
History
The primary reason behind the establishment of the Indian Railways was the profits of the British from the export and import of raw materials and finished products to various parts of India. After independence, the Government of India operated the Indian Railways. The first railway proposal for India to transport raw materials was made at Madras in 1832 by Lord Arthur Cotton. The history of Indian Railways goes back 160 years. On 16 April 1853, the first passenger train ran between Bori Bunder (Bombay) and Thane, covering a distance of 34 km.
Also, in the beginning, Indian Railways worked on coal, but due to development railways started working on electricity and other factors.
It was powered by three locomotives named Sahib, Sultan and Sindh, and had thirteen carriages. The first railway workshop was established in 1862 at Jamalpur near Munger in Bihar. It gradually became one of the major industrial units of India, with iron and steel foundries, rolling mills, and more.
Also, in 1864, the North got its first station – Delhi Junction. The city’s oldest, it was a major station and junction and remains so to this day. It was first established in 1864 near Chandni Chowk when trains started operating from Howrah/Calcutta to Delhi. The present building was commissioned in 1903. The next important station in the north was Lucknow. It was the headquarters of the Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway (O&R), whose first line from Lucknow to Kanpur was built in April 1867. Now known as Lucknow Charbagh station, it is part of the Northern Railway.
In 1880, the Darjeeling Steam Tramway (later Darjeeling Himalayan Railway) started its first section between Siliguri and Kurseong. The line was extended to Darjeeling in 1881. The line operated on a narrow gauge and was granted World Heritage status in 1999, making it the first railway in Asia to receive such status.
The Kalka Shimla Railway (KSR) connects Chandigarh to the foothill town, Kalka, near Shimla at an altitude of 2276 m. This narrow-gauge railway (2 ft 6 in) of 96.54 km (59.99 mi) in length was opened to traffic on 9 November 1903. It was granted World Heritage status in 2008.
In the last 160 years of its existence, the railways in India has grown and expanded manifold, yet there are still unknown areas to be covered. Slowly but steadily railways is connecting every part of India, which is much easier today than before with continuous innovations in technology.
List Of Ministers Who Served In Indian Railways
| NAME | DATE OF JOINING | DURATION |
| JOHN MATHAI | 15 AUGUST 1947 | 1 YEAR 38 DAYS |
| N. GOPALASWAMI | 22 SEPTEMBER 1948 | 3 YEARS 234 DAYS |
| LAL BAHADUR SHASTRI | 13 MAY 1952 | 4 YEARS 28 DAYS |
| JAGJIVAN RAM | 7 DECEMBER 1956 | 5 YEARS 124 DAYS |
| SWARAN SINGH | 10 APRIL 1962 | 1 YEAR 164DAYS |
| H.C. DASAPPA | 21 SEPTEMBER 1963 | 261 DAYS |
