
Introduction
- ISRO or Indian Space Research Organization is India’s space agency that was founded in 1969 to help develop an indigenous Indian space research program. ISRO maintains one of the biggest fleets of remote sensing (IRS) and communication (INSAT) satellites catering to the needs of the nation through a network of centers, offices, and research institutes in different parts of the country. ISRO functions in a variety of areas like broadcasting, weather forecasting, disaster management, geographic information systems, navigation, cartography (maps), telemedicine, distance education satellites, etc. ISRO is a significant body and spearheads research in space science in India while playing a huge role in the development of the country through educational, agricultural, communication and defence sector projects. ISRO has its headquarters in Bengaluru. S. Somanath, an eminent rocket scientist has been appointed as the Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Space Secretary recently. He has played a major role in the development of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk-III (GSLV Mk-III). He joined the GSLV Mk-III project in 2003, and served as Project Director from 2010 to 2014. He is an expert in the area of system engineering of launch vehicles. Later on, he contributed to the development of the indigenous cryogenic stages for the GSLV.
Formation

The Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established by Jawaharlal Nehru in 1962 under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE).
Eminent scientist Dr. Vikram Sarabhai had a big role in this development. He understood the need for space research and was convinced of the role it can play in helping a nation to develop.
INCOSPAR set up the Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) at Thumba, near Thiruvananthapuram at India’s southern tip. TERLS is a spaceport used to launch rockets.
The INCOSPAR became ISRO in 1969.
The Department of Space was created in 1972 and ISRO became a part of it and remains so to date. The Space Department reports directly to the Prime Minister of the country.
During 1975-76, Satellite Instructional Television Experiment (SITE) was conducted. It was hailed as ‘the largest sociological experiment in the world’. It was followed by the ‘Kheda Communications Project (KCP)’, which worked as a field laboratory for need-based and locale-specific program transmission in the state of Gujarat.
During this phase, the first Indian spacecraft ‘Aryabhata’ was developed and launched using a Soviet Launcher.
Another major landmark was the development of the first launch vehicle SLV-3 with a capability to place 40 kg in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), which had its first successful flight in 1980.
The ’80s was the experimental phase wherein, Bhaskara-I & II missions were the major steps in the remote sensing area whereas ‘Ariane Passenger Payload Experiment (APPLE)’ became the forerunner for the future communication satellite systems.
Antrix Corporation Limited (ACL) is a Marketing arm of ISRO for the promotion and commercial exploitation of space products, technical consultancy services, and transfer of technologies developed by ISRO.
=> ISRO has many facilities each dedicated to a specialized field of study in space. A few of them are as below:-
- Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), Thiruvananthapuram
- Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), Thiruvananthapuram
- Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC-SHAR), Sriharikota
- Space Applications Centre (SAC), Ahmedabad
- National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), Hyderabad
ISRO Organisation Structure
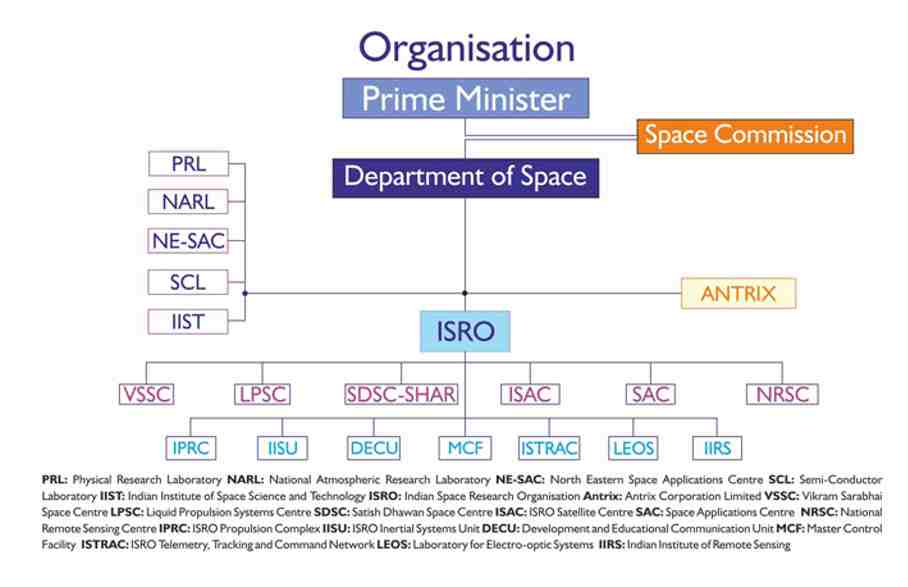
ISRO Vision & Objectives

