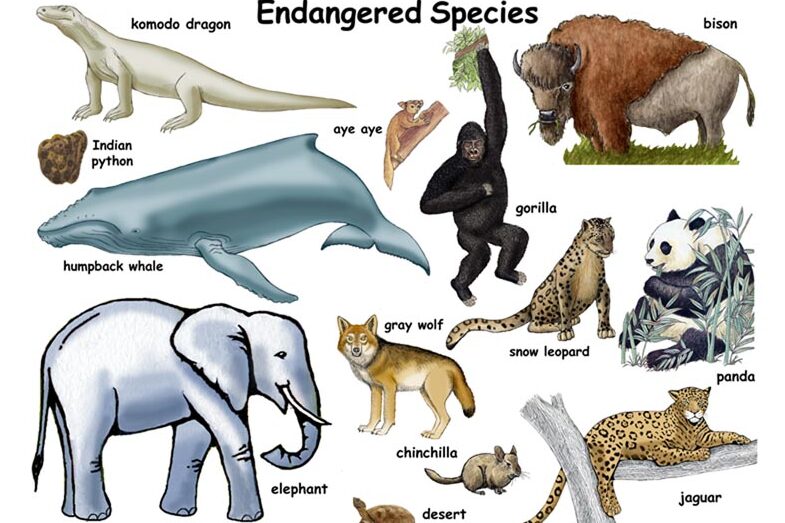

Introduction
- Earth is filled with amazing creatures both large and small, but many of our planet’s species face threats on several fronts, with thousands on the brink of disappearing forever. While extinction happens naturally, humans have played a significant role in accelerating the process -deforestation, overhunting, overfishing, building development, and climate change all seriously impact the lives of animals. But not everyone is aware so many species are struggling to survive. Many nations have laws that protect conservation-reliant species which for example forbid hunting, restrict land development or create protected areas.
