
The Earth is what we all have in common
– Wendell Berry, Novelist
Introduction
- Earth is the third planet from the sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large amounts of water can be found throughout the Solar System, Only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth’s surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth’s polar ice, lakes, and rivers.
=> Facts About The Earth;
- The Earth is the densest planet in the solar system.
- Earth has a powerful magnetic field.
- Earth is the fifth-largest planet in our solar system.
- Earth is formed over 4.5 billion years ago.
- Earth is the planet we live on and the only planet to support life.
- Earth is a largest rocky planet in the solar system.
Interior Of The Earth
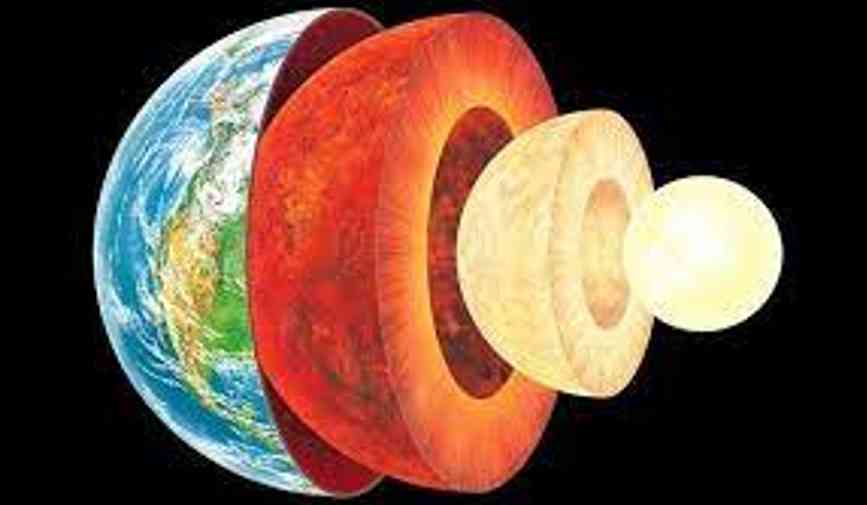
- The Earth’s radius is 6370 km. It is rather difficult to make observations or collect samples of the material from inside of the earth due to its internal composition. Most of our understanding of the interior of the earth is based on direct or indirect sources.
Direct Sources Of Information
1. Surface Rock

- It is the most readily available solid earth material to make direct observations. Laboratory experiments on surface rocks and minerals provide important information about the interior of the Earth.
2. Mining

- Rocks that we get from mining areas are another source that gives us information about Earth’s interior. Through mining and drilling operations we have been able to observe the earth’s interior directly up to a depth of a few kilometers.
3. Deep Ocean Drilling Project

- Scientists have undertaken some major projects to penetrate the surface of oceans to assess the conditions in crustal portions. Deep Drilling projects have provided a large volume of information through the analysis of materials collected at different depths.
4. Volcanic Eruptions

Volcanic eruption forms an important source of obtaining direct information through laboratory analysis of molten materials (magma) that are thrown onto the surface of the Earth.
Indirect Sources Of Information
1. Meteors

- Meteors are bits of interplanetary material falling through Earth’s atmosphere and heated by friction. Meteors that at times reach the earth are an important source of information about the interior structure of the Earth.
2. Gravitation

- The reading of the gravity at different places is influenced by many factors which is the distribution of mass, distance from the center of the earth.
3. Magnetic Field
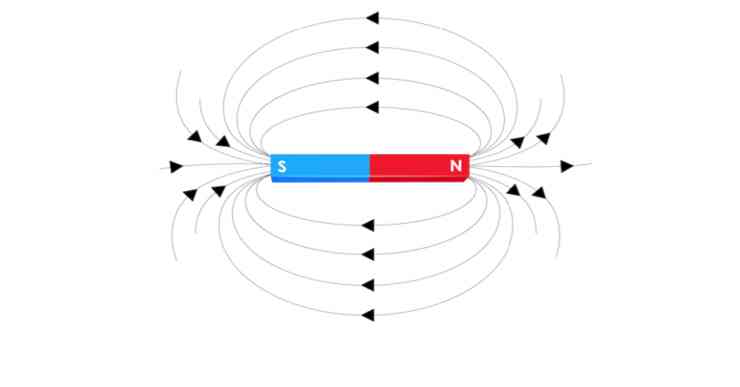
- Magnetic surveys provide information about the distribution of magnetic materials in the crustal portion.