ISRO’s vision is stated as “Harness space technology for national development while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration.” Dr. Vikram A Sarabhai is considered the founding father of space programs in India.
ISRO established two major space systems, INSAT for communication, television broadcasting, and meteorological services, and the Indian Remote Sensing Satellites (IRS) system for resources monitoring and management. ISRO has developed two satellite launch vehicles, PSLV and GSLV, to place INSAT and IRS satellites in the required orbits to fulfill its objectives.
Mission

Design and development of launch vehicles and related technologies for providing access to space.
Design and development of satellites and related technologies for earth observation, communication, navigation, meteorology and space science.
Indian National Satellite (INSAT) programmes for meeting telecommunication, television broadcasting and developmental applications.
Indian Remote Sensing Satellite (IRS) program for management of natural resources and monitoring of environment using space-based imagery.
Space-based Applications for Societal development of the nation.
Research and Development in space science and planetary exploration.
Upcoming Missions:-
Gaganyaan Mission: India’s maiden space mission, Gaganyaan, will be launched in 2023.
Chandrayaan-3 Mission: Chandrayaan-3 is likely to be launched during the third quarter of 2022.
=> Three Earth Observation Satellites (EOSs):
EOS-4 (Risat-1A) and EOS-6 (Oceansat-3) — will be launched using Isro’s workhorse PSLV, the third one, EOS-2 (Microsat), will be launched in the first developmental flight of the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
These satellites will be launched in the first quarter of 2022.
Other:-
Shukrayaan Mission: The ISRO is also planning a mission to Venus, tentatively called Shukrayaan.
Own Space Station: India is planning to launch its own space station by 2030, joining the league of the US, Russia, and China to an elite space club.
ISRO Milestones