Definition Of Endangered Species
- An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss poaching and invasive species. The International Union for Conservation of Nature Red list lists the global conservation status of many species, and various other agencies assess the status of species within particular areas. An endangered species is a type of organism that is threatened by extinction. Species become endangered for two main reasons: loss of habitat and loss of genetic variation.
Reason
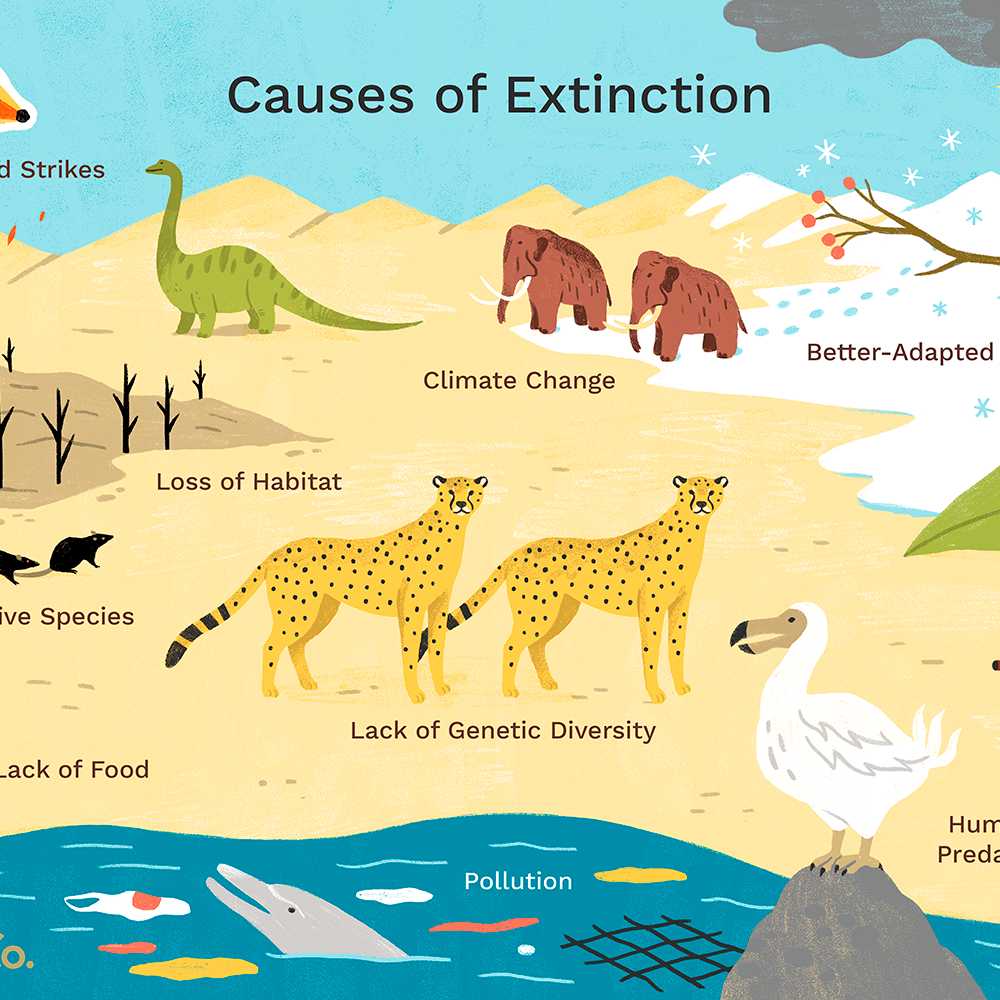
1. Loss Of Habitat
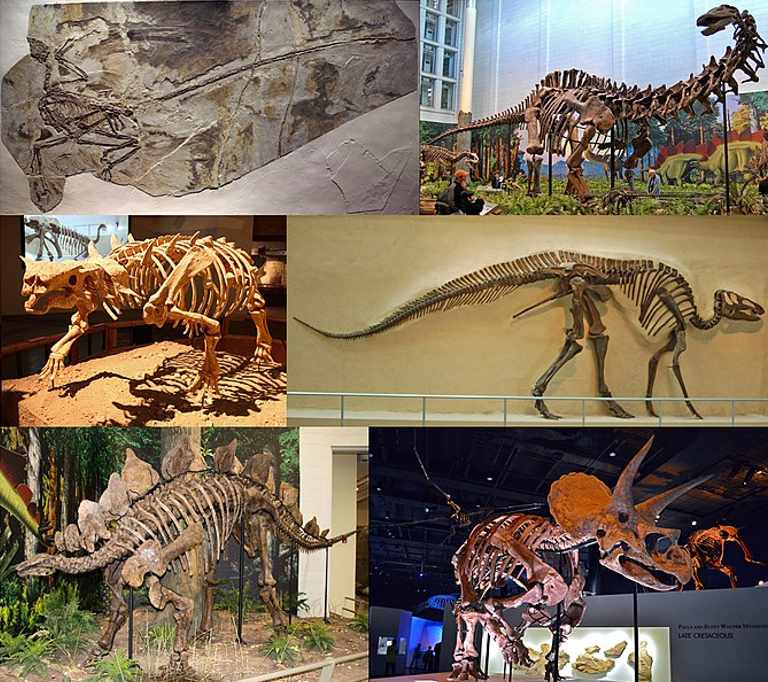

