
- Juvenile delinquency means the involvement of a minor in any anti-social activity. A person below the age of 18 is immature and his acts are considered puerile. There are various factors in an individual that may lead to his delinquent behavior like poverty, inappropriate parental upbringing, unemployment, peer pressure, etc. There are numerous laws to deal with juvenile offenders. Juvenile delinquency is a very severe issue. To overcome this problem significant steps should be taken.
Who Is Juvenile?
Any person between the age of 10 to 18 years is referred to as a Juvenile. The word juvenile means immature or childish. A young person under the age of 18 is not considered to be mature enough to be titled an adult. As the word itself invokes the terms like immature and childish, it is assumed that a person beneath the age of 18 is not mature enough to make the right decisions in life, their acts are often considered as puerile which are outcomes of an immature mindset.
What Does Juvenile Delinquency Mean ?
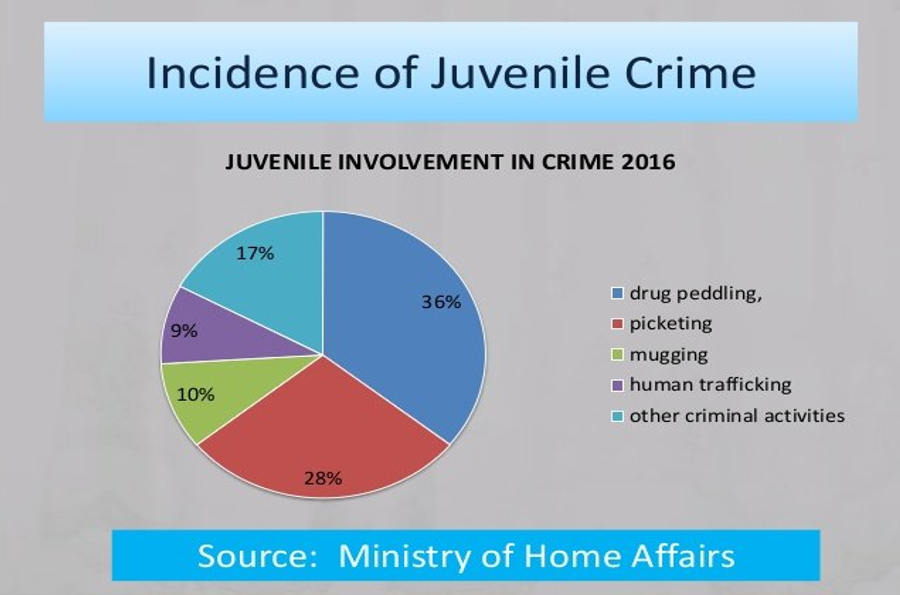
- Juvenile delinquency refers to any crime or illegal activity performed by any person below the age of 18. As it is already mentioned that a person under 18 years is perceived as immature and his actions are the outcome of a puerile mindset. They don’t pay scrupulous attention to their actions that’s why they are more prone to give their assent to wrong actions.
Causes Of Juvenile Delinquency

- There are various factors in an individual that may lead to his delinquent behavior. A minor who is deprived of basic education has more tendency of developing delinquent behavior as education provides the right mindset to a person. Besides this there are other factors as well like poverty, peer pressure, the bad family setup, etc. There are manifold reasons behind this i.e why juveniles use to commit crimes. Some of the major reasons are elaborated on below:-
1. Poverty
It would not be wrong to say that poverty is the key factor that leads to juvenile delinquency. It can be described as a condition where the basic needs of a family-like food, shelter, clothing, etc. are not fulfilled.
It is truly said by Mahatma Gandhi that “ poverty is the worst form of violence “. It is hard to assume that in our country there are children, who use to suffer for food, do not use to get sufficient nutrients, and are even deprived of a proper place to live, etc.
We might always wonder that why juveniles use to commit crimes? why do they choose the wrong path?
As we know that poverty adversely affects a child’s mind. The urge to eat and live properly forces them to choose the wrong path. When their basic needs are not satisfied they wish to fulfill them by hook or by crook.
Obviously, it could not be the justification for committing a crime but it’s true that their situation compels them to do so.