| S.K. PATIL | 9 JUNE 1964 | 2 YEARS 276 DAYS |
| C.M. POONACHA | 13 MARCH 1967 | 1 YEAR 388 DAYS |
| RAM SUBHAG SINGH | 14 FEBRUARY 1969 | 263 DAYS |
| PANAMPILLY GOVINDA MENON | 4 NOVEMBER 1969 | 106 DAYS |
| GULZARILAL NANDA | 18 FEBRUARY 1970 | 1 YEAR 27 DAYS |
| K. HANUMANTHAIAH | 18 MARCH 1971 | 1 YEAR 126 DAYS |
| T.A. PAI | 23 JULY 1972 | 196 DAYS |
| LALIT NARAYAN MISHRA | 5 FEBRUARY 1973 | 1 YEAR 331 DAYS |
| KAMLAPATI TRIPATHI | 11 FEBRUARY 1975 | 2 YEARS 40 DAYS |
| MADHU DANDAVATE | 26 MARCH 1977 | 2 YEARS 124 DAYS |
| T.A. PAI | 30 JULY 1979 | 168 DAYS |
| KAMLAPATI TRIPATHI | 14 JANUARY 1980 | 303 DAYS |
| KEDAR PANDEY | 12 NOVEMBER 1980 | 1 YEAR 63 DAYS |
| PRAKASH CHANDRA SETHI | 15 JANUARY 1982 | 230 DAYS |
| A.B.A. GHANI KHAN CHOUDHURY | 2 SEPTEMBER 1982 | 2 YEAR 120 DAYS |
| BANSI LAL | 31 DECEMBER 1984 | 1YEAR 175 DAYS |
| MOHSINA KIDWAI | 24 JUNE 1986 | 119 DAYS |
| MADHAVRAO SCINDIA | 22 OCTOBER 1986 | 3 YEARS 41 DAYS |
| GEORGE FERNANDES | 2 DECEMBER 1989 | 343 DAYS |
| JANESHWAR MISHRA | 21 NOVEMBER 1990 | 212 DAYS |
| C.K. JAFFER SHARIEF | 21 JUNE 1991 | 4 YEARS 118 DAYS |
| RAM VILAS PASWAN | 1 JUNE 1996 | 1 YEAR 291 DAYS |
| NITISH KUMAR | 19 MARCH 1998 | 1 YEAR 139 DAYS |
| RAM NAIK | 6 AUGUST 1999 | 69 DAYS |
| MAMTA BANERJEE | 13 OCTOBER 1999 | 1 YEAR 153 DAYS |
| NITISH KUMAR | 20 MARCH 2001 | 3 YEARS 63 DAYS |
| LALU PRASAD YADAV | 22 MAY 2004 | 5 YEARS |
| MAMTA BANERJEE | 22 MAY 2009 | 1 YEAR 362 DAYS |
| DINESH TRIVEDI | 12 JULY 2012 | 251 DAYS |
| MUKUL ROY | 20 MARCH 2012 | 186 DAYS |
| C.P. JOSHI | 22 SEPTEMBER 2012 | 36 DAYS |
| PAWAN KUMAR BANSAL | 29 OCTOBER 2012 | 194 DAYS |
| C.P. JOSHI | 13 MAY 2013 | 32 DAYS |
| MALLIKARJUN KHARGE | 17 JUNE 2013 | 343 DAYS |
| D.V. SADANANDA GOWDA | 26 MAY 2014 | 167 DAYS |
| SURESH PRABHAKAR PRABHU | 9 NOVEMBER 2014 | 2 YEARS 298 DAYS |
| PIYUSH GOYAL | 3 SEPTEMBER 2017 | 3 YEARS 307 DAYS |
| ASHWINI VAISHNAW | 7 JULY 2021 | PRESENT |
Structure






- Indian Railways is generally divided into three categories: First Class, Second Class, and Third Class. The headquarter of Indian Railways is in Delhi. Apart from this, there are also some luxury trains on some special routes like Lucknow, Delhi. The Indian Railways divides its operations into zones, which are further divided into divisions, each with a divisional headquarters. There are a total of 18 zones (including Metro Railway, Kolkata) and 68 divisions on the Indian railway system. The Pamban Bridge is the railway bridge that connects Rameswaram on Pamban Island with mainland India. Opened on 24 February 1914, it was the first sea bridge in India. The rail bridge is, for the most part, a traditional bridge resting on concrete piers, but it has a double-leaf bascule section, which can be raised to allow ships and barges to pass. Vembanad Bridge is the longest railway bridge in India.