A loss of habitat can happen naturally. Dinosaurs, for instance, lost their habitat about 65 million years ago.
The hot, dry climate of the Cretaceous period changed very quickly, most likely because of an asteroid striking the Earth. The impact of the asteroid forced debris into the atmosphere, reducing the amount of heat and light that reached Earth’s surface. The dinosaurs were unable to adapt to this new, cooler habitat. Dinosaurs became endangered, and then extinct. When a habitat is destroyed, the carrying capacity for indigenous plants, animals, and other organisms is reduced so that populations decline, sometimes up to the level of extinction. Habitat loss is perhaps the greatest threat to organisms and biodiversity. Habitat loss is probably the greatest threat to the variety of life on this planet today.
2. Loss Of Genetic Variation
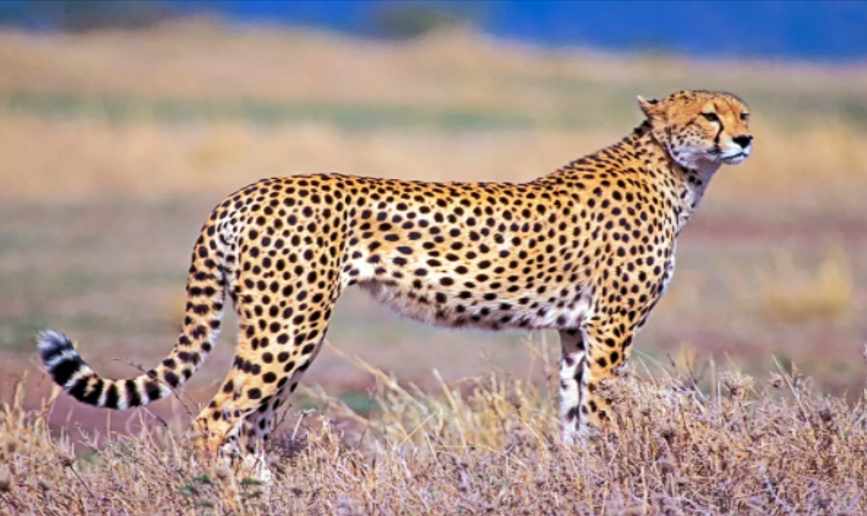

Genetic variation is the diversity found within a species. Genetic variation allows species to adapt to changes in the environment. Usually, the greater the population of a species, the greater its genetic variation. Groups of species that have a tendency to inbreed usually have little genetic variation, because no new genetic information is introduced to the group.
Loss of genetic variation can occur naturally. Cheetahs are a threatened species native to Africa and Asia. These big cats have very little genetic variation. Biologists say that during the last ice age, cheetahs went through a long period of inbreeding. As a result, there are very few genetic differences between cheetahs. They cannot adapt to changes in the environment as quickly as other animals, and fewer cheetahs survive to maturity. Cheetahs are also much more difficult to breed in captivity than other big cats, such as lions.
3. Report Of Red List

The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) keeps a “Red List of Threatened Species.” The Red List defines the severity and specific causes of a species’ threat of extinction. The Red List has seven levels of conservation. Each category represents a different threat level.
- Least concern
- Near threatened
- Vulnerable
- Endangered
- Critically endangered
- Extinct in the wild
- Extinct
Endangered Animals

