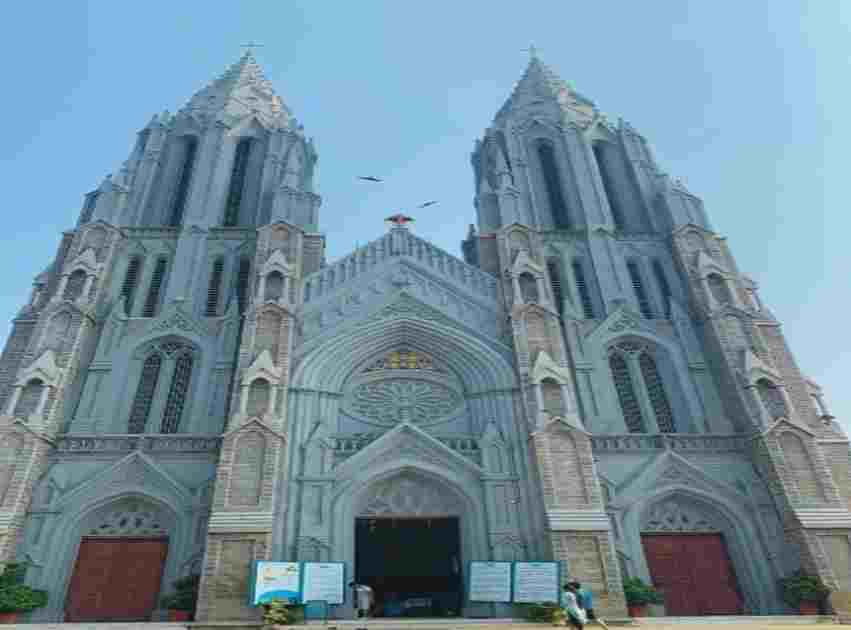

- Philomena’s Church, Mysore
- Mary’s Basilica, Bangalore
- Holy Trinity Church, Bangalore
- Bethel Assembly of God Church, Bangalore
- Andrew’s Church, Bangalore
- Most Holy Redeemer Church, Belthangady
5. Jain Temples In Karnataka
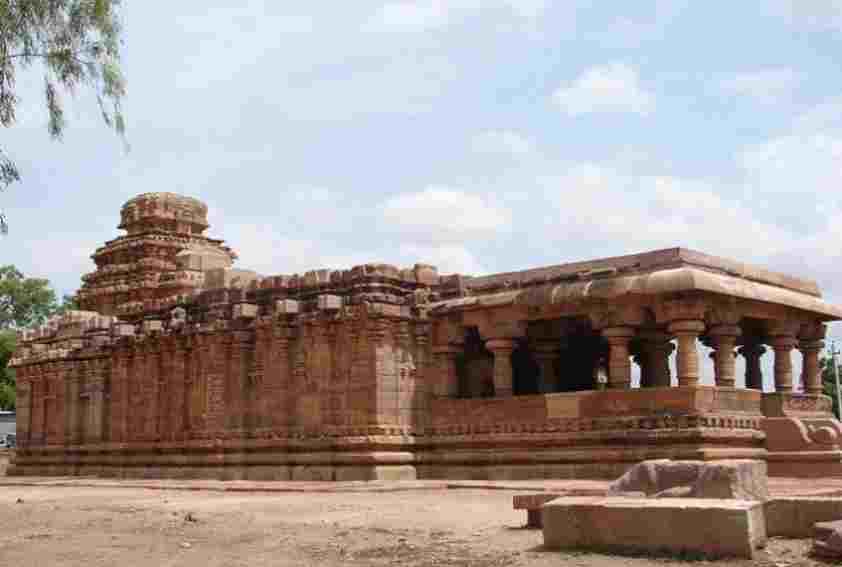

- Saavira Kambada Basadi Jain Temple (Moodabidri)
- Lakkundi Jain Temple(Udupi)
- Varanga Jain Temple (Udupi)
- Karkala Jain Temple (Udupi)
- Dharmasthala Jain Temple (Dharmasthala)
- Chaturmukh Basadi (Karkala)
- Sravanabelgola babubali (Hassan)
- Panchkuta Basadi (Kambadahalli village)
6. Buddhist Temples In Karnataka
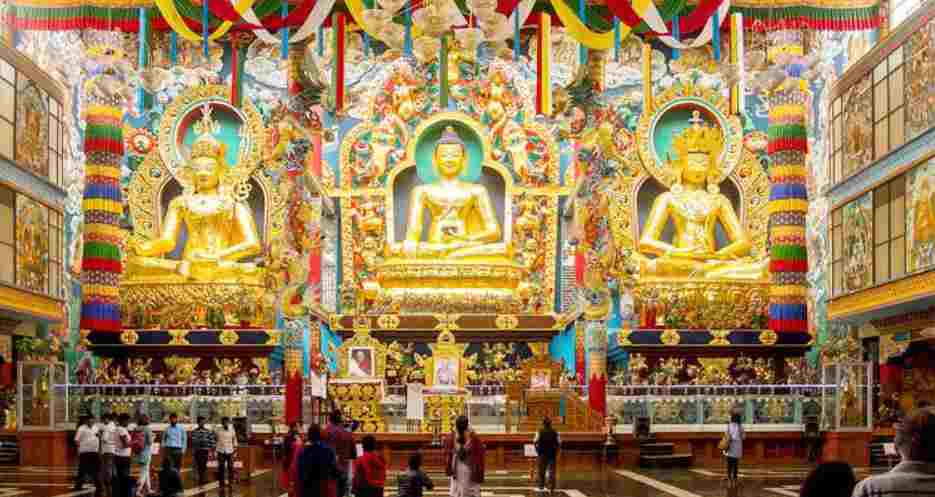

- Namdroling Monastery in Bylakuppe
- Tibetan Monastery in Mundgod
List Of Cuisines In Karnataka

- Neer Dosa – Authentic Karnataka Food Item
- Korri Gassi
- Kundapura Koli Saaru
- Mysore Masala Dosa
- Allugedda
- Mysore Pak
- Coorg Pandi Curry
- Haalbai
- Bisi Bele Bath
- Rava Kesari
- Mangalorean Biryani
- Kane Rava Fry
- Udupi Sambar
- Mango Chutney
- Mysore Bonda
- Sagu
- Ennegai
- Jolada Rotti
- Ragi Mudde
- Gojju
- Khara Pongal
- Chitranna
- Tatte Idli
- Chiroti
- Maddur Vada
- Pori Urundai
Important Points To Remember Regarding Karnataka State
| Sl.No | Question | Answer | Image | Description |
| 1. | State | Karnataka |
 |
Karnataka is a state in the southwestern region located in India. |
| 2. | Capital | Bengaluru |
 |
Known as both the “Garden City” and “The Silicon Valley of India” |
| 3. | Area | 1,91,791 sq.km | ||
| 4. | Population | 6,10,95,297 People | ||
| 5. | Language | Kannada |
 |
Different languages, including Tulu, Konkani, Kodava, and Beary, to name a few are also included but Kannada is the most widely spoken language in this state. |
| 6. | State formation day | 1 November (1956) | ||
| 7. | Rivers | Vrishabhavathi, Netravati, Tungabhadra, Godavari, Krishna, Cauvery, North Pennar, South Pennar, Palar, and West Flowing Rivers. |
 |
|
| 8. | State dance | Yakshagana, Dollu kunitha. |
 |
|
| 9. | Traditional dress | Mysore silk |
 |
The Coorgi dress style is similar to that of Karnataka, although with minor differences |
| 10. | State festival | Dussehra |
 |
|
| 11. | State famous food | Bisi bele bath |
 |
|
| 12. | No. of districts in Karnataka | 31 | ||
| 13. | State animal | Asian elephant |
 |
Scientific name- Elephas maximus |
| 14. | State bird | Indian roller |
 |
Scientific name- Coracias indica |
| 15. | State flower | Lotus |
 |
Scientific name- Nelumbo indica |
| 16. | State fish | Carnatic carp |
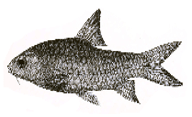 |
Scientific name- Hypselobarbus carnaticus |
| 17. | State butterfly | Southern Birdwing |
 |
Scientific name- Troides minos |
| 18. | State tree | Sandalwood |
 |