The first Indian-made sounding rocket was the RH-75 (Rohini-75). It was launched by TERLS in 1967. It weighed just 32 kg. Series of Rohini Sounding Rockets were developed by ISRO for atmospheric and meteorological studies.
ISRO built its initial satellite in 1975 and named it Aryabhata. This was launched by the Soviet Union.
The first Indian-built launch vehicle was SLV-3 and it was used to launch the Rohini satellite in 1980.
The first INSAT satellite was launched in 1982. It was a communication satellite. It was named INSAT-1A, which failed in orbit. The next communication satellite INSAT-1B was launched in 1983.
Established in 1983 with the commissioning of INSAT-1B, the Indian National Satellite (INSAT) system is one of the largest domestic communication satellite systems in the Asia-Pacific region with nine operational communication satellites placed in geostationary orbit. The INSAT system provides services to telecommunications, television broadcasting, satellite newsgathering, societal applications, weather forecasting, disaster warning and Search and Rescue operations.
The first IRS (remote-sensing satellite) was launched in 1988.
The first lunar mission, Chandrayaan I was launched in 2008.
It also launched the Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) or the Mangalyaan in 2014. With this, India became the first country to achieve success in putting a satellite in the Mars orbit in its maiden attempt and the first space agency to do so.
ISRO has launched many small satellites mainly for experimental purposes such as INS-1C, Aryabhatta, APPLE, Rohini Technology Payload, YOUTHSAT, etc. The experiment includes Remote Sensing, Atmospheric Studies, Payload Development, Orbit Controls, recovery technology, and more.
Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine launched in August 2016, ISRO successfully conducted the Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine test. It uses Hydrogen as fuel and oxygen from the atmospheric air as the oxidizer. ISRO’s Advanced Technology Vehicle (ATV), which is an advanced-sounding rocket, was the solid rocket booster used for the test of Scramjet engines at supersonic conditions. This test was the first short-duration experimental test of ISRO’s Scramjet engine with a hypersonic flight on Mach 6. The new propulsion system complemented ISRO’s reusable launch vehicle that had a longer flight duration. In 2017, ISRO created another world record by launching 104 satellites in a single rocket. It launched its heaviest rocket yet, the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle-Mark III, and placed the GSAT 19 in orbit.
India’s Manned Mission to Space also called Gaganyaan, this project is part of the government’s ambition to make India a global low-cost provider of services in space. The launch vehicle for this mission will carry heavy payloads into space. For this purpose, GSLV Mk-III is being developed with a cryogenic engine. ISRO has already tested the GSLV Mk-III with an experimental crew module (Re-entry & Recovery technology) and Crew Escape System (CES).
ISRO has also launched many operational remote sensing satellites, starting with IRS-1A in 1988. Today, India has one of the largest constellations of remote sensing satellites in operation. The data from these satellites are used for several applications covering agriculture, water resources, urban planning, rural development, mineral prospecting, environment, forestry, ocean resources, disaster management, etc.
Navigation services are necessary to meet the emerging demands of the Civil Aviation requirements and to meet the user requirements of the positioning, navigation, and timing based on the independent satellite navigation system. ISRO worked jointly with the Airport Authority of India (AAI) in establishing the GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) system to meet the Civil Aviation requirements. Similarly, it established a regional satellite navigation system called the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) to meet the user requirements of the positioning, navigation, and timing services.
ISRO has influenced educational institutions by its activities like making satellites for communication, remote sensing, and astronomy. The launch of Chandrayaan-1 increased the interest of universities and institutions towards making experimental student satellites. Some important Academic Institute Satellites are – Kalamsat-V2, PRATHAM, SATHYABAMASAT, SWAYAM, Jugnu, etc.
Launch Vehicles
- ISRO has developed three types of launch vehicles (or rockets) namely, the PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle), the GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle), and Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mark III or LVM). Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) are two operational launch vehicles of India. They are used to carry spacecraft into space.
1. PSLV
It is a third-generation launch vehicle. It is termed as the ‘Workhorse of Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO)‘.
It is the first launch vehicle of India that has liquid stages. There is a total of 4 stages in this launch vehicle.
- First Stage – PS 1 – PSLV uses the S139 solid rocket motor that is augmented by 6 solid strap-on boosters.
- Second Stage – PS 2 – PSLV uses an Earth storable liquid rocket engine for its second stage, known as the Vikas engine, developed by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre.
- Third Stage – It is a solid rocket motor that provides the upper stages high thrust after the atmospheric phase of the launch.
- Fourth Stage – The PS4 is the uppermost stage of PSLV, comprising of two Earth storable liquid engines.
The first successful launch of PSLV was in October 1994.
It has the following variants:-
- PSLV – G: It has strap-on motors
- PSLV – CA: It does not have strap-on motors
- PSLV – XL: It has strap-on motors
=> The capacity of payloads:-
- It can carry the payload of 1750 kg to sun-synchronous polar orbits (SSPO) (Altitude – 600 Kms).
- It can carry the payload of 1425 kg to Geosynchronous and Geostationary Orbits (GTO).
It has launched Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) Satellites.
PSLV – Recent Developments in 2019-2020.
- There have been 52 launches by PSLV. The launches of 2019 and 2020 are given below:-
[wpdatatable id=28]
2. GSLV
=> GSLV-Mk II is the largest launch vehicle developed by India. The salient features of this launch vehicle are as follows:-
It is a fourth-generation launch vehicle.
It has three stages.
- First stage – The 138-tonne solid rocket motor is augmented by 4 liquid strap-ons.
- Second stage – One Vikas engine is used in the second stage of GSLV.
- Third Stage – Developed under the Cryogenic Upper Stage Project (CUSP), the CE-7.5 is India’s first cryogenic engine, developed by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre.
It has four liquid-engine strap-ons.
The first flight by GSLV was on 18th April 2001.
The capacity of payloads:-
- It can carry 2500 kgs INSAT class of communication satellites and place it to GTO.
- It can carry 5000 kgs heavy satellites to multiple smaller satellites in LEO.
Challenges for ISRO
1. Mere contribution to Global Space Economy:-
India accounts for only 2% of the global space economy. The two key reasons for the same are lack of space-specific laws and effective monopoly enjoyed by ISRO over all space-related activities.
2. International Treaties:-
India’s current space activities are currently governed by a few international treaties along with two national policies which are Satellite Communication Policy (SATCOM) and Remote Sensing Data Policy (RSDP). SATCOM policy was introduced in 1997 and is aimed at developing the space and satellite communications industry within India. In 2000, norms for the implementation of the 1997 policy were introduced. The RSDP was introduced in 2001 and revised in 2011. It lays down clear guidelines for the distribution of satellite remote sensing data within India and states that the GOI is the exclusive owner of all data received from Indian Remote Sensing Satellites (IRS) to which private entities can only acquire a license through the nodal agency.
3. Not having Domestic Space Law:-
Up until recently, the need for a domestic space law was not felt as space was seen as more of an international issue rather than a domestic one. Furthermore, the private sector has only recently shown willingness to invest and play a bigger role in India’s space sector after realizing the potential of commercial space activity.
Movies On ISRO
1. Mission Mangal