But if this is the case then every poor kid should commit crimes to fulfill their basic desires. Then why some use to commit crimes and others don’t? Why only some of them choose the wrong path and others use to choose the path of hard work ?
- Well, this is the point where it comes about the parental upbringing of a child. This is the most crucial thing that, how parental upbringing use to affect a child’s mindset.
2. How Parental Upbringing Effects Juvenile Delinquency?
A child’s mind is like a pot in making, it will take the shape we will give to it.
The thought process of parents is directly used to affect a child’s mindset. Whatever will be inculcated in a child’s mind at an early age, it will stay forever.
There is a high probability that due to being deprived of basic needs, somehow the poor kids have a higher tendency of getting a thought to choose the wrong path or commit crimes to fulfill their basic needs.
At the point when this thought used to pop up in their mind, how does parental upbringing helps to avoid it?
Let us discuss this;
It is very obvious that no parent would ever teach his kid to choose the wrong path then, how this thought comes into a child’s mind?
=> Let us assume a situation that there are two kids:-
There is child A, whose parents have never taught him to commit crimes like stealing and pickpocketing, etc. to fulfill his basic needs. But nor have his parents taught him that, how committing crimes for fulfilling basic desires can have bad consequences. They didn’t guide him that, how hard work can one day help him to overcome poverty.
Now there’s a child B
His parents have also not taught him to commit crimes to fulfill his basic needs. But they have inculcated in his mind that what can be the bad consequences of committing crimes. They have taught him that how hard work will one day help him to achieve success and overcome poverty.
Now there comes a time when child A and child B both use to be depressed due to being deprived of their basic needs.
At this point, the thought of committing crimes like stealing, pickpocketing, etc. comes into both of their minds.
But only child A use to choose the wrong path, whereas child B didn’t. why?
- Well, this is because, when this thought comes into the mind of child B, he is able to recall that, his parents have taught him about the consequences of committing a crime. He can overpower this thought of committing a crime by all the positive thoughts inculcated in his mind by his parents. His upbringing helps him to question whether his thoughts are wrong or right, he can differentiate.
Whereas child A can’t do that because his parents didn’t inculcated these teachings in his mind .
So this is how , right parental upbringing can avoid juvenile delinquency and wrong parental upbringing can lead to increase in juvenile delinquency.
But all those who juveniles who use to commit crime , are always not from poor families this means only poverty can’t be the reason for juvenile delinquency. There are other reasons as well like
3. Unemployment
Unemployment is a very profound problem in today’s scenario. It can be described as a situation where one who is capable of working is actually seeking to work but is unable to find any work. It is very unfortunate that there are many educated as well as uneducated people who are still unemployed and are not able to get jobs. Talking about educated unemployed people. Since childhood, it is inculcated in our minds that if we will study wholeheartedly and will work hard we will get success and a well-paying job.
But when a person used to study and work so hard but still is unable to find an appropriate job then he is not able to meet the needs of his family. Children of such people suffer a lot, an unemployed person is not able to raise his children properly. His children use to be deprived of education and lack of education is a major factor why juveniles commit crimes. Education teaches a child a lot of things, on the contrary, a child deprived of education is deprived of the right mindset as well.
So in some or the other way unemployment leads to Juvenile delinquency.
Besides this, there are many juveniles who belong to Well-settled families but still somehow even they use to commit crimes, a possible reason for this can be peer pressure.
4. How Peer Pressure Can Lead To Juvenile Delinquency?
Who is a peer?
- Our friends, our peers are people of our age or close to it who use to have almost similar interests .
What is peer pressure?
- Peer pressure is the influence of our friends on us. Which molds our behavior and beliefs. It’s when we want to do something because we want to be fully accepted and valued by our friends. Our friends use to affect our choices.
There are numerous kids who belong to well-off families. But peer pressure makes them feel that whatever they are having or whatever their parents are providing them is not sufficient. The desire to get more forces them to commit crimes and to choose the wrong path to fulfill their desires.
Peer pressure can be positive as well as negative. Positive peer pressure can help in the enhancement of a person, whereas negative peer pressure can lead to Juvenile delinquency.
Sometimes the stress can actually be from our peers. They use to give us pressure, to do something we are not comfortable with but we will do it just because we want to be accepted by them. These activities can be, doing drugs or drinking, taking dangerous risks when driving a car, or having sex before we feel ready.