1. Bengal Tigers
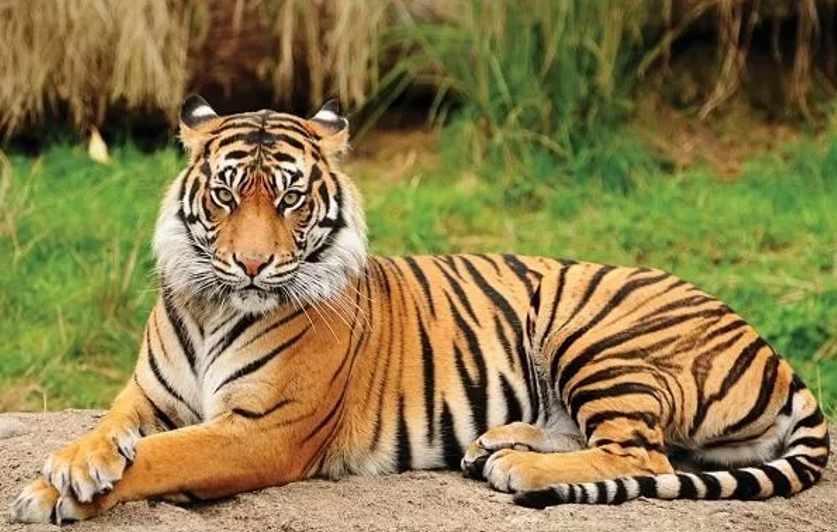

- Tiger habitat has been destroyed, degraded, and fragmented by human activities. Tigers need wide swaths of habitat for their survival since they have large home ranges and are very territorial. Fewer tigers can survive in small, scattered islands of habitat, which leads to a higher risk of inbreeding and makes tigers more vulnerable to poaching as they venture beyond protected areas to establish their territories. . In retaliation, tigers are sometimes killed or captured. “Conflict” tigers can end up for sale in black markets. One of the world’s largest, and most uniquely-adapted, tiger populations are found in the Sundarbans—a large mangrove forest area shared by India and Bangladesh on the coast of the Indian Ocean. It is also the only coastal mangrove tiger habitat in the world. These mangrove forests harbor a variety of species, including tigers, and protect coastal regions from storm surges and wind damage. However, rising sea levels caused by climate change threaten to wipe out these forests and the last remaining habitat of this tiger population.
Act To Prevent Tiger:-
- To prevent the population of tigers, the Ministry of Environment and Forests proposes to bring in amendments to the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
2. Blue Whale

Blue whales are federally listed as endangered. The main reason whales were so in demand was their whale oil. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the oil from the whales was used as fuel for the lights and lanterns in so many homes and businesses. It was also used as a lubricant during the industrial revolution. The special oil from sperm whales was used to make candles and used as a lubricant. Blue whales, being the largest whale, had the most mass and the most blubber and oil and therefore were a prized commodity.
This species was once abundant, but advances in whaling technology made it easier for people to hunt them. With the rise of factory ships, blue whale populations plummeted. They are now protected internationally by a moratorium on whaling, and their numbers are rising. Ship noise, entanglement, and collisions may affect them in areas with high human activity, but occurrences of these events are rare. The effect that climate change will have on blue whales is uncertain.
Act To Prevent Blue Whale:-
- Blue whales are protected under both the Endangered Species Act and the Marine Mammal Protection Act.
3. Baer’s Pochard
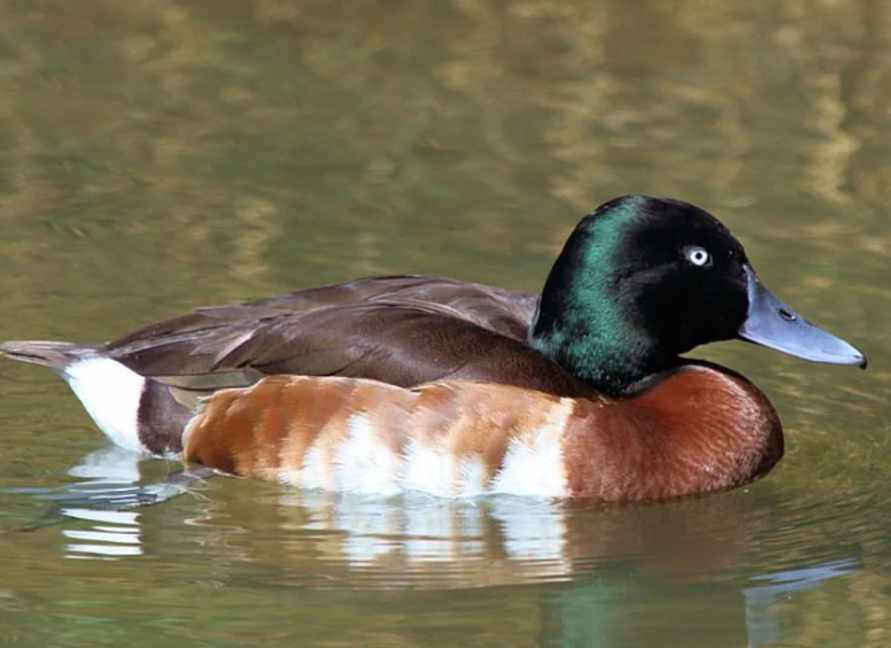

