
Introduction
India is the world’s largest democracy and has the longest constitution that was written keeping into consideration every individual. When creating the living document, the requirements and development of each region of India were taken into account. The executive, judiciary, and legislative branches of Indian democracy are each responsible for overseeing a certain area of the nation.
The Cabinet is the nucleus of the council of ministers established in the government, which is in charge of managing the nation and acting as its representatives. The cabinet is made up of the ministers and officials in charge of the important departments of the government, such as the railways, the home ministry, the finance ministry, and the defence ministry. All significant choices regarding the actual decision-making are made by the cabinet. It provides guidance to the Prime Minister on the strategies and course of the nation’s expansion. The Prime Minister, who also serves as the head of the governing cabinet, is in charge of it.
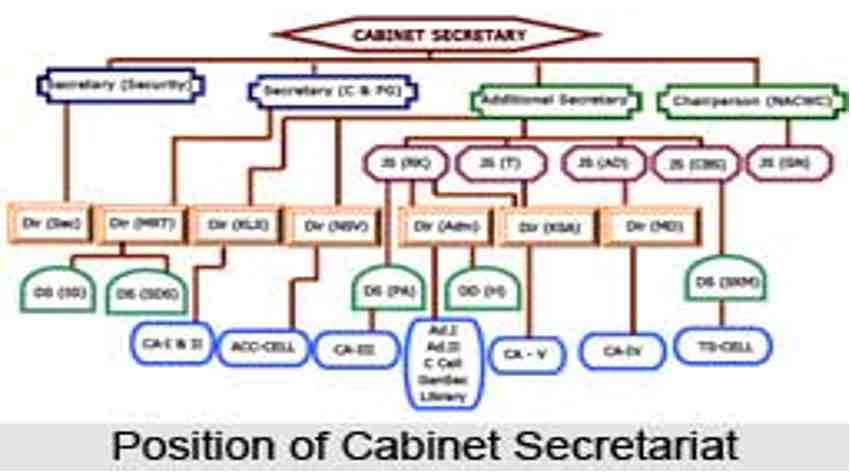
- The authority known as the Cabinet Secretariat is at the centre of national administration. A transaction of business regulations from 1961 and an allocation of business from 1961 specify the two main duties of the Cabinet Secretariat. The primary requirement for efficient maintenance of all governmental duties is what led to the foundation of this body. The Prime Minister’s Office (PMO), the ministries of defence, home affairs, and foreign affairs, as well as the ministry of finance, are all housed in the same cabinet secretariat facility. Because of this, it is referred to as the centre of the nation’s administration. The cabinet secretariat is a magnificent structure created by Herbert Baker in a Rajputana-inspired form that makes the structure airy and cool. The structure of the building also resembles a dome, which regulates the temperature and provides relief from the oppressive heat of Indian summers. The Rashtrapati Bhawan’s north and south buildings are combined into the secretariat building. The ministries of defence and foreign affairs are located in the southern section, and the ministries of finance and home affairs are located in the northern section. The cabinet secretariat also includes other crucial elements outside the main offices of several ministries. There is the Cabinet Secretary’s Office, the head of India’s Research and Analysis Wing (RAW), and the NIC cell.
History
The Executive Council of the Viceroy, which served as the forerunner to the cabinet, formerly had a Secretariat under the direction of the Viceroy’s Private Secretary. Initially, the function of this Secretariat was limited to handling paperwork for the Executive Council, but as the workload of the several departments reporting to the Council grew, so did the Secretariat’s duties. The private secretary eventually earned the title of secretariat secretary. And as the Secretariat’s primary function changed to coordinating the work of the departments throughout time, this job grew in influence. The secretariat was renamed the cabinet secretariat in 1946, and the secretary was given the title of cabinet secretary.
The duties of the Secretariat underwent significant changes following Independence in 1947. He is not a member of any ministry while being the most Senior Secretary. The Cabinet Secretariat established a number of committees to address economic, military, and intelligence issues. After Independence, the majority of the departments were housed under the Cabinet Secretariat until being transferred to the appropriate ministries. The incumbent of the job is responsible for making sure that the civil service is capable of handling the daily issues it faces and that the employees are treated fairly and decently at work.
- The Cabinet Secretary is the senior-most IAS officer in India and serves as the head of all civil services. The position, as it is currently called, was established prior to independence when it was given the responsibility of handling papers together with a nominal representative. However, over time, it developed steadily to rank among the most powerful posts in the nation. In addition to having several duties, a cabinet secretary also serves as the ex-officio head of the civil services. Since independence, the duties of the cabinet secretary have undergone numerous significant changes, and they currently fall within the purview of the common secretary of the cabinet secretariat. N.R. Pillai served as India’s first Cabinet Secretary, and Rajiv Gauba, who has held the position since 2019, is the incumbent. The cabinet secretary’s current address is 32, Prithviraj Road, New Delhi, and they are paid 18th Level Pay.
Roles And Responsibilities