Let us understand it better with an example.
Our peers may create pressure on us like, in a party where we do not prefer drinking if our peers will see that (you are not a kid anymore that, you want to drink soft drink, grow up dude).
This statement can create pressure on us as we will feel insulted and as a result, we will drink.
We might be careful about not driving, while we are drunk and suddenly some of our friends says that (you are such a coward, don’t even know how to drive properly). This sentence will create pressure on us again and we will feel insulted and will do the thing we were not willing to do just to prove that we are not a coward we might do it.
This is how peer pressure can force juveniles to commit crimes.
Responding to peer pressure is a part of human nature but some people are more likely to be influenced and others may have more power to resist.
5. Why The Problem Of Juvenile Delinquency Should Be Taken Seriously ?
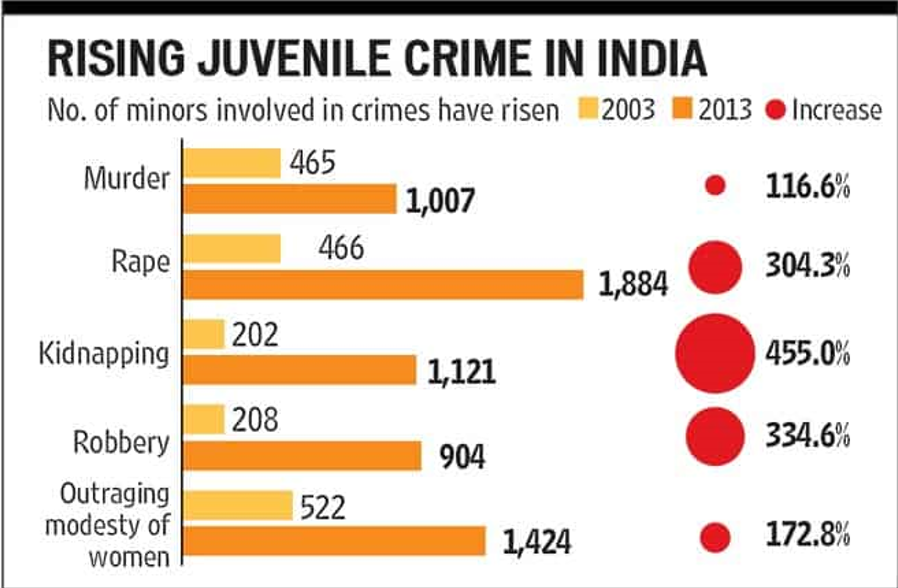
Juvenile delinquency is a very severe issue. As it is believed that children are the future of our nation, if the children will choose the wrong path, another country will suffer. We need people who will think about their development and will add some value to the economy, not people who will become a threat to the nation.
Juveniles are at an age where their thought process can be molded. Their mindset can be given the right direction. After a certain age, it becomes difficult to change the thought process of a person. Juveniles have more tendency of being influenced, that’s why Juvenile delinquency should be taken as a serious problem and should be corrected before it’s too late.
Juvenile Justice System

The term ‘juvenile’ has been defined in clause (h) of Section 2 of the Juvenile Justice Act, 1986. The term ‘delinquency’ has been defined in the clause of section 2 of the Juvenile Justice Act, 1986.
Juvenile Justice Act, 1986, was the first central legislation on Juvenile Justice, prior to which each state had its own enactment on juvenile justice, which differed in the way juveniles were treated by the different state legal systems. The Indian Constitution provides in clause (3) of Article 15 and clauses € and (f) of Article 39, Article 47, and Article 45.
On 20th November 1989, the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Convention on the Rights of the Child i.e. right to survival, protection, development, and participation. The Government of India, ratified the said UN Convention on the 11th December 1992, and re-enacted the existing law, viz., Juvenile Justice Act, 1986.
However, since it did not yield the expected result, so the government proposed an act called the Juvenile Justice (Care and protection of children) Act, 2000. The Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2000, which has replaced the earlier Juvenile Justice Act, 1986, has been enforced in the entire country except the State of Jammu & Kashmir from 1st April 2001.