Scientific name- Santalum album |
| 19. | State emblem | |||
| 20 | State song | Jaya bharata jananiya tanujate | Which means -Victory to you mother India | |
| 21. | State flag | Yellow and red color flag |
 |
|
| 22 | State Fruit Of Karnataka | Mango |
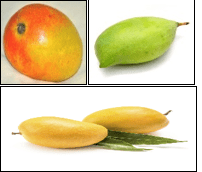 |
Scientific name- Mangifera indica Varieties such as Neelum, Pairi / Raspuri, Totapuri, Alphonso, and Mulgoa |
Districts And Taluks In Karnataka
| Code | District and headquarters | Established on | Subdivisions (taluk) | Area |
| BK | Bagalkot Headquarters- Bagalkot | 15 August 1997 | Badami Bagalkot, Bilgi, Ilkal, Hunagunda, Rabkavi Banhatti, Terdal, Guledgudda, Jamkhandi, Mudhol | 6,575 km2 (2,539 sq mi) |
| BN | Bangalore Urban Headquarters- Bangalore | 1 November 1956 | Anekal, Yelahanka, Bangalore North, Bangalore East, Bangalore South | 2,190 km2 (850 sq mi) |
| BR | Bangalore Rural Headquarters- Bangalore | 15 August 1986 | Devanahalli, Doddaballapura, Hosakote, Nelamangala | 2,259 km2 (872 sq mi) |
| BG | Belagavi Headquarters- Belagavi | 1 November 1956 | Athni Bailhongal, Belgaum, Chikodi, Gokak, Hukkeri, Khanapur, Kagawad, Mudalagi, Nippani, Kittur, Raybag, Ramdurg, Saundatti, Yaragatti | 13,415 km2 (5,180 sq mi) |
| BL | Bellary Headquarters- Bellary | 1 November 1956 | Bellari, Kampli, Kurugodu, Sanduru, Siruguppa | 4,252 km2 (1,642 sq mi) |
| BD | Bidar Headquarters- Bidar | 1 November 1956 | Bidar, Basavakalyan, Kamalnagar, Hulasuru, Chitgoppa, Bhalki, Homnabad, Aurad | 5,448 km2 (2,103 sq mi) |
| BJ | Vijayapura Headquarters- Vijayapura | 1 November 1956 | Vijayapura, Indi, Muddebihal, Babaleshwar, Nidagundi, Tikota, Devara Hippargi, Talikote, Chadchan, Sindgi, Basavana Bagevadi, Almel | 10,498 km2 (4,053 sq mi) |
| CJ | Chamarajanagar Headquarters- Chamarajanagar | 15 August 1997 | Chamarajanagar, Gundlupet, Kollegal, Hanur, Yelandur | 5,101 km2 (1,970 sq mi) |
| CB | Chikballapur Headquarters- Chikballapur | 10 September 2007 | Bagepalli, Chikballapur, Chintamani, Gauribidanur, Gudibanda, Sidlaghatta | 4,524 km2 (1,747 sq mi) |
| CK | Chikmagalur Headquarters- Chikmagalur | 1 November 1956 | Chikmagalur, Kadur, Koppa, Mudigere, Kalasa, Narasimharajapura, Sringeri, Ajjampura, Tarikere | 7,201 km2 (2,780 sq mi) |
| CT | Chitradurga Headquarters- Chitradurga | 1 November 1956 | Challakere Chitradurga Hiriyur Holalkere Hosadurga Molakalmuru | 8,440 km2 (3,260 sq mi) |
| DK | Dakshina Kannada Headquarters- Mangalore | 1 November 1956 | Bantwal Beltangadi Mangalore Moodabidri Kadaba Puttur Sulya | 4,560 km2 (1,760 sq mi) |
| DA | Davanagere Headquarters- Davanagere | 15 August 1997 | Channagiri Davanagere Harihar Honnali Jagalur Nyamati | 4,460 km2 (1,720 sq mi) |