4. Seismic Activity

- Seismic Activity is one of the most important sources of information about the interior of the Earth. Body waves generated by an earthquake helped in understanding the interior structure of the earth.
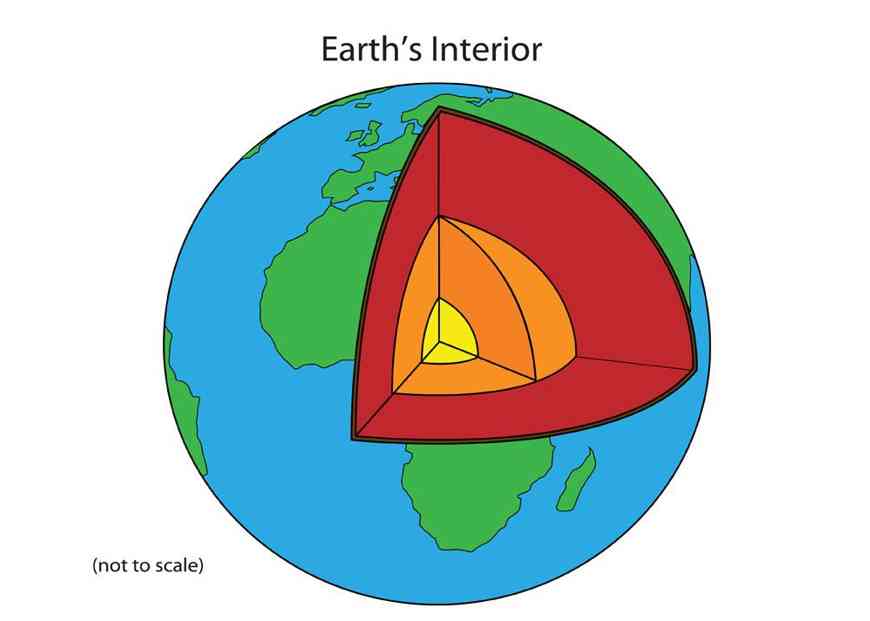
Structure Of Earth
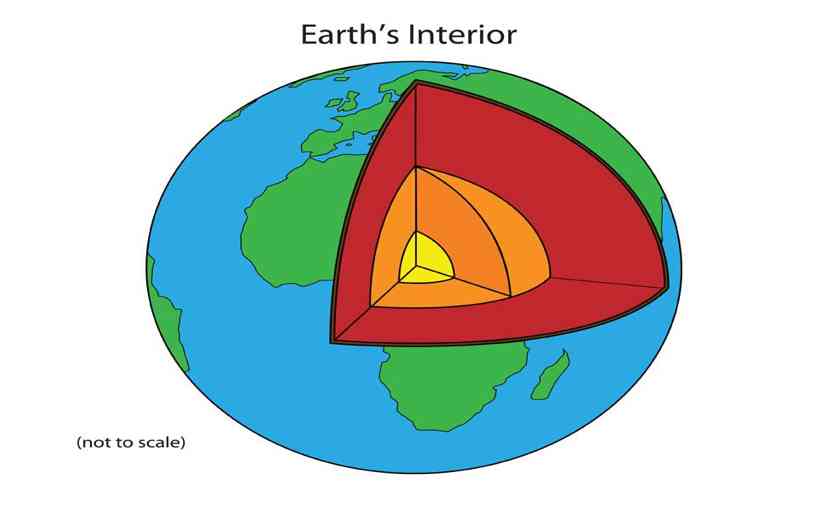
The internal structure of Earth refers to concentric spherical layers subdividing the solid Earth. It consists of an outer silicates solid crust, a highly viscous asthenosphere and solid mantle, a liquid outer core whose flow generates the Earth’s magnetic field, and a solid inner core.