- Baer’s pochard came into sharp focus in 2012 when it was listed as Critically Endangered by the IUCN. It has undergone a rapid decline in recent decades, pushing this duck to the edge of extinction. Habitat loss, harvesting of birds and eggs are all thought to be key factors. With a population estimate once numbering around 20,000 birds, worryingly there may now be fewer than 1000 individuals remaining in the wild.
Act To Prevent Baer’s Pochard:-
- A Species Action Plan was prepared in 2014 and adopted by the Partners of the East Asian – Australasian Flyway Partnership (EAAFP) in January 2015. The Baer’s Pochard Task Force (BPTF) is now working to implement the Action Plan and save Baer’s pochard from extinction.
4. Kashmir Red Stag

- They were threatened, due to habitat destruction, over-grazing by domestic livestock, and poaching. In the 1940s, Hangul’s population was between 3000 and 5000, but overgrazing by domestic livestock and poaching led to its habitat destruction. In the early 1970s, the first-ever census of the Hangul was carried by IUCN and there were only 170 Hangul at that time, sounding alarm bells. Soon after the census, various initiatives were carried out by the State Government of Jammu and Kashmir to save the animal from extinction. As per the 2019 census, there are only 237 Hanguls (sex ratio of 15.5 males per 100 females and 15.5 fawns per 100 females).
Act To Prevent Kashmir Red Stag:-
- In the 1970s, the Government of Jammu and Kashmir along with the support of IUCN and World Wildlife Fund (WWF) prepared a project for the protection of the habitat of Hangul or the Kashmir stag.
5. Siberian Crane
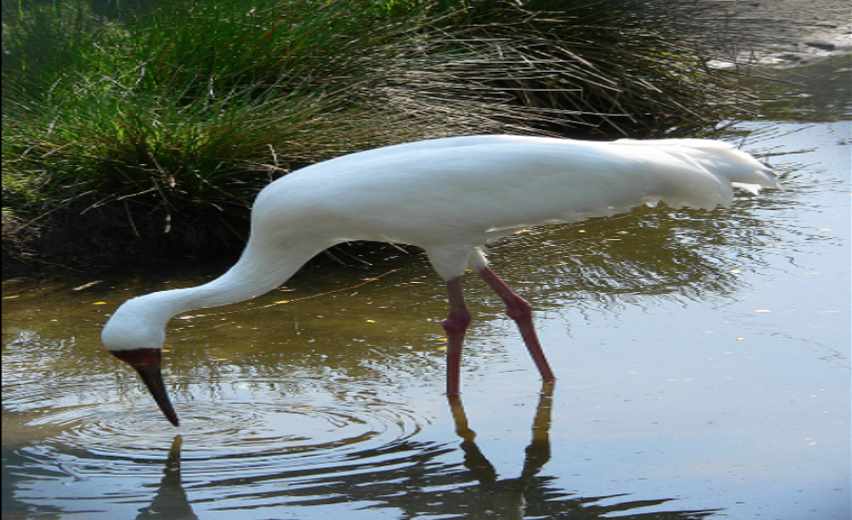