The most senior and well-known IAS officer in the nation is the Cabinet Secretary. He is the head of several national authorities and is directly answerable to the prime minister. As a result, the cabinet secretary carried out a number of duties, some of which are detailed below. The Prime Minister, President, and Vice-President of the country are all responsible to the Cabinet Secretary, who is required to inform them of all significant information regarding the Cabinet’s Decisions and Operations.
The Government of India’s Transaction of Business Rules, 1961, and Allocation of Business Rules, 1961, are administered by the Cabinet Secretariat. By enforcing compliance with these regulations, the rules make it easier for government ministries and departments to conduct business. By providing inter-ministerial coordination, settling disagreements across ministries and departments, and forging consensus through regular and ad hoc Secretaries Committees, the Secretariat also aids in government decision-making. Through this method, new policy initiatives are also encouraged. The Cabinet Secretariat makes sure that the President of India, the Vice-President, and Ministers are kept informed of their important operations by providing a monthly summary of all departments’ activities. The Vice-President and Ministers receive a monthly report of all departments’ significant actions. The management of significant national crises and the coordination of the actions of numerous ministries in such a crisis are additional duties of the Cabinet Secretariat. Using a monthly overview of their actions, it makes sure that the Vice-President, Ministers, and the President of India are kept informed of the important activities of all departments. Additionally, one of the duties of the Cabinet Secretariat is to coordinate the actions of the various ministries at times of serious crises in the nation.
Functions

The Cabinet Secretary’s functions include the following:-
- Is in charge of the Cabinet Secretariat.
- Serves as the central government’s principal coordinator.
- Serves as the head of the Civil Services Board, which among other things recommends empanelment of officers for the levels of secretary, additional secretary, and joint secretary (apart from personnel under the Ministry of External Affairs).
- Serve as the committee’s chairperson for administration.
- Serve as the Conference of Chief Secretaries of States’ chairperson.
- Recommends that officials with the rank of secretary and additional secretary be sent to the Cabinet’s Appointments Committee (apart from those who work for the Ministry of External Affairs) (ACC).
- Serves as the head of the Senior Selection Board, which makes recommendations to the Appointments Committee of the Cabinet about the posting of officers holding the level of joint secretary in the Union Government (ACC).
- Serves as the Prime Minister’s Principal Advisor.
- Help the Council of Ministers in any way you can.
- Creates the Cabinet’s agenda and keeps minutes of its meetings.
- Give the administration some continuity and stability during a crisis.
Powers And Famous Initiatives