Scientific understanding of the internal structure of Earth is based on the observations of Topography and Bathymetry.
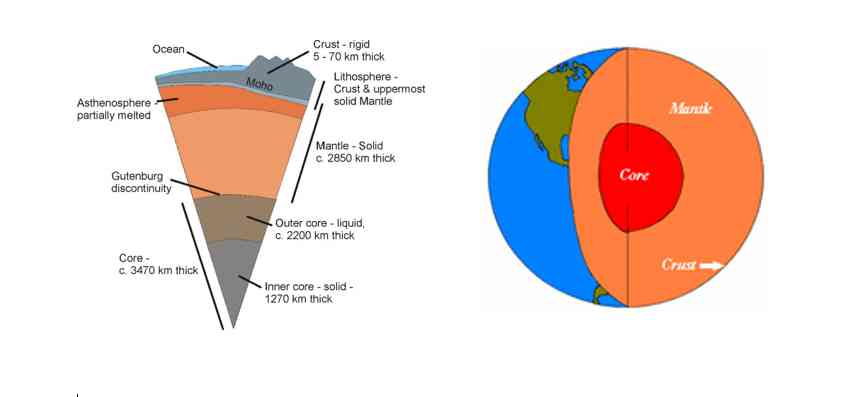
The structure of Earth can be defined in two ways:
- Mechanically, it can be divided into Lithosphere, Asthenosphere, mesospheric mantle, outer core, and the inner core.
- Chemically, Earth can be divided into the crust, upper mantle, lower mantle, outer core, and inner core.
The Layers Of The Earth
- Earth comprises four separate layers. Most geologist believes that as the Earth cooled, the heavier and the denser material sank into the center and the lighter ones rose towards the top. Due to this, the outermost layer is made of the lightest materials such as rocks and granites and the innermost layer consists of nickel and iron. Let’s discuss different layers of Earth.
Different Layers Of The Earth
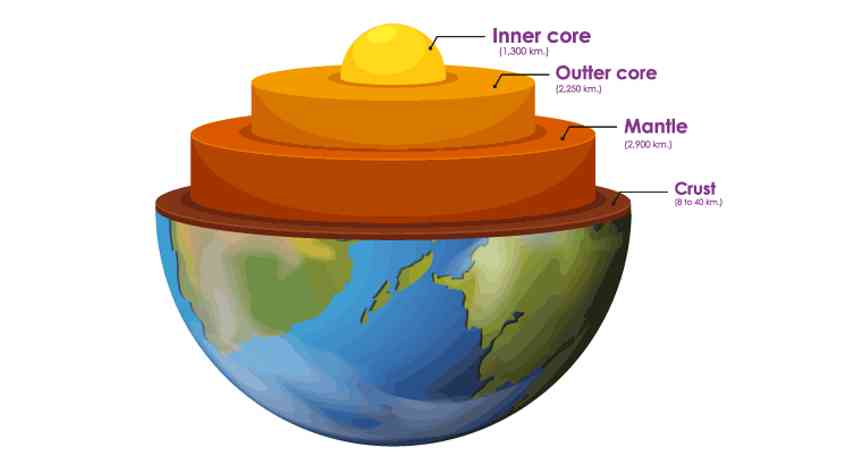
=> Chemically, Earth can be divided into the following:-
1. Crust
2. Mantle
- Upper mantle
- Lower mantle
3. Core
- Outer core
- Inner core
The Crust

The crust is the outermost layer of the earth making up 0.5-1.0 percent of the earth’s volume and less than 1 percent of Earth’s mass.
Density increases with depth and the average density is about 2.7g/cm3.
The thickness of the crust varies in the range of 5-30 km in the case of the oceanic crust and as 50- 70 km in the case of the continental crust.
The continental crust is thicker than the oceanic crust.
The temperature of the crust increases with depth.