This Critically Endangered species is now only found in one main population in East Asia, with a few birds remaining in the historic Western/Central population. The Eastern population breeds in northeastern Siberia and winters at Poyang Lake in the Lower Yangtze River Basin in China. In the Western/Central population, a single crane continues to winter along the south coast of the Caspian Sea in Iran. This population is bred just south of the Ob River in Russia.
Historically, Siberian Cranes of the Central Asian Flock overwintered in wetlands in the Etawah and Mainpuri districts of India. In the nineteenth century, after the creation of artificial wetlands in Bharatpur, Rajasthan state, in northwestern India, Siberian Cranes were observed in the Bharatpur wetlands regularly. The Keoladeo (Ghana) National Park (KNP) was established in Bharatpur on the eastern fringe of the Punjab Plains in 1967, and since the 1960s regular monitoring of Siberian Cranes was provided. KNP was the last consistently confirmed wintering area for the species. In the park and surrounding area, they used the open wetlands and habitats that are maintained by a system of artificial water impoundments surrounded by dikes.
Act To Prevent Siberian Crane:-
- The project aims to protect a network of globally important wetlands in Asia for migratory waterbirds and uses the Siberian crane as a flagship species, linking activities at 16 key wetlands along the species’ western and eastern flyways in Russia, Kazakhstan, Iran, and China
6. Barkudia Insularis
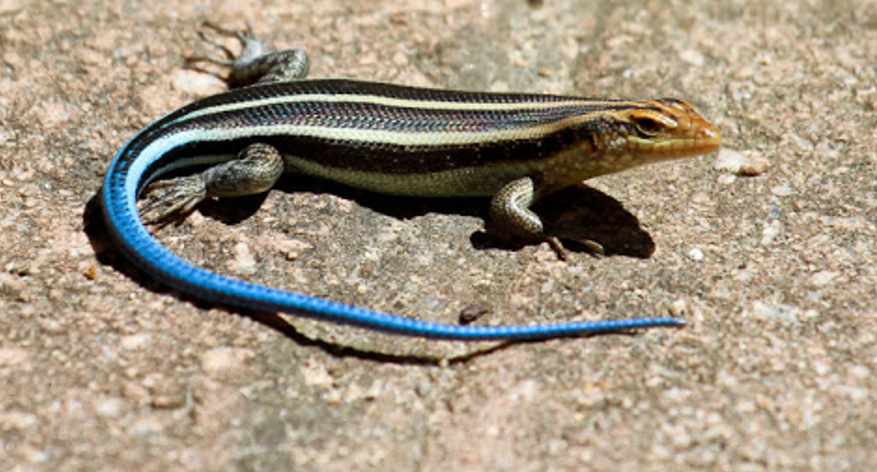

Barkudia insularis commonly known as the Madras spotted skink is a critically endangered limbless skink that was described in 1917 by Nelson Annandale and rediscovered in the wild in 2003. Little is known about the species but it is believed to be found only in the mangrove habitats near Barkud Island in Chilka Lake, Odisha, India. The lizard looks like a large earthworm that lives in the subsoil and probably feeds on small arthropods.
The holotype was found in loose earth near the roots of a banyan tree of Badakudaisland of Chilka Lake in 1917. The most recent report of the species is from 2003.
7. Andaman Shrew
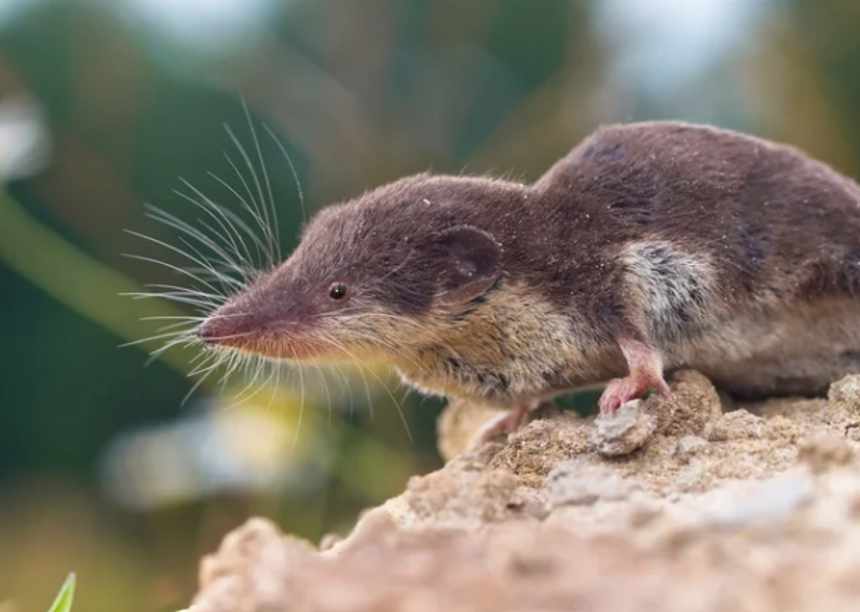