There Are A Total Of 29 Types Of Train That Run In India










- Rajdhani Express
- Duronto Express
- Shatabdi Express
- Jan Shatabdi Express
- Sampark Kranti Express
- Garib Rath Express
- Humsafar Express
- Kavi Guru Express
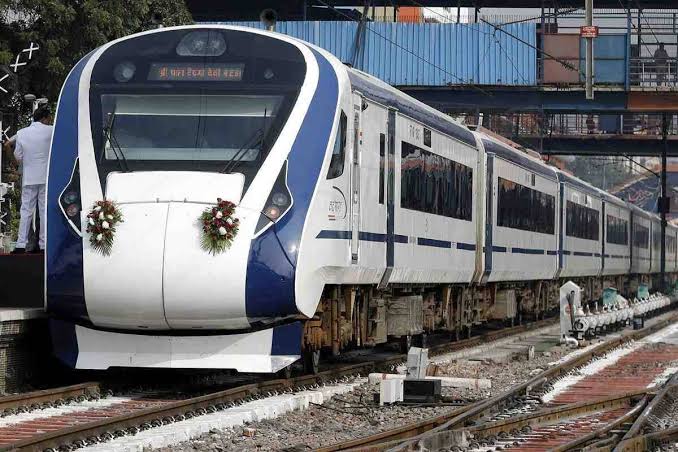
- Vande Bharata Express
- Tejas Express
- Gatimaan Express
- Vivek Express
- Rajya Rani Express
- Jan Sadharan Express
- UDAY Express
- Antyodaya Express
- Mahamana Express
- Suvidha Express
- Yuva Express
- Double Decker Express
- AC Express
- Intercity-Express
- Express
- Superfast Express
- Passenger
- Suburban
- Mountain Railways
- Luxury Trains
Services
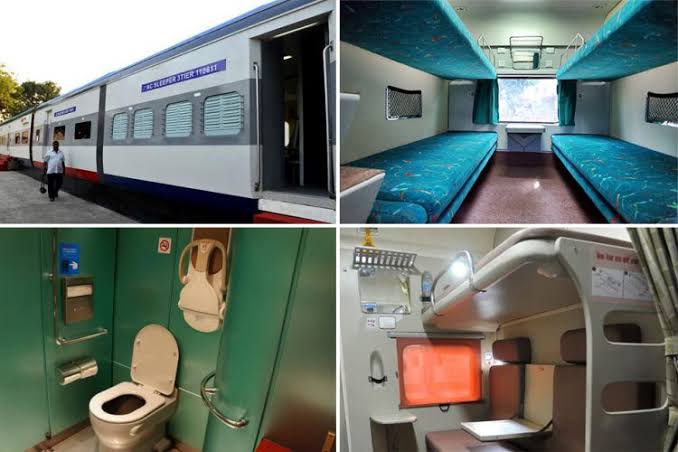

The main objective is to provide transportation. The railway is considered to be one of the fastest road routes of travel. Indian Railways allows us to travel across India connecting different states. Not only this it also provides food, water, and sanitation facilities as well as other facilities as per our ticket booking and preference. Indian Railways also provides its facilities in local stations to make transportation and movement from one place to another cheaper and easier for common people.
Railways have a workforce of about 14 lakh employees. It is the only civil service of its kind in India and it forms a cadre of bureaucrats specialized in human resource management in the Government of India. The total sanctioned strength of the service is ‘478’ after the Cadre Reorganization Order as on 09.03.2019.
The Indian Railway Personnel Service (IRPS) is a Group ‘A’ Central Civil Services cadre of the Government of India. Officers are recruited by UPSC through a very prestigious civil services exam.
Anyone can apply for jobs in Railways through Railway Recruitment Board. Get all the information on their official website.
Networks
- It is spread all over India, as well as connects us with Nepal. The Indian Railways network is spread over 67,956 km with 13,169 passenger trains and 8479 goods trains and approximately 7349 railway stations. Not only this, but apart from being an energy-efficient and economical mode of transport and transportation, the railway network is also ideal for long-distance travel and movement of bulk goods. Indian Railways is the preferred carrier of automobiles in the country.
Current Updates

A few years after that first train, the engineers of the Indian Railways took on the major task of building a track at Bhore Ghat.
Indian Railways is going to increase the number of Vande Bharat Express semi-high speed trains. 10 new Vande Bharat Express, popularly known as Train 18, will be run till August 2022, connecting 40 cities.