How Juvenile Justice System Is Different From Criminal Justice System?
In the case of juvenile offenders, only in serious cases, FIR and charge sheets are filled, and in such cases, the punishment for the offense exceeds seven years.
Grant of bail to the juvenile offenders in conflict with law is a rule.
The criminal trial aims at finding the guilt or innocence with the object to punish the offender but juvenile trial aims at reformation and rehabilitation of the errant juvenile who is in conflict with the law.
In most jurisdictions, including Minnesota, when juvenile cases go to trial, the child is not afforded a jury trial like in adult court. Rather, one judge is the finder of fact at a trial. While difference makes for shorter trials since the lawyers do not have to spend days picking a jury, the juvenile and his/her lawyer do not get the benefit of multiple finders of fact. The child is still considered innocent until proven guilty, the prosecutor only has to convince one person of guilty beyond a reasonable doubt, versus an entire jury.
In adult court, if the defendant is found guilty, they are “convicted”, whereas in juvenile court the child is “adjudicated, delinquent”.
Is It Right To Be Liberal With Juvenile Offenders And What Is The Probability That They Will Not Commit Crimes Again?
- Well, it depends upon the situation or case that should juvenile offenders be treated liberally or not. Let’s take a look at some cases of juvenile offenders.
Nirbhaya Gang-Rape
- The 2012 Delhi gang-rape and fatal assault is a widely known case in which one of the criminal was minor.. This was a very severe case and handling it liberally could lead to increase in such crime. Tackling this case with liberally will work as a loophole of the system , it would be assumed that committing such severe crime will not have bad consequences . That’s why such cases should not at all be handled liberally.
Teen Kills Brother For 40 Rs
- A boy killed his brother for 40 Rs! In Aurangabad, a 14-year-old admitted to murdering his brother a day after their tussle for money. This is a case that needs to be handled liberally as this is a case of immature mindset, the child needs the right direction of thoughts.
Conclusion
- We can say that nothing one does for a child can ever be wasted. Small acts of kindness done towards the child can have great impact and may go a long way in transforming a deviant juvenile into a great man. One should also not forget that children are great imitators. So if society is to improve, we must necessarily forgive the children, even if they are delinquents but at the same time, societal interest cannot be put to stake. If we show mercy towards them, even the most hardened juvenile delinquent may be reformed. There is a dire need to create a mechanism for assessing the needs and requirements of the juveniles and this should be reviewed regularly. India needs to adopt a model which could balance between the need to rehabilitate the juvenile offenders and at the same time take responsibility for his crime and ensure justice for the victims. As a parting note one would say that “every child one encounters is a divine appointment” and we must do our best to uphold the sanctity of this divine entity, if the society is to flourish and thrive.
Top 13 Important Facts About Juvenile Delinquency
The delinquency rates are much higher among boys than girls i.e girls commit less crime than boys.
From 1994 to 2004, there was a 21% increase in the number of youth who were held in adult jails.
In 2006, nearly 20% of people were arrested for violent crimes.
Were under the age of 18 and boys represented 83% of juvenile arrests for these violent crimes.
In 2006, about one-quarter of boys reported they carried a handgun by the age of 17, while 11% reported they belonged to a gang.
More than 25% of persons arrested for property crimes were under age 18 and boys made up 68% of juvenile arrests for property crimes, according to 2006 figures.
Girls are more often arrested for status offenses than for criminal offenses. Boys are arrested for criminal offenses more than girls are.
Violent crimes committed by juveniles in 2006 occurred most often between 3 p.m. and 4 p.m.–around the time the school day ended.
Though overall rates have been declining over the past years, approximately 1.7 million delinquency cases are disposed of in juvenile courts annually.
Approximately 57 percent of adjudicated youth are placed on probation.
Youth in the juvenile justice system are identified as eligible for special education services at three to seven times the rate of youth outside the system
When a student is suspended or expelled, there is a significant increase in his or her likelihood of being involved in the juvenile justice system the subsequent year.
A high percentage of youth (65 to 70 percent) involved with the juvenile justice system have a diagnosable mental health disorder and nearly 30 percent of those experience severe mental health disorders.
Many incarcerated youth are marginally literate or illiterate and have already experienced school failure.