- The Andaman shrew or Andaman white-toothed shrew is a critically endangered species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to the South Andaman Island of India. They are usually active by twilight or at night and have specialized habitat requirements. Habitat loss due to selective logging, natural disasters such as tsunamis, and drastic weather changes are thought to contribute to current population declines.
8. Bugun Liocichta

- The Bugun liocichla is a passerine bird species from the family Leiothrichidae closely related to the Emei Shan liocichla. First spotted in 1995 in Arunachal Pradesh, India, it was described as a new species in 2006. The description was made without the collection of a type specimen as they were too few to risk killing one. It is thought to be an endangered species, with a small population, and a very restricted distribution range within which commercial development threatens the habitat. The bird has been named in honor of the efforts of the Bugun community of Singchung village in West Kameng district in conserving the wildlife and forest of the area.
How To Prevent The Species From Endangered
Learn about endangered species in your area.
Visit a national wildlife refuge, park or other open space.
Make your home wildlife-friendly.
Native plants provide food and shelter for native wildlife.
Herbicides and pesticides may keep yards looking nice but they are in fact hazardous pollutants that affect wildlife at many levels.
Slow down when driving.
Recycle and buy sustainable products.
Never purchase products made from threatened or endangered species.
Harassing wildlife is cruel and illegal.
Protect wildlife habitat.
Documentary About Endangered Species

- Racing Extinction is a 2015 documentary about the ongoing anthropogenic mass extinction of species and the efforts from scientists, activists, and journalists to document it by Louie Psihoyos. The film received one Oscar nomination, for Best Original Song, and one Emmy nomination for Exceptional Merit in Documentary Filmmaking. The film deals with several examples of the overarching theme of the Anthropogenic, in that the spread of Homo sapiens has caused the greatest mass extinction since the KT event 66 million years ago, including global warming and poaching, and the efforts of scientists, photographers, and volunteers to protect endangered species. The film implicates overpopulation, globalization, and animal agriculture as leading causes of extinction.

Netflix raising awareness on some of the most beautiful, terrifying, cutest, and fiercest threatened and endangered animals on the planet. These are the 8 documentaries about endangered species on Netflix.
- Humpback Whale
- More Than Honey
- Snow Wolf Family And Me
- Last Chance To See
- Virunga
- Polar Bear: Spy On The Ice
- Martin Clunes: A Line Called Mugie
- The Ivory Game
Top 13 Interesting Facts About Endangered Species
Human activity can also contribute to a loss of habitat. Development for housing, industry and agriculture reduces the habitat of native organisms. This can happen in a number of different ways. Development can also endanger species indirectly.
Human activity can also lead to a loss of genetic variation. Overhunting and overfishing have reduced the populations of many animals
More than 40,000 species are threatened with extinction which is still 28% of all assessed species.
In 2012, the IUCN Red List listed 3,079 animal and 2,655 plant species as endangered (EN) worldwide.
According to a WWF study, without mitigation efforts, projected sea-level rise—about a foot by 2070—could destroy nearly the entire Sundarbans tiger habitat.
Blue whales are also one of the loudest animals on Earth. Their songs can reach nearly 200 decibels (louder than a jet engine).
Bugun liocichla was the first bird discovered since India’s Independence.
Killing or injuring any animal is a cognizable offense under sections 428 and 429 Indian Penal Code.
Baer’s Pochard is one of the critically endangered species in India.
Vaquita is both the smallest and the most endangered marine mammal in the world.
Ostriches have the strongest immune system of any animal in the world.
Turritopsis dohrnii is called immortal jellyfish because they can potentially live forever.
The National Endangered Species day is celebrated on the third Friday of May every year.
Some FAQs Or Also Ask Question
What defines an endangered species?
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction.
What are the 10 most endangered?
Giant Panda, Siberian Tiger, Whooping Crane, Blue Whale, Asian Elephant, Sea Otter, Snow Leopard, Gorilla, Vaquita, Rhinoceros.
What species is most endangered?
Vaquita is most endangered species.
What animals went extinct in 2022?
The Vaquita went extinct in 2022.
What causes endangered?
Species become endangered for two main reasons: loss of habitat and loss of genetic variation.