- Although each ministry is in charge of carrying out government policies, plans, and programs, they frequently enlist the help of the cabinet secretariat when it comes to inter-ministerial cooperation. The committee of secretaries (CCS) meeting is where inter-ministerial disputes are settled. The cabinet secretary chairs a committee that has been constituted to go over specific issues and recommendations from other government secretaries. These committees might remove obstructions or offer supplementary interagency solutions. A monthly report that ministries and departments submit to the cabinet secretariat includes information on a variety of topics, including important policy matters, CoS decision compliance, sanctions for prosecutions that have been pending for more than three months, and deviations from ToB rules, the implementation of e-Governance, etc.
Famous Initiatives include:-
Both the Government of India (Business Transaction) Regulation 1961 and the Government of India (Business Distribution) Regulation 1961 were created in compliance with Article 77(3) of the Indian Constitution. Ministries, departments, offices, and secretariats are listed in the AoB rules’ first schedule. The second schedule outlines the tasks given to each ministry and division within the Indian government.
The ToB Rules specify how the Indian government will dispose of businesses. According to the general or specific regions of ministries that can be used to receive the necessary local trial counseling offered to the ToB directive, India’s business governments are typically disregarded. In addition, the ToB Rules specify which situations call for the approval of the president, the cabinet, and its committees. The second schedule to the ToB rules lists cases that require cabinet approval, while the first schedule lists cases that need Cabinet Committee approval. The third schedule of the ToB rules specifies the cases that must be reported to the President and Prime Minister. Because of this, even if the majority of government business is conducted at the departmental level, there are some situations—or types of situations—that are crucial from a national perspective and necessitate approval from the cabinet or a cabinet committee.
List Of Cabinet Secretaries In India
| Serial Number | Name | Tenure |
| 1 | N.R. Pillai | February 1950- May 1953 |
| 2 | Y.N. Sukthankar | May 1953- July 1957 |
| 3 | M.K. Vellodi | July 1957- June 1958 |
| 4 | Vishnu Sahay | June 1958- November 1960 |
| 5 | B.N. Jha | November 1960- March 1961 |
| 6 | Vishnu Sahay | March 1961- April 1962 |
| 7 | S.S. Khera | April 1962- November 1964 |
| 8 | Dharma Vira | November 1964- June 1966 |
| 9 | D.S. Joshi | June 1966- December 1968 |
| 10 | B. Sivaraman | January 1969- November 1970 |
| 11 | T. Swaminathan | November 1970- November 1972 |
| 12 | B.D. Panday | November 1972- March 1977 |
| 13 | N.K. Mukarji | March 1977- March 1980 |
| 14 | S.S. Grewal | April 1980- April 1981 |
| 15 | C.R. Krishnaswami Rao Saheb | April 1981- February 1985 |
| 16 | P.K. Kaul | February 1985- August 1986 |
| 17 | B.G. Deshmukh | August 1986 – March 1989 |
| 18 | T.N. Seshan | March 1989- December 1989 |
| 19 | V.C. Pande | December 1989- December 1990 |
| 20 | Naresh Chandra | December 1990- July 1992 |
| 21 | S. Rajagopal | August 1992- July 1993 |
| 22 | Zafar Saifullah | July 1993- July 1994 |
| 23 | Surendra Singh | August 1994- July 1996 |
| 24 | T.S.R. Subramanian | July 1996- March 1998 |
| 25 | Prabhat Kumar | March 1998- October 2000 |
| 26 | T.R. Prasad | November 2000- October 2002 |
| 27 | Kamal Pandey | November 2002- June 2004 |
| 28 | B.K. Chaturvedi | June 2004- June 2007 |
| 29 | K.M. Chandrashekar | June 2007- June 2011 |
| 30 | Ajit Seth | June 2011- June 2015 |
| 31 | P.K. Sinha | June 2015- August 2019 |
| 32 | Rajiv Gauba | August 2019- Present till August 2023 |
Conclusion

- As the administrative head, the Cabinet Secretariat offers secretarial support to the cabinet and its many committees. The role has importance. The highest senior public officer typically receives it. They are in charge of all the Civil Services listed in the Indian Constitution. The position of a Cabinet Secretary is the most desirable and powerful in the Indian Civil Services. It is the link between all the cabinets and provides a major hand in the smooth functioning of the government.
Top 13 Facts About Indian Cabinet Secretariat
The Cabinet Secretary is the highest-ranking executive official and Civil Servant in the Indian Government.
The Cabinet Secretary is the Ex-Officio Head of the Civil Services Board, Cabinet Secretariat, Indian Administrative Service (IAS), and all Civil Services operating under the government’s Business Rules, 1961.
The Cabinet Secretary is the Indian Administrative Services Senior most Cadre position, ranking eleventh in the Indian order of precedence.
The Cabinet Secretary’s term has been extended to four years from 2010 with an effective amendment that was brought in that year.
N.R. Pillai was India’s first Cabinet Secretary.
Rajiv Gauba is the current and eleventh Cabinet Secretary of India.
The residence of the Cabinet Secretary is 32, Prithviraj Road, New Delhi, and his annual salary is ₹2,50,000 plus allowances.
The Secretariat’s functions changed dramatically after the country gained independence in 1947.
The Cabinet Secretary does not represent any ministry since the designation represents the senior-most secretary representing the government.
The Cabinet Secretariat has already established a series of committees on economic, defense, and intelligence issues, proposing amendments, changes, and improvements.
A Cabinet Secretary in India is appointed by the working President to aid and advise the Council of Ministers headed by the Indian Prime Minister.
The cabinet secretariat has three wings- the civil wing, the military wing, and the intelligence wing.
Sarla Grewal was the first Indian female Cabinet Secretary.

For deep details, you can read the full article. Click the link below :