The outer covering of the crust is of sedimentary material and below that lie crystalline, igneous and metamorphic rock.
The lower layer of the crust consists of basaltic and ultra-basic rocks.
It is brittle in nature.
Oceanic crust is denser as compared to the continental crust.
Continental crust covers land and Oceanic crust covers ocean.
The elements of crust are Silica and Aluminum and it is often called SIAL.
The lithosphere is the region consisting of the crust and uppermost solid mantle.
The mean density of the materials in the crust is 3g/cm3.
The discontinuity between the hydrosphere and crust is termed the Conrad Discontinuity.
=> Most Abundant Elements of the Earth’s Crust
1) Oxygen 46.6%
2) Silicon 27.7%
3) Aluminum 8.1%
4) Iron 5.0%
5) Calcium 3.6%
The Mantle
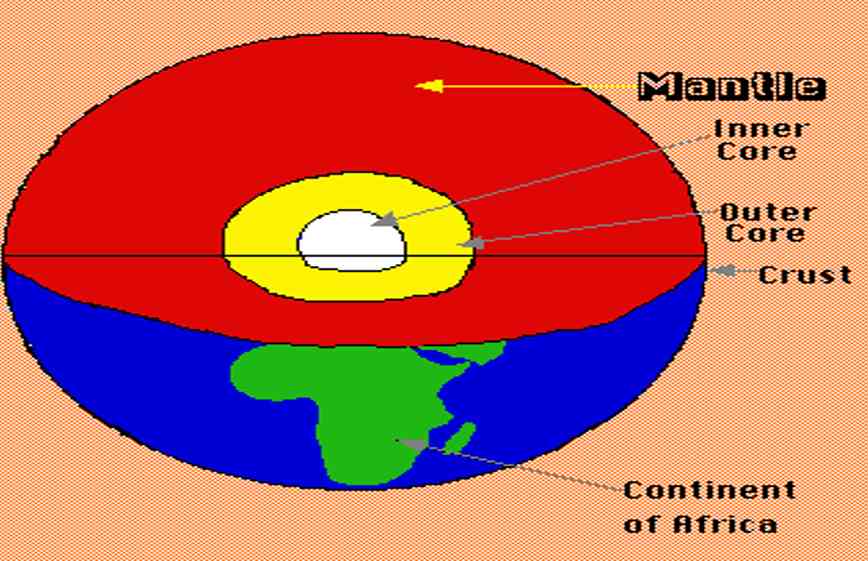
The second layer or the interior beyond the crust is called as the mantle.
The thickness of the mantle is about 2900kms.
Approx 84% of the earth’s volume and 67% of the earth’s mass is occupied by the mantle layer.
The major constituent elements of the mantle are silicon and magnesium and hence it is called as SIMA.
The density of layer is higher than the crust and varies from 3.3- 5.4 g/cm3.
It is dense, hot and semi solid.
It is the largest layer of the earth.
The discontinuity between the crust and mantle is called as the Mohorovicic discontinuity or Moho discontinuity.
The discontinuity between the upper mantle and the lower mantle is known as Repetti discontinuity.
It forms about 83%of the earth’s volume and holds 67%of the earth’s mass.
The lower mantle extends beyond the Asthenosphere. It is in a solid state.
The mantle is composed of silicate rocks that are rich in iron and magnesium.
Regarding its constituent elements, the mantle is made up of 45% oxygen, 21% silicon and 21% magnesium.