After the failure of GSLV-F06 on 25 December 2010, due to a small mistake by Project Director Tara Shinde, Rakesh Dhawan, a fellow scientist working with her, takes the blame on herself. The MoM (Mars Orbiter Mission) is regarded as an impossible mission by his co-workers due to its aim of reaching Mars with its tight budget. Eventually, the MoM satellite is finally launched on PSLV on 5 November 2013, and is named Mangalyaan and is successfully inserted into Earth’s orbit.
2. Antariksham 9000 Kmph

This 2018 space adventure movie revolves around a satellite moving into the darker side of the moon, and the crisis that one of the Indian satellites, Mihira has lost connection with the Space Station and is losing its speed. The system codes to make any repairs are known only to Dev (Varun Tej) – a passionate scientist at the station. Dev had quit the Space station five years ago – and this story forms a flashback.
3. Tik Tik Tik

The movie Tik Tik Tik centres around the event of an asteroid striking the neighbourhood of Chennai, Ennore. Soon, scientists predict that another asteroid with an estimated size of 60 square kilometres is going to hit another place. Eventually, RAW decides to send M. Vasudevan (Jayam Ravi), a trained magician and an escape artist, along with his team and a team of scientists to get a hold of a missile in a space centre. This plot leads to a happy ending, destroying the asteroid.
Top 13 Interesting Facts About ISRO
ISRO was formed on independence Day, 1969 by Dr.Vikram Sarabhai.
SLV-3 was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on July 18, 1980. Former President A P J Abdul Kalam was the Project Director of SLV-3. The SLV-3 weighed 17 tonnes and had a payload of 40 kg. The SLV-3 put 35 kg Rohini Satellite into orbit.
ISRO also developed Bhuvan, a web-based 3D satellite imagery tool that is the Indian incarnation of Google Earth.
ISRO has 13 centers spread all across India.
ISRO’s first lunar mission, Chandrayaan I was approximately amounted to 390 crore rupees which are 8-9 times lesser than the expense of a similar mission by NASA.
Antrix the corporate arm of ISRO, deals with the commercialization of space products, consultancy, and technology transfer developed by the ISRO. It has clients worldwide – Europe, the Middle East, and SE Asia.
ISRO’sMars mission is the cheapest so far, just 450 crores i.e Rs 12 per km, equivalent to an auto fare. In 2008-09, the Indian Space and Research Organisation successfully launched a lunar orbiter, Chandrayaan-1, which discovered evidence of water on the moon. Mangalyaan was developed from technology tested during the Chandrayaan mission.
INDIA (ISRO) is the only country that has reached the MARS in its maiden attempt and that also in just 400 crores. The US failed in their first 5 attempts. The Soviet Union failed in its first 8 attempts. China & Russia also failed in their first attempt.
When Indian scientists asked for the methodologies and engineering assistance from the US for the Mars mission long back, they refused. But the Indian scientists tried hard and developed a new methodology and engineering indigenously and made this historical achievement with a much cheaper cost.
ISRO is one of the six space agencies in the world with the capability to build and launch satellites from its own soil. When most of the countries rely on US-based GPS systems for their navigational purpose, India has successfully launched its own navigational satellite, IRNSS.
ISRO has to date launched 23 consecutive successful PSLV launches.
Apart from launching India’s 65 satellites, ISRO has also launched 29 foreign satellites to date.
ISRO has an elder cousin, like the formation of the nation itself, Pakistan started their Space and Upper Atmosphere Commission (SUPARCO) quite earlier than that of India. SUPARCO was launched in 1961 but ISRO was started in 1969. While ISRO has already launched 77 satellites to date, SUPARCO could only send two, and that too with assistance by foreign nations.
Some FAQs Or Also Ask Question
Is NASA and ISRO same?
No, NASA and ISRO are two different organizations where research is carried out related to space.
How can I get a job in ISRO?
By qualifying the IIST exam or by taking the test by ISRO centralized recruitment board.
Which country owns ISRO?
ISRO is an independent organization in India and it has its headquarters in Bengaluru.
What is ISRO famous for?
ISRO got famous after its Mangalyan Mission, 2014 due to its cost effective strategies.
Who made 1st rocket in India?
Tipu Sultan, the ruler of Mysore, successfully developed the first rocket in India in 1792.
What is ISRO future?
For the near future, ISRO is working on various SSLV’S (Small Satellite launch Vehicles)
ISRO Chairman ?
Shri S. Somanath is the present chairman of ISRO.