| DH | Dharwad Headquarters- Dharwad | 1 November 1956 | Annigeri Alnavara Dharwad Hubli Hubli City Kalghatgi Kundgol Navalgund | 4,260 km2 (1,640 sq mi) |
| GA | Gadag Headquarters- Gadag | 24 August 1997 | Gadag-Betigeri Mundargi Nargund Gajendragad Lakshmeshwar Ron Shirhatti | 4,656 km2 (1,798 sq mi) |
| GU | Kalaburagi Headquarters- Kalaburagi | 1 November 1956 | Afzalpur Aland Chincholi Chitapur Gulbarga Kamalapura Kalagi Jevargi Sedam Shahbad Yedrami | 10,951 km2 (4,228 sq mi) |
| HS | Hassan Headquarters- Hassan | 1 November 1956 | Alur Arkalgud Arsikere Belur Channarayapattana Hassan Holenarsipur Sakleshpur | 6,814 km2 (2,631 sq mi) |
| HV | Haveri Headquarters- Haveri | 24 August 1997 | Byadgi Hangal Haveri Hirekerur Ranibennur Rattihalli Savanur Shiggaon | 4,823 km2 (1,862 sq mi) |
| KD | Kodagu Headquarters- Madikeri | 1 November 1956 | Madikeri Kushalanagar Virajpet Somvarpet Ponnampet | 4,102 km2 (1,584 sq mi) |
| KL | Kolar Headquarters- Kolar | 1 November 1956 | Bangarapet Kolar Kolar Gold Fields Malur Mulbagal Srinivaspur | 3,969 km2 (1,532 sq mi) |
| KP | Koppal Headquarters- Koppal | 24 August 1997 | Gangawati Kanakagiri Kuknur Karatagi Koppal Kushtagi Yelbarga | 7,189 km2 (2,776 sq mi) |
| MA | Mandya Headquarters- Mandya | 1 November 1956 | Krishnarajpet Maddur Malavalli Mandya Nagamangala Pandavapura Shrirangapattana | 4,961 km2 (1,915 sq mi) |
| MY | Mysore Headquarters- Mysore | 1 November 1956 | Heggadadevana kote Hunsur Krishnarajanagara Mysore Nanjangud Piriyapatna Saragur T.Narsipur | 6,854 km2 (2,646 sq mi) |
| RA | Raichur Headquarters- Raichur | 1 November 1956 | Devadurga Lingsugur Manvi Maski Raichur Sindhnur Sirwar | 8,440 km2 (3,260 sq mi) |
| RM | Ramanagara Headquarters- Ramanagara | 10 September 2007 | Channapatna Kanakapura Ramanagara Magadi | 3,556 km2 (1,373 sq mi) |
| SH | Shimoga Headquarters- Shimoga | 1 November 1956 | Bhadravati Hosanagara Sagar Shikaripura Shimoga Sorab Thirthahalli | 8,477 km2 (3,273 sq mi) |
| TU | Tumkur Headquarters- Tumkur | 1 November 1956 | Chiknayakanhalli Gubbi Huliyar Koratagere Kunigal Madhugiri Pavagada Sira Tiptur Tumkur Turuvekere | 10,597 km2 (4,092 sq mi) |
| UD | Udupi Headquarters- Udupi | 25 August 1997 | Udupi Brahmavara Karkal Kapu Kundapura Hebri Byndoor | 3,880 km2 (1,500 sq mi) |
| UK | Uttara Kannada Headquarters- Karwar | 1 November 1956 | Ankola Bhatkal Dandeli Haliyal Honnavar Joida Karwar Kumta Mundgod Siddapur Sirsi Yellapur | 10,291 km2 (3,973 sq mi) |
| VN | Vijayanagara Headquarters- Hospet | 18 November 2020 | Harapanahalli Hagaribommanahalli Hoovina Hadagali Hospete Kottur Kudligi | 5,644 km2 (2,179 sq mi) |
| YD | Yadgir Headquarters- Yadgir | 30 December 2009 | Gurumitkal Hunasagi Shahpur Shorapur Vadagera Yadgir | 5,234 km2 (2,021 sq mi) |