The Core
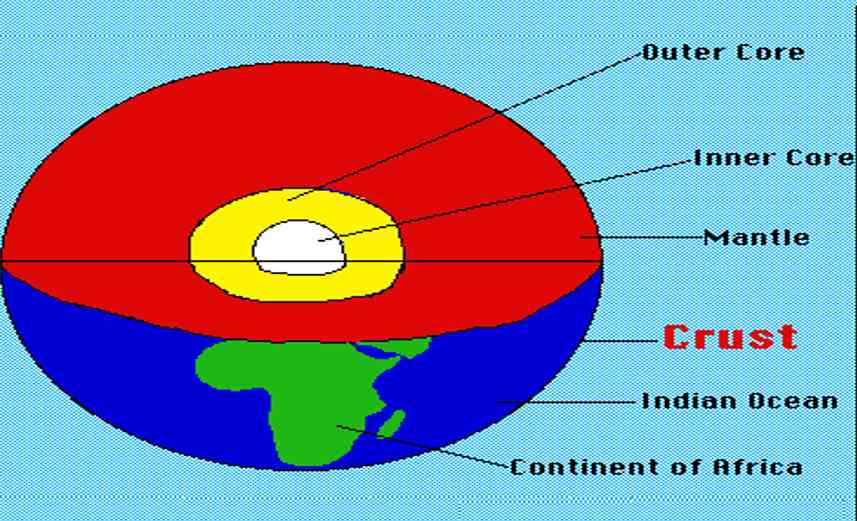
1. The outer core
The outer core, surrounding the inner core lies between 2900 km and 5100 km below the earth’s surface.
The outer core is composed of iron mixed with nickel.
The outer core is not under enough pressure to be solid, so it is liquid even though it has a composition similar to the inner core.
The density of the outer core ranges from 9.9 g/cm3 to 12.2 g/cm3.
The temperature of the outer core ranges from 4400 c in the outer regions to 6000 c near the inner core.
Dynamo theory suggests that convection in the outer core, combined with the Corioliss effect, gives rise to Earth’s magnetic field.
2. The Inner core
The inner core extends from the center of the earth to 5100 km below the earth’s surface.
The inner core is composed of iron and some nickel.
Earth’s inner core rotates slightly faster relative to the rotation of the surface.
The solid inner core is too hot to hold a permanent magnetic field.
The density of the inner core ranges from 12.6 g/cm3 to 13g/cm3.
The core accounts for just about 16% of the earth’s volume but 33% of the earth’s mass.
At 6000 c, this iron core is as hot as the sun’s surface but the crushing pressure caused by gravity prevents it from becoming liquid.
Lehmann discontinuity separates the solid inner core from the liquid outer core.
Temperature, Pressure And Density Of Earth’s Interior
The temperature increases towards the centre of the earth. However, the rate of increase of temperature is not uniform from the surface towards the earth’s centre.
The temperature at the centre is estimated to lie somewhere between 3000c and 50000 c.
Such a high temperature inside the earth may be due to chemical reactions under high-pressure conditions and the disintegration of radioactive elements.
The pressure also increases from the surface towards the centre of the earth due to the huge weight of the overlying rocks.
Due to the increase in pressure and the presence of heavier materials towards the earth’s centres, the density of the earth‘s layers also goes on increasing.
The materials of the innermost part of the earth are very dense.
Top 13 Interesting Facts About Earth’s Interior
1) The upper portion of the mantle is called Asthenosphere, extending up to 400km. The word Astheno means weak. It is the main source of magma that finds its way to the surface during volcanic eruptions.
2) The crust and the uppermost part of the mantle are called Lithosphere. Its thickness ranges from 10-200 km. The lithosphere is subdivided into tectonic plates.
3) Gutenberg Discontinuity lies between the mantle and the outer core.
4) The Earth’s interior is composed of four layers three solid and one liquid.
5) The Earth is composed of four different layers:
- The crust (1 percent of Earth’s volume)
- The mantle(84 percent)
- The liquid outer core
- The solid inner core (15 percent)
6) The density of the earth’s layers also gets on increasing towards the center.
7) The portion of the interior beyond the crust is called the Mantle.
8) The upper portion of the mantle is called Asthenosphere.
9) The core-mantle boundary is located at the depth of 2900 km.
10) The crust is the uppermost and the thinnest layer of the Earth.
11) The mantle extent is up to 2900 km beneath the crust.
12) The mantle is the layer of the earth that lies below the crust and is by far the largest layer making up 84% of the earth’s volume.
13) There are two types of crust which are dense and thin oceanic crust and less dense and thicker continental crust.