The work of Gandhinagar Rajdhani Railway Station in the Indian state of Gujarat has been completed and is ready for inauguration on 16th July.
Currently, the shortest route of the slowest passenger train in India is Barkakana Sidhwar Passenger with a record distance of 6 km.
Due to COVID, the catering service is not available and the charges for the catering services are excluded from the fare. Also, blankets and linen will not be provided in the train.
As of May 2021, Indian Railways’ shipments stood at 73.45 Million Tonnes (MT), comprising 35.62 MT (Coal), 9.77 MT (Iron Ore), 3.38 MT (Food Food), 2.22 MT (Fertilizers) and 3.15 MT ( cement, except). clinker). By May 5, 2021, Indian Railways has enabled Wi-Fi at 6,000 railway stations. The government is going to bring out a ‘National Rail Scheme’ to enable the country to integrate its rail network with other modes of transport and develop a multi-modal transport network.
Union Railway Minister Piyush Goyal said the Indian Railways “will never be privatized”, but added that private investment should also be encouraged to enhance passenger services and improve infrastructure.
There are 12.54 lakh (2020) people working in Indian Railways. Apart from this, there is Chairman (Railway Board) and Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Sunit Sharma. Modi government took its first step to privatize railways and invited private players to run 151 trains.
Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation Limited (IRCTC) will cancel the operation of the country’s first private train Tejas Express from Monday (November 23, 2020). In view of the shortage of passengers, IRCTC has decided to stop the operation of Lucknow-Delhi and Mumbai-Ahmedabad Tejas Express.
Railways are likely to replace pantry cars with third AC coaches in 300 trains.
Indian Railways And Their 13 Interesting Facts
Lord Dalhousie is called the father of Indian Railways.
The “X” sign written on the last compartment of the train means the last vehicle on board. If a train passes through a station without an “X” sign, it indicates that the coaches are different. It works like an alert system.
Miraj Junction, established in 1886 by the South Central Railway, holds a historical place in the history of Indian Railways by transporting water to drought-hit Latur by train.
Pune-Secunderabad Shatabdi is the cleanest train in India.
Maharaja Express, Palace on Wheels, Royal Rajasthan on Wheels, The Golden Chariot and The Deccan Odyssey are 5 luxury trains operated and maintained by Indian Railways.
Vande Bharat Express is the fastest train service provided by Indian Railways, with an initial speed of 180 km/h while Mettupalayam Ooty Nilgiri Passenger train is the slowest train in India, traveling at a speed of 10 km/h.
The Vivek Express is spread over 4273 km of rail tracks, and with a running time of 80 hours and 15 minutes and approximately 55 scheduled stops, the Vivek Express covers the longest train route in India.
Mathura Junction is the largest railway junction in India, 7 routes are connected from this station to all the major cities of India.
Indian Railways is often described as the “transport lifeline of the nation”. Also, Indian Railways is the fourth largest railway network in the world.
Indian Railways is the largest network in Asia. In addition, the first railway on the Indian subcontinent ran from Bombay to Thane, a distance of 21 miles.
Indian Railways launched National Rail Plan, Vision 2024, to expedite the implementation of important projects, such as multitrack congested routes, achieving 100% electrification, speed up to 160 km/h on Delhi-Howrah and Delhi-Mumbai routes Upgrading to 130 km/h speed on all other Golden Quadrilateral-Golden Diagonal (GQ/GD) routes and elimination of all level crossings on GQ/GD route by 2024.
There are 8 railway museums in India – in Delhi, Pune, Kanpur, Mysore, Kolkata, Chennai, Ghoom and Tiruchirappalli.
The National Railway Museum in Delhi is the most visited museum in India, with lakhs of tourists coming to see the rich heritage of the museum.
The “engineering miracle” still stands as a testament to the prowess of railway engineering. It was granted World Heritage status in 2005.