Top 13 Interesting Facts About Karnataka State
It was revealed that the land was founded on November 1, 1956, and was formerly known as the ‘Mysore state.’ It was only in 1973 that the name was revised and changed to Karnataka.
Karnataka is home to 13 different languages, including Tulu, Konkani, Kodava, and Beary, to name a few. Kannada is the most widely spoken language in the state.
Hampi is a well-known UNESCO World Heritage Site recognized for its temples and ancient complexes. The town bears evidence of the Vijayanagar Empire’s grandeur, which is supposed to have lasted longer than the Mughal Empire.
Silk, sandalwood, and spices, among other things, are produced in enormous quantities in Mysore. The Karanji Lake near Mysore, on the other hand, is known for its walk-through aviary, which is India’s largest.
Karnataka is the largest coffee exporter in the country and is also known for beautiful plantation crops in the state.
Many national parks and wildlife sanctuaries have been established in Karnataka, and the presence of the Western Ghats has allowed the tiger population to recover. According to a report, the appearance of these wild cats has revitalized nature sanctuaries and parks.
58 feet tall gomateshwara statue is the world’s biggest monolithic statue situated at Shravanabelagola, a town 144 km away from Bangalore.
Jog Falls is a Sharavati River waterfall in the Western Ghats near Sagar Taluk in Shivamogga District. A plunge waterfall falls vertically without making contact with the rocks as it descends. Gersoppa Falls, popularly known as the “Jog Falls,” is India’s second-highest plunge waterfall.
Karnataka has won a total of 8 Jnanpith literary awards.
The only unit in India with the authority to manufacture and supply the ‘Indian Flag.’ It was established in 1957 and is located in Bengeri, Hubli.
Rava Idli is a popular Idli variety that was accidentally created during World War II due to a lack of rice. Instead of rice, semolina (durum wheat) was utilized, resulting in a delectable culinary item that has been treasured for decades.
Within the state of Karnataka, the district of Vijayapura, also known as Bijapur, sees the passage of five rivers, including the tributaries of Krishan, Doni, Bhima, Ghataprabha, and Malaprabha. The ‘Five Rivers Land’ is another name for the district.
Karnataka’s history tells the valiant account of a queen who stood her own and opposed the British colonial power decades before Rani Laxmibai’s ascenttory. Rani Chennamma, also known as Kittur Chennamma, was the queen of Kittur, which used to be a prince chevalier. She revolted against the Kappa tax and launched an armed uprising against the East India Company.

For deep details, you can read the full article. Click the link below :



